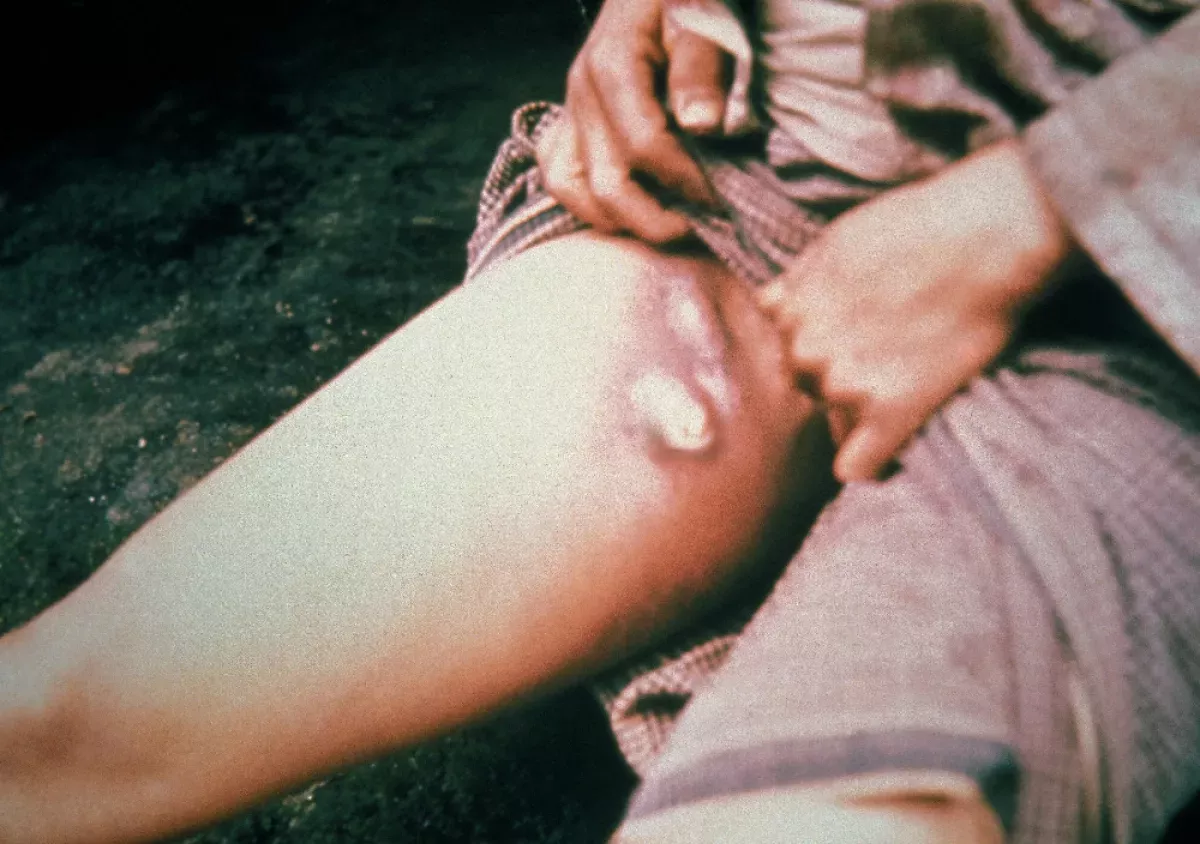
Bubonic plague, caused by Yersinia pestis, manifests 1-7 days post-exposure with flu-like symptoms: fever, headache, and vomiting. A hallmark symptom is swollen, painful lymph nodes (buboes) near the bacteria's entry point. Acral necrosis, skin darkening, can also occur. Buboes may rupture. It is one of the three forms of plague.
1900: Plague Cases in the US
Between 1900 and 2015, the United States had 1,036 human plague cases.
1900: Plague in San Francisco
From 1900 to 1904, the plague infected people in Chinatown in San Francisco.
1902: Chinese Exclusion Act
In 1902, authorities made permanent the Chinese Exclusion Act.
1904: Plague in San Francisco
From 1900 to 1904, the plague infected people in Chinatown in San Francisco.
1907: Plague in Oakland and East Bay
From 1907 to 1909, the plague infected people in the locales of Oakland and the East Bay.
1909: Plague in Oakland and East Bay
From 1907 to 1909, the plague infected people in the locales of Oakland and the East Bay.
1924: Last Major US Outbreak
In 1924, the last major outbreak in the United States occurred in Los Angeles.
1940: Bombing of Ningbo
In 1940, the Imperial Japanese Army Air Service bombed Ningbo with fleas carrying the bubonic plague.
1941: Changde Plague Drop
In 1941, 40 members of Unit 731 air-dropped plague-contaminated fleas on Changde.
1959: Pandemic Considered Active
According to the World Health Organization, in 1959, the pandemic was considered active until worldwide casualties dropped to 200 per year.
1994: Plague Outbreak in India
In 1994, a plague outbreak in five Indian states caused an estimated 700 infections (including 52 deaths) and triggered a large migration of Indians within India as they tried to avoid the disease.
2003: Oran Outbreak Control
In 2003, targeted chemoprophylaxis, sanitation, and vector control played a role in controlling the Oran outbreak of the bubonic plague.
2010: Global Plague Cases
In 2010, globally there were 3,248 documented cases of the Bubonic plague.
2012: Madagascar Epidemics
From 2012 to 2017, Madagascar began to host regular epidemics of the Bubonic plague.
2013: Discovery of Plague Victims in England
In 2013, archeologists in England uncovered a burial mound to reveal 17 bodies, mainly children, who had died of the Bubonic plague and dental core analysis revealed the presence of Yersinia pestis.
2015: Plague Cases in the US
In 2015, 16 people in the western United States developed plague, including 2 cases in Yosemite National Park.
2015: Global Plague Cases
In 2015, globally there were 3,248 documented cases of the Bubonic plague resulting in 584 deaths.
