Vaccination is the process of administering a vaccine to stimulate the immune system and develop immunity against a specific disease. Vaccines contain weakened, live, or killed microorganisms, or components thereof, triggering the body's adaptive immune response and preventing illness. A high vaccination rate within a population leads to herd immunity, which protects vulnerable individuals who cannot be vaccinated due to health conditions. This indirect protection is crucial for safeguarding those at higher risk from infectious diseases. Vaccination is a cornerstone of public health, significantly reducing the incidence and severity of preventable illnesses.
1905: U.S. Supreme Court upholds compulsory vaccination laws
In 1905, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld compulsory vaccination laws in the landmark case Jacobson v. Massachusetts, ruling that laws could require vaccination to protect the public from dangerous communicable diseases.
1959: WHO calls for the eradication of smallpox worldwide
In 1959, the WHO called for the eradication of smallpox worldwide, as smallpox was still endemic in 33 countries.
1963: Introduction of the measles vaccine
In wealthy nations, the number of measles cases had dropped dramatically after the introduction of the measles vaccine in 1963.
1966: Smallpox cases worldwide
In 1966, according to the WHO there were about 100 million cases of smallpox worldwide, causing an estimated two million deaths.
1974: Smallpox confined to parts of Asia and Africa
By 1974, the WHO smallpox vaccination program had confined smallpox to parts of Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, Ethiopia and Somalia.
1974: WHO adopts goal of universal vaccination by 1990
In 1974 the WHO adopted the goal of universal vaccination by 1990 to protect children against six preventable infectious diseases: measles, poliomyelitis, diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, and tuberculosis.
1974: Vaccination prevents deaths
In 1974, a WHO-funded study by The Lancet estimates that, during the 50-year period starting in 1974, vaccination prevented 154 million deaths, including 146 million among children under age 5.
1977: Last case of smallpox acquired outside a lab
In 1977, the WHO recorded the last case of smallpox infection acquired outside a laboratory in Somalia.
1979: Smallpox eradicated
In 1979, smallpox was finally eradicated, after killing an estimated 300–500 million people in the 20th century.
1980: WHO declares the world free of smallpox
In 1980, the WHO officially declared the world free of smallpox.
1990: Vaccination rates in developing countries
In the 1980s, leading up to 1990, only 20 to 40% of children in developing countries were vaccinated against six diseases.
1998: Publication of paper linking vaccines and autism
In 1998, a paper by Andrew Wakefield concluded that eight of the twelve patients developed behavioral symptoms consistent with autism following the administration of the MMR vaccine. The article was later criticized for lack of scientific rigor and data falsification.
2000: Vaccinations prevent deaths
According to a 2021 paper, vaccinations against various diseases have prevented an estimated 50 million deaths from 2000 to 2019.
2000: Establishment of the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization
In 2000, the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization was established to strengthen routine vaccinations and introduce new and underused vaccines in countries with a per capita GDP of under US$1,000.
2001: Thimerosal removed from US childhood vaccines
In 2001, thimerosal was removed from childhood vaccines in the United States as a precaution, even though evidence supported its safety and efficacy. Thimerosal was used as a preservative to prevent the growth of bacteria and fungi in multi-dose vials of vaccine.
2003: Cost of SARS outbreak
In 2003, the SARS outbreak in East Asia cost $54 billion.
2004: Co-authors retract vaccine-autism link
In 2004, 10 of the original 12 co-authors of the 1998 paper (excluding Wakefield) published a retraction stating that no causal link was established between MMR vaccine and autism as the data were insufficient.
2006: Eradication of polio possible with improved sanitation
By 2006 global health experts concluded that the eradication of polio was only possible if the supply of drinking water and sanitation facilities were improved in slums.
2007: Studies on effectiveness of vaccines in the US
In 2007, studies regarding the effectiveness of vaccines on mortality or morbidity rates of those exposed to various diseases found almost 100% decreases in death rates, and about a 90% decrease in exposure rates in the United States.
2009: H1N1 pandemic vaccine adverse events
In 2009, Pandemrix, a vaccine for the H1N1 pandemic that was given to around 31 million people, was found to have a higher level of adverse events than alternative vaccines, resulting in legal action. The CDC carried out a population-based study and found the FDA-approved 2009 H1N1 flu shots were not associated with an increased risk for neurological disorder.
2009: Public Health Law Research report on vaccination effectiveness
