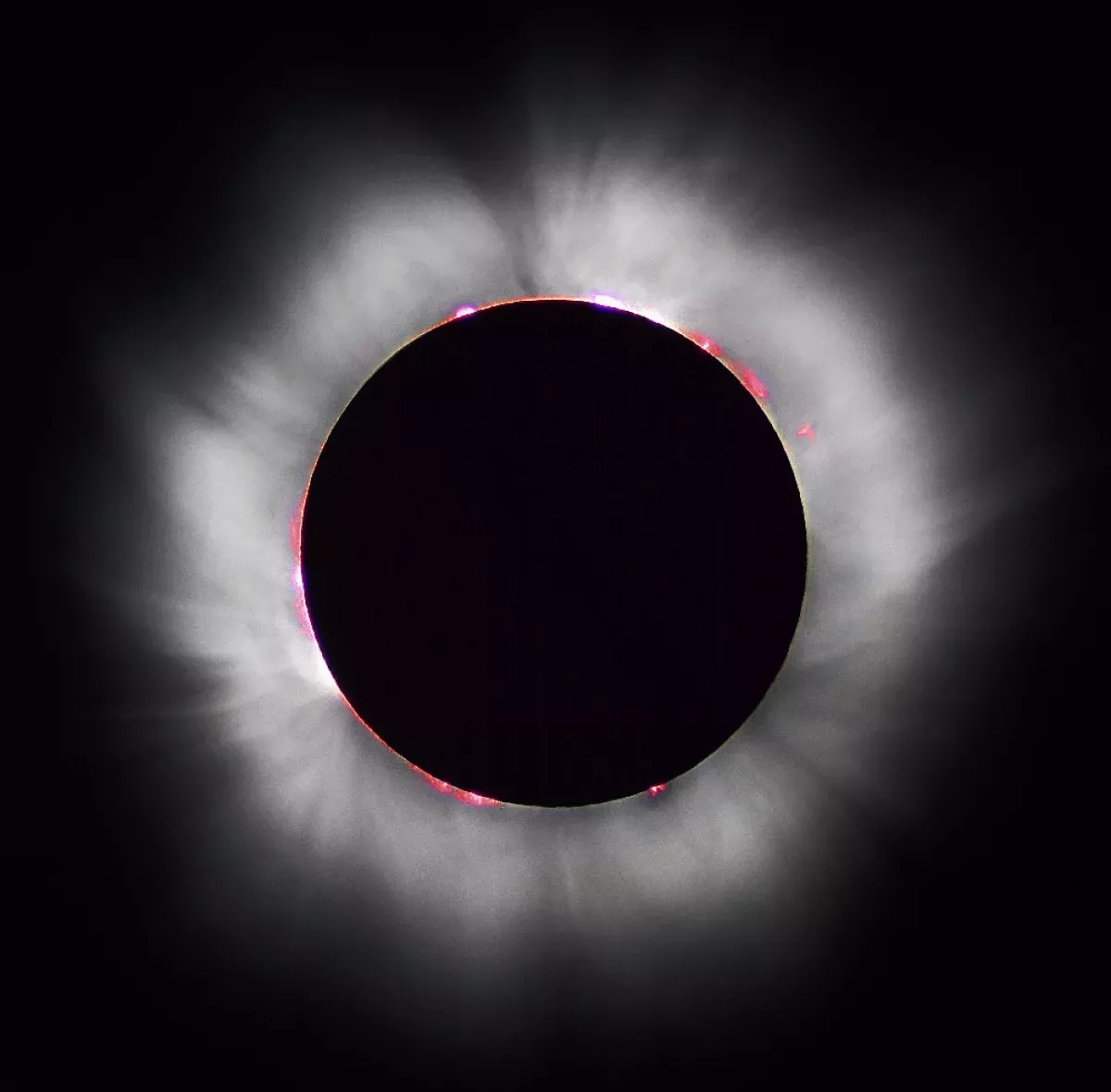
A solar eclipse happens when the Moon moves between the Earth and the Sun, blocking the Sun's light partially or totally from a small area on Earth. This alignment occurs roughly every six months during the new moon phase when the Moon's orbit is closest to Earth's orbit. A total solar eclipse completely obscures the Sun, while partial and annular eclipses only obscure a portion. Unlike lunar eclipses visible from Earth's night side, solar eclipses are only visible from a small region. Total solar eclipses happen on Earth about every 18 months, but recur at any specific location only once every 360 to 410 years.
May 29, 1919: Confirmation of Einstein's Theory
On May 29, 1919, observations made during a total solar eclipse helped confirm Einstein's theory of general relativity. Arthur Eddington compared the apparent distance between stars with and without the Sun between them.
1935: Year with Five Solar Eclipses
The year 1935 was one of the years since the Gregorian calendar was instituted in 1582, that had five solar eclipses.
1954: Allais Effect Observation
In 1954, Maurice Allais reported observing unusual movements during a solar eclipse, contributing to the Allais effect.
June 20, 1955: Total Solar Eclipse
On June 20, 1955, the longest total solar eclipse of the 20th century occurred, lasting 7 minutes and 8 seconds.
1959: Allais Effect Observation
In 1959, Maurice Allais reported observing unusual movements during a solar eclipse, contributing to the Allais effect.
1966: Gemini 12 Eclipse Observation
In 1966, the crew of Gemini 12 observed a total solar eclipse from space.
1970: Saxl Effect Observation
In 1970, Saxl and Allen observed a sudden change in motion of a torsion pendulum, known as the Saxl effect, during a solar eclipse.
June 30, 1973: Long Total Solar Eclipse
On June 30, 1973, a total solar eclipse lasted 7 minutes and 3 seconds. Observers aboard a Concorde supersonic aircraft stretched totality for this eclipse to about 74 minutes by flying along the path of the Moon's umbra.
1997: Gravitational Shielding Effect Suggestion
During the 1997 solar eclipse, Wang et al. observed data suggesting a possible gravitational shielding effect, generating debate.
1999: Mir Eclipse Observation
In 1999, the partial phase of a total eclipse was visible from the Mir space station.
