The Internet is a global network of interconnected computer networks communicating via TCP/IP. It's a network of private, public, academic, business, and governmental networks, spanning from local to global scales, connected through diverse electronic, wireless, and optical technologies. It facilitates a wide array of resources and services, including the World Wide Web, email, internet telephony, streaming media, and file sharing.
1945: Internet term usage
In 1945, the word Internet was used by the United States War Department in a radio operator's manual.
1965: Packet Switching Research at NPL
In 1965, Donald Davies at the United Kingdom's National Physical Laboratory (NPL) independently started research into packet switching, one of the fundamental Internet technologies.
1967: Symposium on Operating Systems Principles
After the Symposium on Operating Systems Principles in 1967, packet switching from the proposed NPL network and routing concepts proposed by Baran were incorporated into the design of the ARPANET, an experimental resource sharing network proposed by ARPA.
October 1969: ARPANET Development Begins
On October 29, 1969, ARPANET development began with two interconnected network nodes between the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and the Stanford Research Institute (now SRI International).
1971: ARPANET expands to 15 sites
By the end of 1971, 15 sites were connected to the young ARPANET.
1972: Computer Networks: The Heralds of Resource Sharing Film
In 1972, the early years of ARPANET were documented in the film Computer Networks: The Heralds of Resource Sharing.
1973: ARPANET International Connections
In 1973, connections were made to Norway (NORSAR and NDRE) and to Peter Kirstein's research group at University College London (UCL), forming the first internetwork for resource sharing.
1974: Publication of "A Protocol for Packet Network Intercommunication"
In 1974, Vint Cerf at Stanford University and Bob Kahn at DARPA published a proposal for "A Protocol for Packet Network Intercommunication". Cerf and his students used the term internet as a shorthand for internetwork.
1974: Internetwork term usage
In 1974, the word Internet was used as the shorthand form of Internetwork.
1981: IPv4 Design
In 1981, Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) was designed to address up to approximately 4.3 billion hosts.
1981: Expansion of ARPANET Access
In 1981, access to the ARPANET was expanded when the National Science Foundation (NSF) funded the Computer Science Network (CSNET).
1982: Standardization of TCP/IP
In 1982, the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) was standardized, facilitating worldwide proliferation of interconnected networks.
1986: NSFNet Provides Access to Supercomputer Sites
In 1986, the National Science Foundation Network (NSFNet) provided access to supercomputer sites in the United States for researchers, first at speeds of 56 kbit/s and later at 1.5 Mbit/s and 45 Mbit/s.
1988: NSFNet Expands Internationally
In 1988, the NSFNet expanded into academic and research organizations in Europe, Australia, New Zealand and Japan, marking the beginning of the Internet as an intercontinental network.
1989: Emergence of Commercial ISPs
Commercial Internet service providers (ISPs) emerged in 1989 in the United States and Australia.
1989: MCI Mail and Compuserve connect to the Internet
In mid-1989, MCI Mail and Compuserve established connections to the Internet, delivering email and public access products to the half million users of the Internet.
January 1990: PSInet Launches Alternate Internet Backbone
On January 1, 1990, PSInet launched an alternate Internet backbone for commercial use.
March 1990: High-Speed Link Between NSFNET and Europe
In March 1990, the first high-speed T1 (1.5 Mbit/s) link between the NSFNET and Europe was installed between Cornell University and CERN.
1990: Tim Berners-Lee Begins Writing WorldWideWeb
Later in 1990, Tim Berners-Lee began writing WorldWideWeb, the first web browser. By Christmas 1990, Berners-Lee had built all the tools necessary for a working Web, including the first Web pages that described the project itself.
1990: ARPANET Decommissioned
The ARPANET was decommissioned in 1990.
1991: Commercial Internet eXchange Founded
In 1991, the Commercial Internet eXchange was founded, allowing PSInet to communicate with the other commercial networks CERFnet and Alternet.
1992: Internet Society (ISOC) Founded
The Internet Society (ISOC) was founded in 1992 with a mission to "assure the open development, evolution and use of the Internet for the benefit of all people throughout the world".
1993: Internet Carries 1% of Telecommunication Information
It is estimated that in 1993 the Internet carried only 1% of the information flowing through two-way telecommunication.
October 1994: First Online Internet Banking Services
