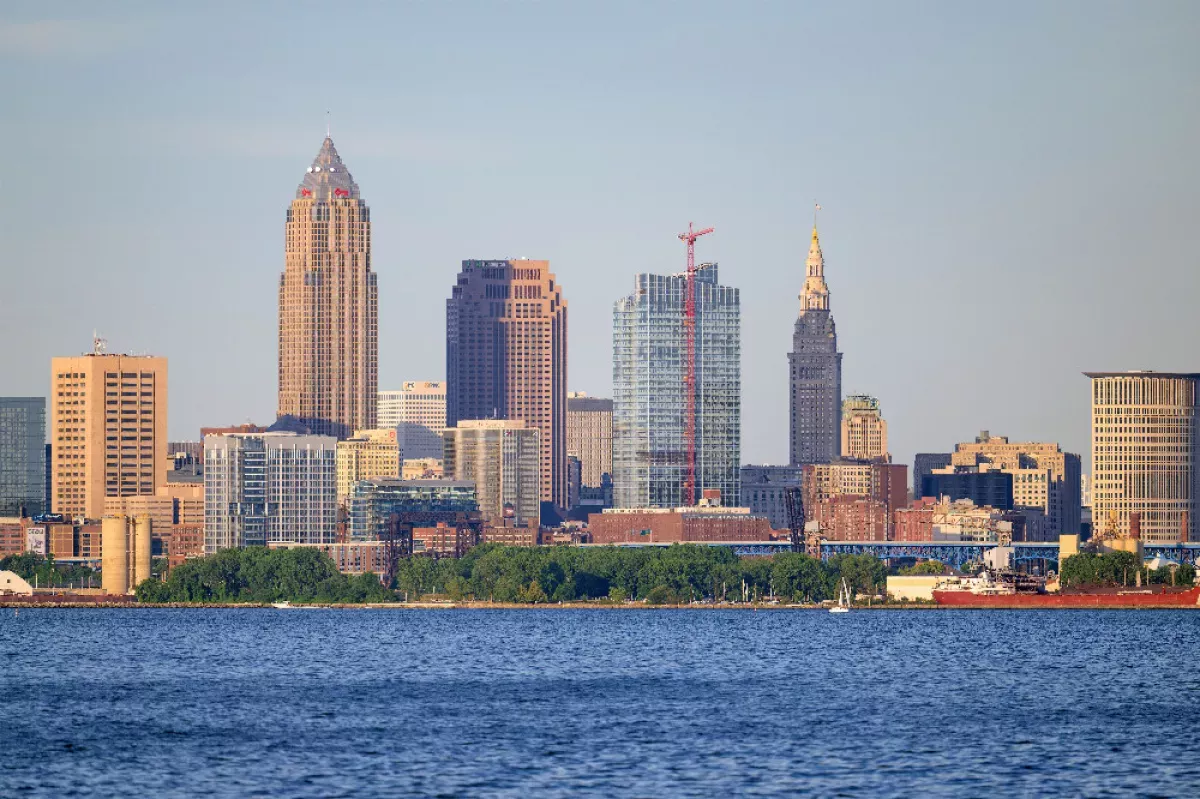
Cleveland is a major city in Ohio, United States, situated on the southern shore of Lake Erie. As the county seat of Cuyahoga County, it holds strategic importance along the Canada-U.S. maritime border. Cleveland is the most populous city on Lake Erie, the second-most populous city in Ohio, and the 53rd-most populous city in the U.S.. It serves as the central hub for a large metropolitan area of over 2 million residents and a combined statistical area nearing 4 million.
1903: 1903 Group Plan
In 1903, many of Cleveland's government and civic buildings began construction as a result of the 1903 Group Plan.
1904: Carnegie Libraries Open
Between 1904 and 1920, 15 libraries built with funds from Andrew Carnegie were opened in the city.
1907: Completion of Cleveland Trust Company Building in 1907
The Cleveland Trust Company Building was completed in 1907.
