Blue is a primary color in both the RGB and RYB color models, situated on the visible light spectrum between violet and cyan, typically associated with wavelengths between 450 and 495 nanometers. It's observed in the daytime sky and deep sea due to Rayleigh scattering. The Tyndall effect explains blue eyes, while aerial perspective causes distant objects to appear more blue.
1900: Lapis Lazuli Value in the Indus Valley Civilisation
Around 1900 BC, Lapis lazuli was highly valued by the Indus Valley Civilisation.
1900: Blue eyes in America
Around 1900, about half of Americans were born with blue eyes.
1902: US Army uniform color until 1902
Blue continued to be the colour of the field uniform of the US Army until 1902, and is still the colour of the dress uniform.
1911: Einstein confirms Rayleigh scattering
In 1911, Albert Einstein confirmed Rayleigh scattering. Rayleigh scattering describes how sunlight passes through the atmosphere, where the blue wavelengths are scattered more widely by the oxygen and nitrogen molecules, resulting in more blue light reaching our eyes.
1950: Blue eyes in America
Around 1950, a third of Americans were born with blue eyes.
1978: Eye color distribution in Denmark
In Denmark in 1978, only 8% of the population had brown eyes. However, due to immigration, today that number is about 11%.
1993: Demonstration of high-brightness blue LEDs
In 1993, Shuji Nakamura of Nichia Corporation demonstrated high-brightness blue LEDs. Simultaneously, Isamu Akasaki and Hiroshi Amano of Nagoya University were working on related LED lighting development.
2006: Nakamura awarded Millennium Technology Prize
In 2006, Nakamura was awarded the Millennium Technology Prize for his invention.
2006: Blue eye statistics in the United States
In the United States, as of 2006, 1 out of every 6 people, or 16.6% of the total population, and 22.3% of the white population, have blue eyes.
2010: Widespread availability of blue lasers
In 2010, lasers emitting in the blue region of the spectrum became widely available to the public with the release of inexpensive high-powered 445–447 nm laser diode technology.
2014: Nobel Prize in Physics awarded to Nakamura, Amano and Akasaki
In 2014, Nakamura, Hiroshi Amano, and Isamu Akasaki were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for their invention of the efficient blue LED.
Mentioned in this timeline
The United States of America is a federal republic located...
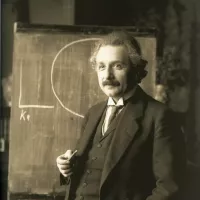
Albert Einstein - was a German-born theoretical physicist renowned for...
Trending

3 months ago Michelle Obama: America 'not ready' for a woman president, cites sexism concerns.

1 hour ago Apple MacBook Pro: Touchscreen, Dynamic Island, and New Interface Coming Soon.

12 minutes ago Ethereum Price Faces Resistance at $1,950 Amidst Market Repricing Concerns.
12 minutes ago BP Receives Hold Ratings Amid Strategy Updates and Increased Rating by Argus.
1 hour ago Whitefox & Fluid Quip collaborate; Low-carbon ethanol boosted; Indoor plants aid climate resilience.
1 hour ago HSBC: Enterprise Software Strong, AI Enhances Capabilities, Valuations Historically Low.
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Susan Rice is an American diplomat and public official prominent...

Barack Obama the th U S President - was the...

Michael Joseph Jackson the King of Pop was a highly...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Bernie Sanders is a prominent American politician currently serving as...