In October 1994, Stanford Federal Credit Union was the first financial institution to offer online Internet banking services to all of its members.
1995: Internet Fully Commercialized in the U.S.
By 1995, the Internet was fully commercialized in the U.S. when the NSFNet was decommissioned, removing the last restrictions on use of the Internet to carry commercial traffic.
1995: Internet impacts Culture and Commerce
Since 1995, the Internet has tremendously impacted culture and commerce, including the rise of near-instant communication by email, instant messaging, telephony (Voice over Internet Protocol or VoIP), two-way interactive video calls, and the World Wide Web with its discussion forums, blogs, social networking services, and online shopping sites.
1996: OP Financial Group Becomes Second Online Bank
In 1996, OP Financial Group became the second online bank in the world and the first in Europe.
1998: IPv6 Standardized
In 1998, IPv6 was standardized, utilizing 128 bits for the IP address.
2000: Internet Carries 51% of Telecommunication Information
By 2000 this figure had grown to 51% of telecommunication information carried over the Internet.
2000: Global Internet Users Reach 390 Million
In 2000, the number of Internet users globally rose to 390 million.
2001: IPv6 Address Specification
In 2001, the IPv6 address specification 2001:db8::/32, a large address block with 2 addresses and having a 32-bit routing prefix, was introduced.
2003: Cyberslacking in the UK
According to a 2003 study by Peninsula Business Services, the average UK employee spent 57 minutes a day surfing the Web while at work.
2004: Howard Dean's Presidential Campaign
In 2004, Howard Dean's presidential campaign in the United States was notable for its success in soliciting donations via the Internet.
February 2005: YouTube Founded
On February 15, 2005, YouTube was founded as a video sharing website.
November 2005: Internet Governance Forum (IGF) Established
On November 16, 2005, the United Nations-sponsored World Summit on the Information Society in Tunis established the Internet Governance Forum (IGF) to discuss Internet-related issues.
2005: Kiva Pioneered Web-Based Service
In 2005, Kiva pioneered the concept of peer-to-peer lending for charitable purposes, offering the first web-based service to publish individual loan profiles for funding.
2005: US Study on Internet Usage by Gender
In 2005, a US study showed that men used the Internet slightly more than women, although this difference reversed in those under 30. Men used the Internet to pay bills, participate in auctions, and download music and videos. Men and women were equally likely to use the Internet for shopping and banking.
November 2006: Internet Included in New Seven Wonders
In November 2006, the Internet was included on USA Today's list of the New Seven Wonders.
2007: Internet Carries Over 97% of Telecommunication Information
By 2007 more than 97% of all telecommunicated information was carried over the Internet.
2008: Submarine Cable Disruption
In 2008, disruptions of submarine communications cables caused blackouts or slowdowns to large areas.
2008: Gender Differences in Internet Usage
In 2008, women significantly outnumbered men on most social networking services, such as Facebook and Myspace. Women watched more streaming content, whereas men downloaded more.
2009: Global Internet Users Reach 1.9 Billion
In 2009, the number of Internet users globally rose to 1.9 billion.
2010: Internet Usage Statistics
By 2010, 22% of the world's population had access to computers with 1 billion Google searches every day, 300 million Internet users reading blogs, and 2 billion videos viewed daily on YouTube.
March 2011: Estimated Internet Users Reach 2.095 Billion
As of March 31, 2011, the estimated total number of Internet users was 2.095 billion (30% of world population).
2011: Internet Advertising Surpasses Cable Television Revenues
In 2011, Internet advertising revenues in the United States surpassed those of cable television.
2011: Energy Usage Estimates for Internet
In 2011, academic researchers estimated the overall energy used by the Internet to be between 170 and 307 GW, less than two percent of the energy used by humanity. The estimate included the energy needed to build, operate, and periodically replace the estimated 750 million laptops, a billion smart phones and 100 million servers worldwide as well as the energy that routers, cell towers, optical switches, Wi-Fi transmitters and cloud storage devices use when transmitting Internet traffic.
2011: Internet Blackout in Egypt and Armenia Connectivity Severed
In 2011, the Internet in Egypt experienced a blackout, with approximately 93% of networks without access, as a form of Internet censorship. Also in 2011, a woman digging for scrap metal severed most connectivity for the nation of Armenia.
2011: IPv4 Address Exhaustion
In 2011, the global IPv4 address allocation pool was exhausted, marking the final stage of IPv4 address exhaustion.