1910: First Great Migration Impact
Beginning in 1910, Cleveland's black population, largely concentrated on the city's East Side, increased significantly as a result of the First Great Migration.
1910: Cleveland Known as the "Sixth City"
By 1910, Cleveland was known as the "Sixth City" due to being the sixth-largest U.S. city at the time. Automotive companies like Peerless, Chandler, and Winton (maker of the first car driven across the U.S.) were based there.
1912: City Club of Cleveland Founded
Founded in 1912, the City Club of Cleveland provides a platform for national and local debates and discussions.
1914: Establishment of Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland
The Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland was established in 1914, becoming one of 12 U.S. Federal Reserve Banks.
October 1915: Signing of the Cleveland Agreement
In October 1915, at Cleveland's Bohemian National Hall, Czech American and Slovak American representatives signed the Cleveland Agreement, advocating for the creation of a unified Czech and Slovak state.
1915: Establishment of Karamu House
Established in 1915, Karamu House is the oldest African American theater in the nation.
1915: Cleveland Indians Name Change
In 1915, the Cleveland Guardians were known as the Cleveland Indians.
1916: Hart Crane Moves to New York City
In 1916, American modernist poet Hart Crane moved to New York City, after dividing his adolescence between Cleveland and Akron.
1916: Opening of the Cleveland Museum of Art
In 1916, the Cleveland Museum of Art opened as part of the City Beautiful movement, supported by wealthy patrons.
1917: Plain Dealer Screen Magazine Debut
From 1917 to 1924, Samuel Brodsky directed the weekly Plain Dealer Screen Magazine, which ran in theaters in Cleveland and Ohio.
1918: Establishment of the Cleveland Orchestra
In 1918, the Cleveland Orchestra was established as part of the City Beautiful movement, supported by wealthy patrons.
May 1919: Prohibition Takes Effect in Ohio in May 1919
In May 1919, Prohibition first took effect in Ohio (although it was not well-enforced in Cleveland).
1919: Cleveland May Day Riots in 1919
In 1919, Cleveland attracted national attention amid the First Red Scare for the Cleveland May Day Riots, in which local socialist and IWW demonstrators clashed with anti-socialists.
1920: Carnegie Libraries Open
Between 1904 and 1920, 15 libraries built with funds from Andrew Carnegie were opened in the city.
1920: Cleveland's Population and Indians' World Series Win in 1920
By 1920, Cleveland had grown into a densely populated metropolis of 796,841, making it the fifth-largest city in the nation, with a foreign-born population of 30%. Also in 1920, the Cleveland Indians won their first World Series championship.
1920: Volstead Act Becomes Law in 1920
In 1920, Prohibition became law with the Volstead Act.
1921: Dangerous Toys Film Production
In 1921, Samuel Brodsky and Robert McLaughlin produced major silent-era features such as Dangerous Toys at their film studio in the Andrews mansion on Euclid Avenue (now the WEWS-TV studio).
1921: U.S. Open Chess Championships
In 1921, the U.S. Open Chess Championships took place in Cleveland and were won by Edward Lasker.
1923: Establishment of the Cleveland Council on World Affairs
In 1923, the Cleveland Council on World Affairs was established, fostering international relations and discussions.
1923: Federal Reserve Bank Building Completion
In 1923, the downtown building of the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland, located on East 6th Street and Superior Avenue, was completed by the Cleveland architectural firm Walker and Weeks.
1924: Republican National Convention Hosted
Cleveland hosted a Republican National Convention in 1924.
1924: End of Plain Dealer Screen Magazine
From 1917 to 1924, Samuel Brodsky directed the weekly Plain Dealer Screen Magazine, which ran in theaters in Cleveland and Ohio.
1924: Council-Manager Government Experiment Begins
From 1924, the city briefly experimented with a council–manager government under William R. Hopkins.
1924: Cleveland Bulldogs Win NFL Championship
In 1924, the Cleveland Bulldogs won the National Football League (NFL) Championship.
