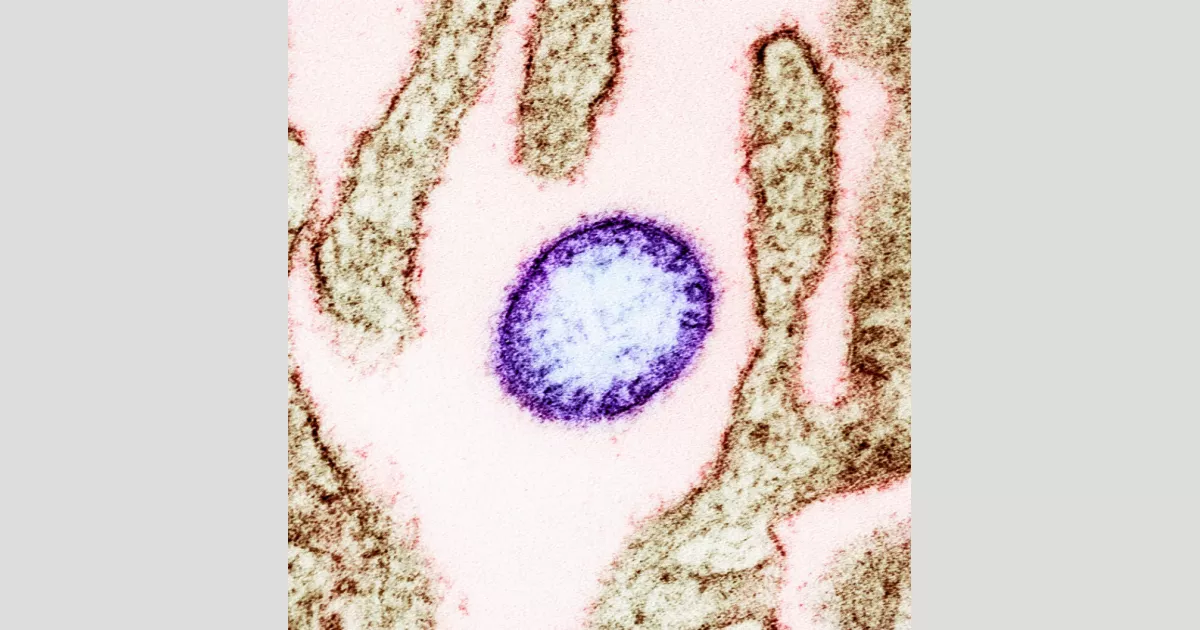
Nipah virus is a zoonotic virus, carried by bats, responsible for Nipah virus infection in humans and animals. It belongs to the Henipavirus genus, sharing this classification with the Hendra virus. Characterized by a high mortality rate (40-75%), Nipah virus has caused multiple outbreaks in Southeast Asia and South East Africa. The virus poses a significant public health threat due to its severity and potential for human-to-human transmission, though this is less common than transmission from animals to humans.
1996: Potential undetected viral spillover into pigs in Malaysia
Retrospective studies suggest that viral spillover into pigs may have been occurring undetected in Malaysia since 1996.
1998: Deforestation identified as key factor in Malaysia NiV outbreak
Deforestation has been identified as the key factor in the Nipah virus outbreak in Malaysia during 1998-1999, as it increased human contact with bats infected with the virus.
1998: Ribavirin treatment during the Nipah virus outbreak in Malaysia
During the 1998-99 Nipah virus outbreak in Malaysia, 140 patients received ribavirin, and their outcomes were compared against historical controls, showing a reduced mortality rate among those treated, though bias may have been present due to the use of historical controls.
1998: First Nipah virus cases identified in Malaysia
In 1998, the first cases of Nipah virus infection were identified during an outbreak of neurological and respiratory disease on pig farms in peninsular Malaysia, resulting in 265 human cases and 108 deaths.
1998: Viral spread aided by transfer of infected pigs
In 1998, the spread of Nipah virus was aided by the transfer of infected pigs to other farms, where new outbreaks occurred.
1998: Nipah virus appears in peninsular Malaysia
Nipah virus first appeared in 1998, in peninsular Malaysia in pigs and pig farmers.
1999: Human cases of Nipah virus reported in Malaysia and Singapore
By mid-1999, more than 265 human cases of encephalitis, including 105 deaths, had been reported in Malaysia, and 11 cases of either encephalitis or respiratory illness with one fatality were reported in Singapore.
1999: Human infections from direct contact with sick pigs
During the 1999 Nipah virus outbreak, the majority of human infections stemmed from direct contact with sick pigs and the unprotected handling of their secretions.
1999: Nipah virus isolated and outbreak spreads to Singapore
In 1999, the Nipah virus was isolated. The outbreak in Malaysia led to the culling of one million pigs and spread to Singapore, causing 11 cases, including one death, among abattoir workers exposed to pigs imported from Malaysia.
1999: Deforestation drives wildlife into closer proximity with human communities
Widespread deforestation and habitat fragmentation drive wildlife, especially fruit bats, the natural reservoirs of the Nipah virus, into closer proximity with human communities and livestock in 1999.
2001: Nipah virus reported from Bangladesh and India
In 2001, Nipah virus was reported from Meherpur District, Bangladesh and Siliguri, India.
2003: Nipah virus outbreak in Bangladesh
The Nipah virus outbreak again appeared in 2003 in Naogaon District in Bangladesh.
2004: Nipah virus outbreak in Bangladesh
The Nipah virus outbreak again appeared in 2004 in Manikganj District, Rajbari District and Faridpur District in Bangladesh.
2005: Nipah virus outbreak in Bangladesh
The Nipah virus outbreak again appeared in 2005 in Tangail District in Bangladesh.
