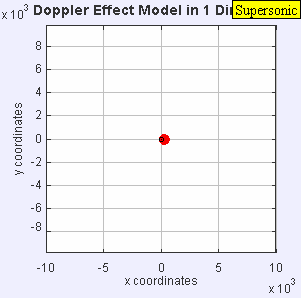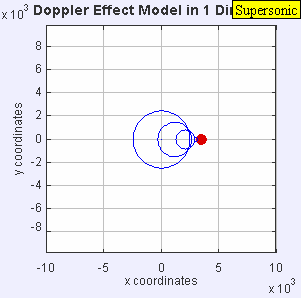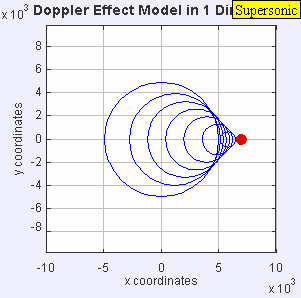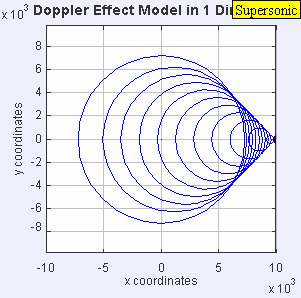
A sonic boom is a loud, explosive sound created by shock waves when an object exceeds the speed of sound. It's caused by the compression of air as the object moves, creating a pressure difference that results in a powerful release of energy, perceived as a loud boom. The sound resembles an explosion or thunderclap due to the rapid and intense nature of the shock waves reaching the ear.
1969: Government Loses Sonic Boom Lawsuit Appeal
In 1969, the government lost its appeal in a class-action lawsuit stemming from the 1964 Oklahoma City sonic boom tests, which had generated 15,000 complaints.
2006: Quiet Spike Testing
In 2006, NASA and Gulfstream Aerospace tested the Quiet Spike on NASA Dryden's F-15B aircraft. The Quiet Spike, designed to weaken shock waves at supersonic speeds, underwent over 50 test flights.
2015: Supersonic Aircraft Defined
In 2015, supersonic aircraft were defined as those capable of exceeding Mach 1, the speed of sound, with typical speeds ranging from 700 to 1,500 mph.
2018: NASA Awards Low Boom Flight Demonstrator Contract
In 2018, NASA awarded Lockheed Martin a $247.5 million contract to construct the Low Boom Flight Demonstrator, aiming to reduce sonic booms to the sound of a car door closing.
October 2023: Low Boom Flight Demonstrator Expected Flight
As of October 2023, the first flight of the Low Boom Flight Demonstrator was expected in 2024.
2024: Expected First Flight of Low Boom Flight Demonstrator
As of October 2023, the first flight of the Low Boom Flight Demonstrator was expected in 2024.
Trending

9 months ago Kyler Gordon Inks 3-Year Extension with Chicago Bears, Securing Future
1 month ago Kamilla Rakhimova Changes Nationality: Representing Uzbekistan in Tennis After Leaving Russia.
Cairo Santos is a Brazilian-American professional football player currently serving as a placekicker for the Chicago Bears in the NFL...
Emmanuel Forbes Jr is an American professional football cornerback He is known for his college career at Mississippi State where...

6 months ago Jake Ferguson signs four-year, $52M contract extension with the Dallas Cowboys.
2 months ago Veronika Khomyn opens up about marriage with Sean McVay; Stafford aims for .500.
Popular

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Thomas Douglas Homan is an American law enforcement officer who...
Matt and Ross Duffer known as the Duffer Brothers are...

William Franklin Graham III commonly known as Franklin Graham is...

Martin Luther King Jr was a pivotal leader in the...

Stranger Things created by the Duffer Brothers is a popular...