1925: Time Magazine Published
From 1925 to 1927, Time magazine was published in Cleveland.
1925: Vladimir Mayakovsky's Poetry Recitation
In 1925, Russian Futurist poet Vladimir Mayakovsky came to Cleveland and gave a poetry recitation to the city's ethnic working class, as part of his trip to America.
1925: Main Library Building Dedicated
The Cleveland Public Library's main building was designed by Walker and Weeks and dedicated in 1925.
1926: Construction of the Terminal Tower Begins in 1926
In 1926, the Van Sweringen brothers commenced construction of the Terminal Tower skyscraper.
1927: Completion of Terminal Tower in 1927
Completed in 1927 as part of the Cleveland Union Terminal complex, the Terminal Tower was the tallest building in North America outside New York City until 1964 and the tallest in the city until 1991.
1927: Time Magazine Published
From 1925 to 1927, Time magazine was published in Cleveland.
1929: Wall Street Crash of 1929
Cleveland was hit hard by the Wall Street Crash of 1929 and the subsequent Great Depression.
1929: National Air Races and Women's Air Derby in 1929
In 1929, Cleveland hosted the first of many National Air Races, and Amelia Earhart flew to the city from Santa Monica, California in the Women's Air Derby.
1930: Dedication of the Terminal Tower in 1930
By 1930, the Terminal Tower building was dedicated as part of Cleveland Union Terminal, and the city had a population of over 900,000.
1930: Dedication in 1930
Completed in 1927 and dedicated in 1930 as part of the Cleveland Union Terminal complex, the Terminal Tower was the tallest building in North America outside New York City until 1964 and the tallest in the city until 1991.
1930: Cleveland Botanical Garden Established
Established in 1930, the Cleveland Botanical Garden in University Circle is the oldest civic garden center in the nation.
1931: Council-Manager Government Experiment Ends
Until 1931, the city briefly experimented with a council–manager government under Daniel E. Morgan before returning to the mayor–council system.
1932: Creation of Superman
In 1932, Joe Shuster and Jerry Siegel, who both attended Glenville High School in Cleveland, created the comic book character Superman.
1933: Goodbye Again Film Release
In 1933, Michael Curtiz's pre-Code classic Goodbye Again, featuring Warren William and Joan Blondell, was released, showcasing Cleveland.
1933: Repeal of Prohibition in 1933
In 1933, Prohibition was eventually repealed nationally by Congress.
1934: Harlan Ellison's Birth
Harlan Ellison, noted author of speculative fiction, was born in Cleveland in 1934.
June 1936: Debut of the Great Lakes Exposition in June 1936
In commemoration of the centennial of Cleveland's incorporation as a city, the Great Lakes Exposition debuted in June 1936 at the city's North Coast Harbor.
1936: Republican National Convention Hosted
Cleveland hosted a Republican National Convention in 1936.
September 1937: End of the Great Lakes Exposition in September 1937
The Great Lakes Exposition, which debuted in June 1936, concluded its second and final season in September 1937.
December 7, 1941: Attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941
On December 7, 1941, Imperial Japan attacked Pearl Harbor and declared war on the U.S. Two of the victims of the attack were Cleveland natives.
1942: Native Land Film Release
In 1942, Labor struggles in Cleveland were depicted in Native Land, narrated by Paul Robeson.
1945: Cleveland Rams Win NFL Championship
In 1945, the Cleveland Rams won the National Football League (NFL) Championship before relocating to Los Angeles.
1946: Django Reinhardt's U.S. Debut
In 1946, gypsy jazz guitarist Django Reinhardt gave his U.S. debut performance in Cleveland.
1946: Cleveland Browns Win AAFC Championship
In 1946, the Cleveland Browns won the All-America Football Conference (AAFC) Championship.
1946: One World Day Inaugurated
Since 1946, Cleveland has annually celebrated One World Day in the Cleveland Cultural Gardens in Rockefeller Park, honoring its diverse ethnic communities.
