A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. It contains an agent resembling a disease-causing microorganism, often in weakened or killed form, or its components. The vaccine stimulates the immune system to recognize the agent as a threat and develop immunity, enabling it to destroy the agent and protect against future encounters with the associated microorganism. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines have been extensively studied and verified.
1928: Diphtheria vaccine contamination incident
In 1928, a Staphylococcus infection resulting from a lack of preservatives in a diphtheria vaccine led to the deaths of 12 out of 21 children inoculated.
1931: Growth of fowlpox virus in embryonated chicken egg documented
In 1931, Alice Miles Woodruff and Ernest Goodpasture documented that the fowlpox virus could be grown in embryonated chicken egg.
1935: Use of eggs for virus propagation
In 1935, eggs were used for virus propagation in the development of a yellow fever vaccine.
1945: Use of eggs for virus propagation in influenza vaccine
In 1945, eggs were used for virus propagation in the development of an influenza vaccine.
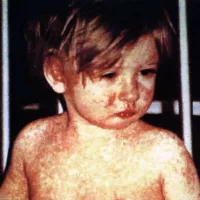
1958: Measles outbreak in the United States
In 1958, the United States experienced a significant measles outbreak, with 763,094 cases reported and 552 deaths.
1959: Growth media and cell culture replaced eggs
In 1959, growth media and cell culture replaced eggs as the standard method of virus propagation for vaccines.
1990: Pertussis vaccine used as adjuvant for anthrax vaccine
In 1990, in preparation for the Persian Gulf campaign, the whole cell pertussis vaccine was used as an adjuvant for anthrax vaccine to produce a more rapid immune response.
1999: DIVA vaccines coined
In 1999, marker vaccines were coined as DIVA vaccines. The first DIVA vaccines and companion diagnostic tests were developed by J. T. van Oirschot and colleagues.
2001: Dengue vaccine study
In 2001, a study identified an issue with dengue vaccines, where the DEN-3 serotype was found to dominate and suppress the response to DEN-1, -2, and -4 serotypes.
2003: Vaccine production via transgenic plants identified
As early as 2003, the idea of vaccine production via transgenic plants was identified.
2005: Thiomersal in U.S. childhood vaccines
As of 2005, the only childhood vaccine in the U.S. that contains thiomersal in greater than trace amounts is the influenza vaccine, which is currently recommended only for children with certain risk factors.
2005: Bananas developed that produce a human vaccine
In 2005, bananas were developed that produce a human vaccine against hepatitis B.
2006: Introduction of shingles vaccine
In 2006, a vaccine was introduced against shingles, a disease caused by the chickenpox virus, which usually affects the elderly.
2008: Measles cases associated with importation
In early 2008, there were 64 suspected cases of measles, with 54 of those infections linked to importation from another country. It was noted that 63 of the 64 individuals either had never been vaccinated against measles or were uncertain whether they had been vaccinated.
2009: HPV vaccine recommended in the UK
As of 2009, the human papillomavirus vaccine is recommended in the UK.
2011: HPV vaccine recommended in the U.S.
As of 2011, the human papillomavirus vaccine is recommended in the U.S.
2013: Vaccine sales concentrated in EU or US
In 2013, 70% of vaccine sales are concentrated in the EU or US, with the companies having the highest market share in vaccine production being Merck, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer and Novartis.
2013: Synthetic third-generation vaccines development
Since at least 2013, scientists have been trying to develop synthetic third-generation vaccines by reconstructing the outside structure of a virus.
2016: DNA vaccine for the Zika virus began testing
In 2016, a DNA vaccine for the Zika virus began testing at the National Institutes of Health. Separately, Inovio Pharmaceuticals and GeneOne Life Science began tests of a different DNA vaccine against Zika in Miami.
2019: WHO characterized vaccine hesitancy
In 2019, the World Health Organization characterized vaccine hesitancy as one of the top ten global health threats.
2020: Development of mRNA vaccines to combat COVID-19
In the year 2020, mRNA vaccines such as BNT162b2 were developed with the help of Operation Warp Speed and massively deployed to combat the COVID-19 pandemic.
2021: WTO evaluates waiving COVID-19 vaccine patents
During the COVID-19 pandemic in 2021, the World Trade Organization and governments around the world evaluated whether to waive intellectual property rights and patents on COVID-19 vaccines to increase access and production.
2021: Karikó and Weissman received Horwitz Prize
In 2021, Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman received Columbia University's Horwitz Prize for their pioneering research in mRNA vaccine technology.
Mentioned in this timeline

Operation Warp Speed was a US government public-private partnership launched...
Pfizer Inc is a multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered...
Measles also known as morbilli or rubeola is a highly...

Miami is a major coastal city in Florida and the...

The World Health Organization WHO is a specialized agency of...

Columbia University located in New York City is a private...
Trending

18 minutes ago Bryce Harper's WBC Performance Raises Doubts About Elite Status and Leadership for Phillies

18 minutes ago Shakira's nomination to the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame sparks legend status.

19 minutes ago Devil Wears Prada 2 Teaser Released, Oscars Buzz, and Hathaway's Fashion Insights.

19 minutes ago Kevin Costner and Brooks Nader: Dating Rumors Spark After Las Vegas Sighting.

1 hour ago Arizona Wildcats Defeat UCF in Big 12 Tournament, Fans Celebrate Victory

1 hour ago Susan Lucci: A Legendary Career and Enduring Impact on Television
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Victoria MacKenzie-Childs is a ceramic artist and co-founder with her...

Paula White-Cain is a prominent American televangelist and key figure...

Markwayne Mullin is an American politician and businessman serving as...

William Franklin Graham III commonly known as Franklin Graham is...