In 2009, Public Health Law Research reported that there is sufficient evidence supporting the effectiveness of requiring vaccinations as a condition for attending child care facilities and schools and that there is strong evidence supporting the effectiveness of standing orders, which allow healthcare workers without prescription authority to administer vaccine as a public health intervention.
2010: The Lancet officially retracts article
In 2010, The Lancet officially retracted the 1998 article by Wakefield, stating that several elements of the article were incorrect, including falsified data and protocols.
2011: Andrew Wakefield found to have falsified data
In 2011, Andrew Wakefield, a leading proponent of the theory that MMR vaccine causes autism, was found to have been financially motivated to falsify research data and was subsequently stripped of his medical license.
2013: Vaccine preventable deaths in children
In 2013, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that 29% of deaths of children under five-years-old were vaccine preventable.
2015: Study confirms no link between autism and MMR vaccine
In 2015, a study confirmed that there is no correlation between vaccines and autism and no link between the MMR vaccine and children who had a normally developed sibling or a sibling that had autism.
2017: Dengvaxia program suspended
In 2017, the mass vaccination program in the Philippines that was using Dengvaxia, the only approved vaccine for Dengue fever, was suspended. This suspension happened because the vaccine was found to increase the risk of hospitalization for Dengue fever by 1.58 times in children of 9 years or younger.
2019: Vaccinations prevent deaths
According to a 2021 paper, vaccinations against various diseases have prevented an estimated 50 million deaths from 2000 to 2019.
December 2020: COVID-19 vaccinations prevent deaths
According to a June 2022 study, COVID-19 vaccinations prevented an additional 14.4 to 19.8 million deaths in 185 countries and territories from December 8, 2020, to December 8, 2021.
2020: Children missed vaccinations due to COVID-19 pandemic
From 2020 onwards, UNICEF reported on the extent to which children missed out on vaccinations due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
December 2021: COVID-19 vaccinations prevent deaths
According to a June 2022 study, COVID-19 vaccinations prevented an additional 14.4 to 19.8 million deaths in 185 countries and territories from December 8, 2020, to December 8, 2021.
June 2022: Study on COVID-19 vaccination impact
According to a June 2022 study, COVID‑19 vaccinations prevented an additional 14.4 to 19.8 million deaths in 185 countries and territories from 8 December 2020 to 8 December 2021.
2022: WHO/UNICEF report on global immunization coverage
In 2022, according to a WHO/UNICEF report, the number of children who did not receive a single dose of the vaccine increased from 13.9 million in 2022 to 14.5 million in 2023.
2023: Vaccination programs get back on track
By summer 2023, UNICEF described vaccination programs as getting "back on track" after disruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
2023: WHO/UNICEF report on global immunization coverage
In 2023, a WHO/UNICEF report found that the number of children who received three doses of the vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis (DTP) stalled at 84% (108 million), a key marker for global immunization coverage. It was also found that the number of children who did not receive a single dose of the vaccine increased from 13.9 million in 2022 to 14.5 million in 2023.
2024: WHO/UNICEF report on global immunization coverage
In 2024, a WHO/UNICEF report found the number of children who received three doses of the vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis (DTP) in 2023 stalled at 84% (108 million).
Mentioned in this timeline
India officially the Republic of India is a South Asian...
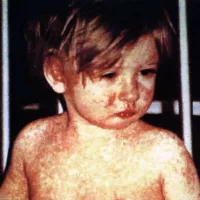
Measles also known as morbilli or rubeola is a highly...

The World Health Organization WHO is a specialized agency of...
Pakistan officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a South...
Massachusetts officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts is a state located...

Smallpox a deadly infectious disease caused by the variola virus...
Trending

3 months ago Michelle Obama: America 'not ready' for a woman president, cites sexism concerns.

1 hour ago Apple MacBook Pro: Touchscreen, Dynamic Island, and New Interface Coming Soon.

13 minutes ago Ethereum Price Faces Resistance at $1,950 Amidst Market Repricing Concerns.
13 minutes ago BP Receives Hold Ratings Amid Strategy Updates and Increased Rating by Argus.
1 hour ago Whitefox & Fluid Quip collaborate; Low-carbon ethanol boosted; Indoor plants aid climate resilience.
1 hour ago HSBC: Enterprise Software Strong, AI Enhances Capabilities, Valuations Historically Low.
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Susan Rice is an American diplomat and public official prominent...

Barack Obama the th U S President - was the...

Michael Joseph Jackson the King of Pop was a highly...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Bernie Sanders is a prominent American politician currently serving as...