1947: Eliot Ness Runs for Mayor
In 1947, Eliot Ness (of the Untouchables) ran for mayor of Cleveland.
1947: Cleveland Browns Win AAFC Championship
In 1947, the Cleveland Browns won the All-America Football Conference (AAFC) Championship.
1948: Cleveland Indians in The Kid from Cleveland
In 1948, players from the Cleveland Indians appeared in The Kid from Cleveland (1949).
1948: Cleveland Browns Win AAFC Championship
In 1948, the Cleveland Browns won the All-America Football Conference (AAFC) Championship.
1949: Cleveland Named All-America City in 1949
In 1949, Cleveland was named an All-America City for the first time.
1949: Harlan Ellison Returns to Cleveland
In 1949, Harlan Ellison moved back to Cleveland. As a young man, he published short stories in the Cleveland News and performed at the Cleveland Play House.
1949: The Kid from Cleveland Film Release
In 1949, The Kid from Cleveland was released, featuring players from the 1948 Cleveland Indians.
1949: Cleveland Browns Win AAFC Championship
In 1949, the Cleveland Browns won the All-America Football Conference (AAFC) Championship.
1950: Cleveland's Population Reaches 914,808 in 1950
In 1950, Cleveland's population reached 914,808.
1950: Cleveland Browns Win NFL Championship
In 1950, the Cleveland Browns won the National Football League (NFL) Championship.
1954: Cleveland Browns Win NFL Championship
In 1954, the Cleveland Browns won the National Football League (NFL) Championship.
1954: Cleveland Indians Win American League Pennant
In 1954, the Cleveland Indians won the American League pennant, making the World Series.
1955: Cleveland Browns Win NFL Championship
In 1955, the Cleveland Browns won the National Football League (NFL) Championship.
1957: U.S. Open Chess Championships
In 1957, the U.S. Open Chess Championships took place in Cleveland and were won by Bobby Fischer.
1961: The Mike Douglas Show Begins
In 1961, The Mike Douglas Show, a nationally syndicated daytime talk show, began in Cleveland on KYW-TV (now WKYC).
1962: Cleveland Pipers Win ABL Championship
In 1962, the Cleveland Pipers, owned by George Steinbrenner, won the American Basketball League championship.
1964: Terminal Tower Height Status Ends in 1964
Completed in 1927 and dedicated in 1930 as part of the Cleveland Union Terminal complex, the Terminal Tower was the tallest building in North America outside New York City until 1964 and the tallest in the city until 1991.
1964: Sister City Partnership with Lima, Peru
In 1964, Cleveland established its inaugural sister city partnership with Lima, Peru, marking the beginning of its global network of cultural, economic, and educational relationships.
1964: Barons Last Calder Cup Victory
In 1964, the Barons were the last Cleveland AHL team to win the Calder Cup until the Cleveland Monsters in 2016.
1964: Cleveland Browns Win NFL Championship
In 1964, the Cleveland Browns won the National Football League (NFL) Championship.
1964: Cleveland National Air Show Inaugurated
Since 1964, the Cleveland National Air Show, succeeding the National Air Races, has been held at Burke Lakefront Airport.
1966: The Fortune Cookie Film
Billy Wilder's The Fortune Cookie (1966) was set and filmed in Cleveland and marked the first onscreen pairing of Walter Matthau and Jack Lemmon.
1966: Hough Riots in 1966
The Hough riots erupted from July 18 to 24, 1966, in Cleveland.
November 1967: Carl B. Stokes Elected Mayor in November 1967
In November 1967, Cleveland became the first major American city to elect an African American mayor, Carl B. Stokes.
July 23, 1968: Glenville Shootout in 1968
The Glenville Shootout took place on July 23, 1968, in Cleveland.
1968: Direct Rail Transit to Airport
In 1968, Cleveland became the first city in the nation to have a direct rail transit connection linking the city's downtown to its major airport.
1968: Cleveland Browns NFL/AFC Championship Game Appearance
In 1968, the Cleveland Browns made it to the NFL/AFC Championship Game.
