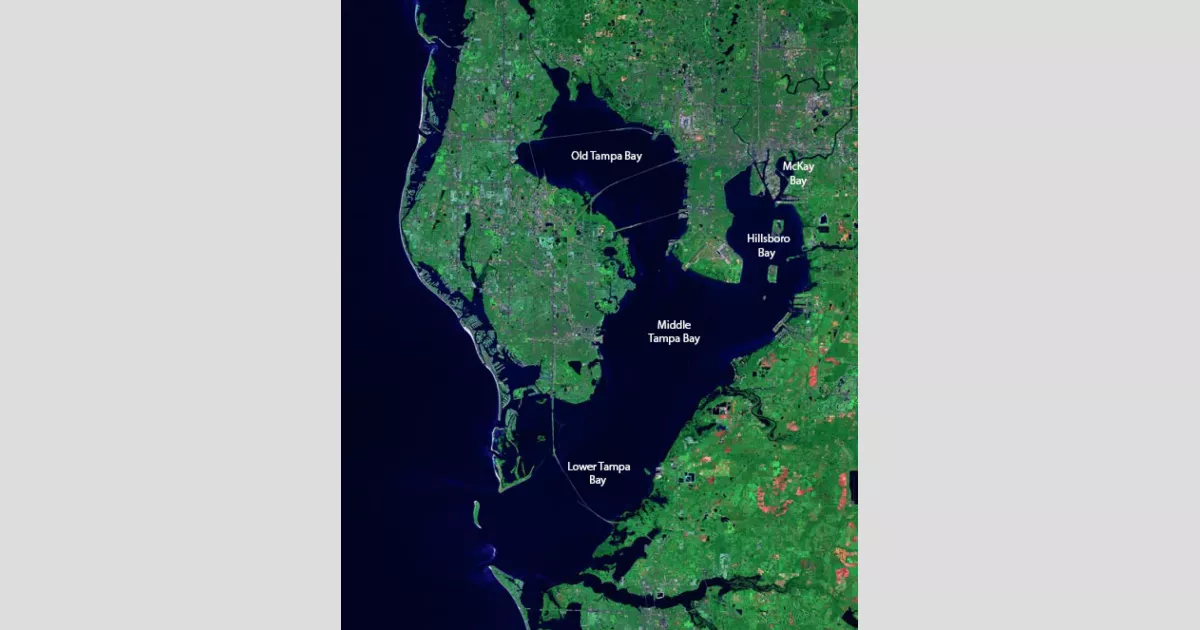
Tampa Bay, a large natural harbor and shallow estuary located on Florida's west-central coast, connects to the Gulf of Mexico. It comprises Hillsborough Bay, McKay Bay, Old Tampa Bay, Middle Tampa Bay, and Lower Tampa Bay. The Hillsborough River is the largest source of freshwater flowing into the bay, entering at downtown Tampa's Hillsborough Bay. Numerous smaller rivers and streams contribute to the bay's watershed, creating a diverse and expansive ecosystem.
1914: World's First Scheduled Air Service
In 1914, the challenges of traveling between Tampa and St. Petersburg led to the establishment of the world's first scheduled air service, the St. Petersburg-Tampa Airboat Line, which operated during the tourist season.
1917: Port of Tampa Expansion
In 1917, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers dredged a new shipping channel from the mouth of Tampa Bay to the Port of Tampa. This development transformed Tampa into a major shipping hub.
1924: Gandy Bridge Opens
The opening of the Gandy Bridge over Old Tampa Bay in 1924 significantly reduced travel time between Tampa and St. Petersburg, shortening the distance to 19 miles (31 km). This improved connectivity facilitated economic growth in the Tampa Bay area.
1946: Sea Level Rise in Tampa Bay
Since 1946, the sea level in Tampa Bay has risen by 8 inches (200 mm), making the region highly vulnerable to the effects of climate change and rising sea levels. Its location, growing population, and the bay's geography further increase the risk from hurricanes.
1990: Tampa Bay Designated Estuary of National Significance
In 1990, the United States Environmental Protection Agency recognized the ecological importance of Tampa Bay by designating it as an "estuary of national significance." Two National Wildlife Refuges, Pinellas and Egmont Key, are situated within the bay, and many of the islands and sandbars are protected due to their sensitive ecosystems and role as bird nesting sites.
2004: Cargill Phosphate Plant Spill
In 2004, a major environmental incident occurred when 65 million gallons of acidic water leaked from a Cargill phosphate plant on Tampa Bay's southern shore. This spill severely damaged the surrounding wetlands.
2010: Tampa Bay's Ecological Recovery
By 2010, thanks to improved water treatment plants and stricter industrial discharge regulations implemented in the 1980s, Tampa Bay's ecological health significantly improved. Seagrass coverage, water clarity, and biodiversity reached levels not seen since the 1950s.
2010: Tampa Bay Area Population Growth
By 2010, the population of the Tampa Bay Area had grown to over 4 million residents. This growth stemmed from the development of communities around the bay, including Tampa, Clearwater, Bradenton, and St. Petersburg.
April 2021: Piney Point Phosphate Plant Disaster
A significant ecological disaster occurred in April 2021 when a wastewater reservoir at the abandoned Piney Point phosphate plant failed. Over 200 million gallons of nutrient-rich mine tailings flowed into lower Tampa Bay, causing a massive red tide algal bloom that killed over 1,000 tons of fish and threatened seagrass beds.
October 2024: Hurricane Impacts on Tampa Bay
In October 2024, Hurricane Milton caused polluted waste from the fertilizer industry, including byproducts from Mosaic's phosphate production, to flow into Tampa Bay. Both Hurricane Milton and Hurricane Helene disrupted phosphate fertilizer production in the area.
Mentioned in this timeline
Climate change encompasses global warming and its far-reaching effects on...

Travel involves the movement of people between geographical locations using...
Trending

6 minutes ago Arizona Wildcats Defeat UCF in Big 12 Tournament, Fans Celebrate Victory

6 minutes ago Susan Lucci: A Legendary Career and Enduring Impact on Television

7 minutes ago Julio Rodriguez Prioritizes WBC Win; Machado Creates Chaos at World Baseball Classic.
1 hour ago Knicks vs Pacers: Injury Updates and Game Notes for March 13, 2026

1 hour ago Photograph of Andrew Anderson, Peter Mandelson, and Jeffrey Epstein surfaces, sparking controversy and raising questions.

1 hour ago James Fishback aims to win Florida after seizing the Gen Z right online.
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Victoria MacKenzie-Childs is a ceramic artist and co-founder with her...

Paula White-Cain is a prominent American televangelist and key figure...

Markwayne Mullin is an American politician and businessman serving as...

William Franklin Graham III commonly known as Franklin Graham is...