2012: ITU reports 34% of individuals regularly connect to the Internet
In 2012, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) reported that 34% of individuals regularly connect to the Internet. The number of unique mobile cellular subscriptions was 3.9 billion in 2012.
2013: Institute for Local Self-Reliance Report on Retail Employment
A 2013 Institute for Local Self-Reliance report stated that brick-and-mortar retailers employ 47 people for every $10 million in sales, while Amazon employs only 14.
2013: Worldwide E-commerce Size
According to International Data Corporation, the size of worldwide e-commerce, when global business-to-business and -consumer transactions are combined, equated to $16 trillion in 2013.
2014: Electricity usage controversy
In 2014, a peer-reviewed research paper highlighted the controversy surrounding estimates of the Internet's electricity usage, noting claims in the literature differing by a factor of 20,000.
2014: Airbnb's Valuation
In 2014, the 700-employee room rental start-up Airbnb was valued at $10 billion, about half as much as Hilton Worldwide, which employs 152,000 people. Uber was valued at $18.2 billion.
2014: World's Internet Users Surpass 3 Billion
In 2014, the world's Internet users surpassed 3 billion, representing 44% of the world's population.
October 2016: Mobile and Tablet Internet Usage Exceeds Desktop
Internet usage by mobile and tablet devices exceeded desktop worldwide for the first time in October 2016.
October 2016: IANA Stewardship Transition
The National Telecommunications and Information Administration, an agency of the United States Department of Commerce, had final approval over changes to the DNS root zone until the IANA stewardship transition on October 1, 2016.
2016: Increase in Malware Variants
In 2016, malware variants have increased.
2016: AP Stylebook Recommends Lowercase 'internet'
In 2016, the AP Stylebook recommended using the lowercase form 'internet' in every case. Also in 2016, the Oxford English Dictionary found that 'Internet' was capitalized in 54% of cases.
2016: Mobile Subscriptions Reach 4.8 Billion
In 2016, the number of unique mobile cellular subscriptions increased to 4.8 billion, representing two-thirds of the world's population, with more than half of subscriptions located in Asia and the Pacific.
2017: Book on Internet's Impact on Mental Health
A 2017 book claimed that the Internet consolidates most aspects of human endeavor into singular arenas, which has fundamentally negative impacts on mental health.
2017: Malware Variants Increase
According to Symantec's 2018 Internet Security Threat Report (ISTR), malware variants number has increased to 669,947,865 in 2017, which is twice as many malware variants as in 2016.
2017: ITU Estimate of Internet Users
In 2017, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) estimated that 48% of individual users regularly connect to the Internet, marking an increase from 34% in 2012.
2018: Symantec's Internet Security Threat Report
According to Symantec's 2018 Internet Security Threat Report (ISTR), malware variants number has increased to 669,947,865 in 2017.
2018: CO2 emissions attributed to global data transfer
According to a non-peer-reviewed study published in 2018 by The Shift Project, nearly 4% of global CO2 emissions could be attributed to global data transfer and the necessary infrastructure. The study also said that online video streaming alone accounted for 60% of this data transfer and therefore contributed to over 300 million tons of CO2 emission per year, and argued for new "digital sobriety" regulations restricting the use and size of video files.
2018: 4G Network Coverage
As of 2018, 80% of the world's population was covered by a 4G network.
2018: Asia Accounts for 51% of Internet Users
By 2018, Asia accounted for 51% of all Internet users, with 2.2 billion out of the 4.3 billion Internet users in the world. China also had 802 million users in 2018.
2019: Highest Internet Penetration
In 2019, Kuwait, Qatar, the Falkland Islands, Bermuda and Iceland had the highest Internet penetration by the number of users, with 93% or more of the population with access.
2020: Predicted Rise in Mobile Subscriptions
In 2020, the number of mobile subscriptions was predicted to rise to 5.7 billion users.
2021: Cybercrime Costs
In 2021, cybercrime was predicted to cost the world economy US$6 trillion, and is increasing at a rate of 15% per year.
2022: Global Internet User Statistics
In 2022, it was estimated that 5.4 billion people use the Internet, more than two-thirds of the world's population, and 54% of the world's Internet users were based in Asia.
2023: Internet Traffic to Pornographic Video Sites
As of 2023, Internet traffic to pornographic video sites rivalled that of mainstream video streaming and sharing services.
Mentioned in this timeline