June 1969: Cuyahoga River Fire
In June 1969, the Cuyahoga River fire spurred Cleveland to action under Mayor Carl B. Stokes, and played a key role in the passage of the Clean Water Act in 1972 and the National Environmental Policy Act later that year.
June 1969: Burning of the Cuyahoga River in June 1969
The burning of the Cuyahoga River in June 1969 brought national attention to the issue of industrial pollution in Cleveland.
1969: Cleveland Browns NFL/AFC Championship Game Appearance
In 1969, the Cleveland Browns made it to the NFL/AFC Championship Game.
1970: Second Great Migration
By 1970, Cleveland's black population had increased significantly due to the First and Second Great Migrations, largely concentrated on the city's East Side.
1971: End of Carl B. Stokes' Mayoral Term in 1971
Carl B. Stokes served as mayor of Cleveland from 1968 to 1971.
1972: Clean Water Act Passage
In 1972, the Clean Water Act was passed, spurred by the Cuyahoga River fire of June 1969, leading to extensive cleanup efforts by the city and the Ohio Environmental Protection Agency (OEPA).
1974: World Series of Rock
Beginning in 1974, the city hosted the World Series of Rock at Cleveland Municipal Stadium.
1977: Cleveland International Film Festival Established
In 1977, the Cleveland International Film Festival was established and has been held in the city since then.
December 1978: Cleveland's Financial Default in December 1978
In December 1978, Cleveland became the first major American city since the Great Depression to enter into a financial default on federal loans.
1978: F.I.S.T. Film Release
In 1978, Labor struggles in Cleveland were also depicted in Norman Jewison's F.I.S.T. with Sylvester Stallone.
1978: The Deer Hunter Scenes
In 1978, the wedding and reception scenes in The Deer Hunter, while set in suburban Pittsburgh, were shot in Cleveland's Tremont neighborhood.
1978: Cleveland Marathon Inaugurated
Since 1978, the Cleveland Marathon has been hosted annually.
1980: Second 1980 U.S. Presidential Debate Hosted
Cleveland hosted the second 1980 U.S. presidential debate.
1980: Final World Series of Rock
In 1980, the city hosted the final World Series of Rock at Cleveland Municipal Stadium.
1980: Tri-C Jazz Fest
The Tri-C Jazz Fest has been held annually in Cleveland at Playhouse Square since 1980.
1983: A Christmas Story Scenes
In 1983, A Christmas Story, set in Indiana, drew many external shots from Cleveland.
1983: Peak Unemployment in Cleveland in 1983
In 1983, during the national recession, Cleveland's unemployment rate peaked at 13.8%, higher than the national average.
1984: Stranger Than Paradise
Clevelander Jim Jarmusch's Stranger Than Paradise (1984) was a favorite of the Cannes Film Festival.
1984: Cleveland Jazz Orchestra Established
The Cleveland Jazz Orchestra was established in 1984.
1986: Cleveland Browns NFL/AFC Championship Game Appearance
In 1986, the Cleveland Browns made it to the NFL/AFC Championship Game.
1987: Cleveland Emerges from Default in 1987
In 1987, Cleveland emerged from financial default.
1987: Cleveland Browns NFL/AFC Championship Game Appearance
In 1987, the Cleveland Browns made it to the NFL/AFC Championship Game.
June 25, 1988: All-Time Record High Temperature in Cleveland on June 25, 1988
The all-time record high in Cleveland of 104 °F (40 °C) was established on June 25, 1988.
1989: Major League Film Release
In 1989, Major League reflected the perennial struggles of the Cleveland Indians.
1989: Cleveland Browns NFL/AFC Championship Game Appearance
In 1989, the Cleveland Browns made it to the NFL/AFC Championship Game.
1991: Terminal Tower Loses Tallest in Cleveland Title in 1991
Completed in 1927 and dedicated in 1930 as part of the Cleveland Union Terminal complex, the Terminal Tower was the tallest building in North America outside New York City until 1964 and the tallest in the city until 1991.