November 2017: Madagascar Plague Outbreak
In November 2017, the Madagascar Ministry of Health reported a plague outbreak to the WHO with more cases and deaths than any recent outbreak in the country, with most cases being pneumonic rather than bubonic.
2017: Madagascar Epidemics
From 2012 to 2017, Madagascar began to host regular epidemics of the Bubonic plague.
June 2018: Idaho Plague Infection
In June 2018, a child was confirmed to be the first person in Idaho to be infected by bubonic plague in nearly 30 years.
May 2019: Mongolia Plague Deaths
In May 2019, a couple died in Mongolia, while hunting marmots and contracted Bubonic Plague.
November 2019: Inner Mongolia Plague Cases
In November 2019, two people in the province of Inner Mongolia, China, were treated for Bubonic Plague.
July 2020: Plague Cases in China and Mongolia
In July 2020, in Bayannur, Inner Mongolia of China, a human case of bubonic plague was reported. Also in July 2020, in Mongolia, a teenager died from bubonic plague after consuming infected marmot meat.
Mentioned in this timeline
India officially the Republic of India is a South Asian...

San Francisco is a major commercial financial and cultural hub...
China officially the People's Republic of China PRC is an...

Los Angeles is the most populous city in California and...

The World Health Organization WHO is a specialized agency of...
Russia officially the Russian Federation is a transcontinental country spanning...
Trending

9 months ago Ed Martin's nomination as D.C. prosecutor faces Republican opposition despite Trump's support and looming deadline.

Ricky Dene Gervais is an English comedian actor writer producer and director known for his significant contributions to television He...
6 months ago Fenerbahçe seeks advantage against 'Flying Dutchman,' Azeri TV cheers, stands with Palestine.

3 months ago Alex Eala Enters Hong Kong Campaign with Career-High Ranking, World No. 51

Ryan Sheckler is an American professional skateboarder entrepreneur and television personality He gained prominence through his skateboarding career and further...

2 months ago Netanyahu Seeks Presidential Pardon Amid Corruption Trial: A Political Maneuver?
Popular

Thomas Douglas Homan is an American law enforcement officer who...

William Franklin Graham III commonly known as Franklin Graham is...

Melania Trump a Slovenian-American former model has served as First...

Jupiter is the fifth and largest planet from the Sun...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Instagram is a photo and video-sharing social networking service owned...