2011: Nipah virus protein model used in movie Contagion
In 2011, the Nipah virus protein model was used in a scene describing the recombination found in a fictional paramyxovirus in the movie Contagion.
2016: Phase 1 clinical trial for m102.4 antibody in Australia
In 2016, a phase 1 clinical trial for the m102.4 monoclonal antibody was conducted in Australia with 40 participants, demonstrating that the treatment was safe and well-tolerated, with no signs of an immunogenic response.
2019: WHO releases R&D roadmap for Nipah virus
In 2019, the World Health Organization (WHO) released an advanced draft of a research and development roadmap to accelerate the creation of medical countermeasures for Nipah virus outbreaks.
September 2021: Nipah virus resurfaces in Kerala, India
In September 2021, Nipah virus resurfaced in Kerala, India, claiming the life of a 12-year-old boy.
February 2023: Nipah virus outbreak in Bangladesh
During January and February 2023, a Nipah virus outbreak occurred in Bangladesh with 11 cases resulting in 8 deaths. This outbreak resulted in the highest number of cases reported since 2015 in Bangladesh, and ten of the 11 cases during the 2023 outbreak had a confirmed history of consuming date palm sap.
September 2023: Nipah virus infections and deaths reported in India
In September 2023, India reported at least five Nipah virus infections and two deaths.
January 2024: Phase I clinical trials commence for ChAdOx1 NipahB vaccine candidate
In January 2024, a candidate vaccine, ChAdOx1 NipahB, commenced Phase I clinical trials after completing laboratory and animal testing.
July 2024: New Nipah virus infection and death in India
In July 2024, a new Nipah virus infection occurred in India, resulting in the death of a 14-year-old boy.
July 2024: Outbreak of Nipah virus confirmed in Kerala, India
In July 2024, an outbreak of Nipah virus was confirmed in Kerala state in India, where a 14-year-old boy died and 60 people were identified as being in the high-risk category of having the disease.
Mentioned in this timeline
India officially the Republic of India is a South Asian...
Africa is the second-largest and second-most populous continent comprising of...
Thailand formerly known as Siam is a Southeast Asian country...
Singapore is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia...
Bangladesh officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a South...

Culling is the process of removing organisms from a group...
Trending
Catherine Princess of Wales is a prominent member of the British royal family As the wife of William Prince of...

3 months ago Bill Gates Urges Rethinking Climate Strategy, Focus on Reducing Human Suffering, Not Just Emissions

9 months ago Vikings Bolster Roster, Sign Matt Harmon and Elijah Williams After Minicamp Tryout.
7 months ago Vikings eye former Bills starter, address need. Silence speaks volumes on strategy.
7 months ago Nipah Virus: Experts call for eco studies amidst Kerala outbreak, bat warnings.
2 months ago Xbox Cloud Gaming Expands: LG Smart TVs in India Offer Console-Free Access
Popular

Thomas Douglas Homan is an American law enforcement officer who...

William Franklin Graham III commonly known as Franklin Graham is...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Jupiter is the fifth and largest planet from the Sun...

Kristi Noem is an American politician who has served as...

Instagram is a photo and video-sharing social networking service owned...