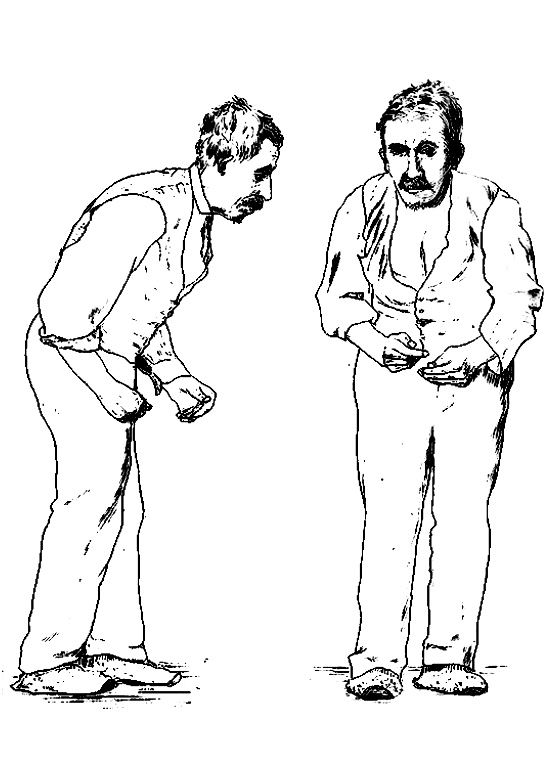
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder affecting the central nervous system, impacting both motor and non-motor functions. Motor symptoms, collectively known as parkinsonism, include tremors, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. Non-motor symptoms, such as dysautonomia, sleep abnormalities, anosmia, behavioral changes, cognitive impairment, psychosis, and anxiety, can manifest at any stage. Symptoms generally develop slowly, with non-motor issues becoming more prominent as the disease progresses.
Mentioned in this timeline

Robin Williams was a highly acclaimed American actor and comedian...
China officially the People's Republic of China PRC is an...

Michael J Fox is a Canadian-American actor and activist who...
Trending
3 months ago India-Bangladesh Ties Strained as Hasina Faces Potential Execution; Extradition Unlikely.
3 months ago Poland accuses Russia of railway sabotage; investigation points towards Russian involvement.
8 months ago Russian Bridges Collapse: Train Derailment Claims Lives Near Ukraine, Leaving Seven Dead

3 months ago Nvidia's Financial Results, Stock Reversal, and Wall Street Disagreement: A Summary
3 months ago Newly Built Chinese Bridge Collapses Months After Opening, Raising Safety Concerns

3 months ago James Franco discusses Hollywood exile during his hiatus, brother Dave comments on his success.
Popular

Kid Rock born Robert James Ritchie is an American musician...

Melania Trump a Slovenian-American former model has served as First...
The Winter Olympic Games a major international multi-sport event held...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Thomas Douglas Homan is an American law enforcement officer who...

Instagram is a photo and video-sharing social networking service owned...