A submarine is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater...
New Zealand is an island country in the southwestern Pacific...
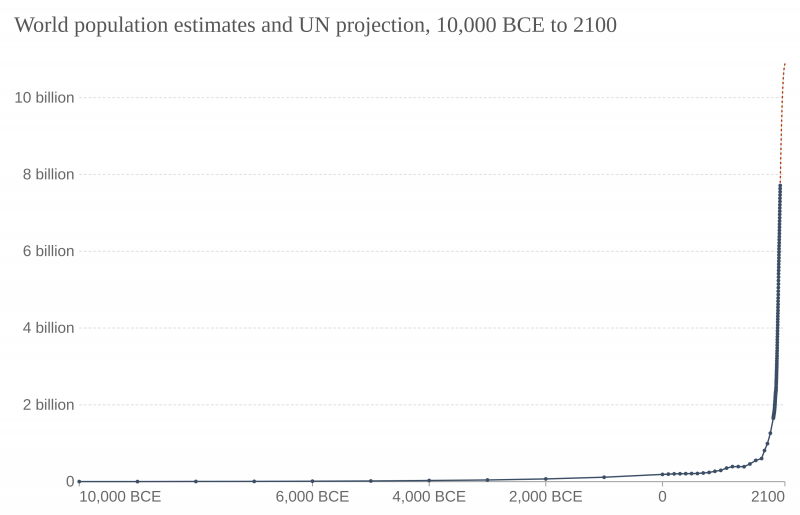
The world population the total number of living humans surpassed...
Africa is the second-largest and second-most populous continent comprising of...
Japan is an East Asian island country located in the...
Australia officially the Commonwealth of Australia encompasses the Australian mainland...
Trending
5 minutes ago SEPTA Adjusts Service in Philadelphia Amidst Intense Blizzard and Heavy Snowfall.
5 minutes ago Hawaiian Airlines to reduce widebody planes, update Airbus A330 cabins.

6 minutes ago Michael Conforto Signs with Chicago Cubs Amidst Dodgers Free Agent Rumors.

2 hours ago Shakira Announces Free Concert in Mexico City's Zócalo for Her Fans

5 hours ago Roman Reigns Pulled From Show, Wins Royal Rumble 2026; Future WWE Plans

4 hours ago Mike Goldberg details Brock Lesnar's transformative impact and influence on the UFC.
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Barack Obama the th U S President - was the...

Bernie Sanders is a prominent American politician currently serving as...

Michael Joseph Jackson the King of Pop was a highly...
The Winter Olympic Games a major international multi-sport event held...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...