2002: Gravitational Shielding Effect Unexplained
In 2002, Wang and a collaborator published a detailed data analysis suggesting that the possible gravitational shielding effect observed during the 1997 solar eclipse still remains unexplained.
April 29, 2014: Last Non-Central Annular Solar Eclipse
On April 29, 2014, the last non-central annular solar eclipse occurred, where the umbra intersected Earth without its central line.
March 20, 2015: Impact on Power System
On March 20, 2015, a solar eclipse was estimated to have a significant impact on the power system, with the electricity sector taking mitigation measures. Continental Europe and Great Britain synchronous areas were estimated to have about 90 gigawatts of solar power, with a temporary decrease of up to 34 GW compared to a clear sky day.
2023: 2023 Hybrid Eclipse
In 2023, a hybrid eclipse occurred where the eclipse appeared total at the midpoint and annular at the beginning and end due to varying distances from the Moon.
2025: Proba-3 Mission
As of 2025, a pair of satellites launched by the European Space Agency (Proba-3 mission) began creating on-demand eclipses relative to one another. These eclipses cannot be seen from earth, but are captured by imaging from one satellite while the other interposes itself between the sun and the imaging satellite.
April 9, 2043: Next Non-Central Total Solar Eclipse
The next non-central total solar eclipse is predicted to occur on April 9, 2043.
Trending
54 minutes ago Ameren Prices $400M Senior Notes, $900M Bonds for Grid Investment, Reshaping Debt
2 hours ago Pokemon Celebrates 30 Years: A Cultural Phenomenon with Multimillion-Dollar Cards
2 hours ago Daylight Saving Time 2026: Prepare to set your clocks forward and lose sleep.

2 hours ago Indiana Investigates CenterPoint Energy Amid Bill Concerns and New Utility Law.

2 hours ago Galatasaray's Champions League opponent revealed; Liverpool legend comments on Juventus match; Real Madrid faces Man City.

4 hours ago Google Maps to fully function in South Korea after data agreement.
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Barack Obama the th U S President - was the...

Susan Rice is an American diplomat and public official prominent...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Michael Joseph Jackson the King of Pop was a highly...

Kashyap Pramod Patel is an American lawyer who became the...