1991: Slovene Independence
In 1991, with Slovene independence, the Consulate General of the Republic of Slovenia in Cleveland ceased to be a consulate for Tito's Yugoslavia.
1991: Normal Yearly Precipitation in Cleveland from 1991-2020
Normal yearly precipitation based on the 30-year average from 1991 to 2020 is 41.03 inches (1,042 mm).
January 19, 1994: All-Time Record Low Temperature in Cleveland on January 19, 1994
The all-time record low in Cleveland of −20 °F (−29 °C) was set on January 19, 1994.
1995: Cleveland Indians Win American League Pennant and Jacobs Field Sellouts Begin
In 1995, the Cleveland Indians won the American League pennant, making the World Series. Also in 1995, Jacobs Field began a streak of 455 consecutive sold-out games.
1995: Cleveland Browns Relocation Announcement
In 1995, the owner Art Modell announced the relocation of the Cleveland Browns.
1997: Cleveland Indians Win American League Pennant
In 1997, the Cleveland Indians won the American League pennant, making the World Series.
1997: Bone Thugs-n-Harmony Grammy Win
In 1997, the Cleveland hip hop group Bone Thugs-n-Harmony won a Grammy for their song "Tha Crossroads".
1997: Air Force One Filming Location
In 1997, the opening shots of Air Force One were filmed in and above Severance Hall.
1999: Return of the Cleveland Browns
Beginning in the 1999 season, the Cleveland Browns returned to the NFL.
2000: Increase in Condominiums, Lofts, and Apartments Since 2000
The number of condominiums, lofts, and apartments in downtown Cleveland has been on the increase since 2000 and especially 2010, reflecting downtown's growing population.
2001: End of Jacobs Field Sellout Streak
Between 1995 and 2001, Jacobs Field sold out 455 consecutive games.
2001: Renovation of Cleveland Arcade in 2001
In 2001, the Cleveland Arcade (also known as the Old Arcade) was renovated as a Hyatt Regency Hotel.
2001: Great Lakes Burning River Fest Inaugurated
Since 2001, the Great Lakes Burning River Fest, a music and beer festival at Whiskey Island, has been sponsored by the Great Lakes Brewing Company.
2003: American Splendor Film Release
In 2003, American Splendor reflected the life of Cleveland graphic novelist Harvey Pekar.
2004: 2004 U.S. Vice Presidential Debate Hosted
Cleveland hosted the 2004 U.S. vice presidential debate.
2007: Spider-Man 3 Doubles for Manhattan
In 2007, Downtown Cleveland doubled for Manhattan in Spider-Man 3.
2007: Michael Symon Named "The Next Iron Chef"
In 2007, chef Michael Symon gained national attention when he was named "The Next Iron Chef" on the Food Network. Also in 2007, Michael Ruhlman collaborated with Anthony Bourdain on an episode of Anthony Bourdain: No Reservations focusing on Cleveland's restaurant scene.
2007: Cavaliers Win Eastern Conference
In 2007, the Cleveland Cavaliers won the Eastern Conference, but were defeated in the NBA Finals by the San Antonio Spurs.
2008: 2008 Democratic Primary Debate Hosted
Cleveland hosted one 2008 Democratic primary debate.
2008: Cleveland Scene Absorbs Cleveland Free Times
In 2008, Cleveland Scene absorbed its competitor, the Cleveland Free Times.
2008: RTA HealthLine Completed
In 2008, the Greater Cleveland Regional Transit Authority (RTA) completed the HealthLine, a bus rapid transit line.
2008: End of Jacobs Field Sellout Record
In 2008, the Major League Baseball record of 455 consecutive sold-out games at Jacobs Field was broken.
June 16, 2010: Hot in Cleveland Premiere
Hot in Cleveland, a comedy that aired on TV Land, premiered on June 16, 2010, and ran for six seasons until its finale on June 3, 2015.
2010: Greenhouse Gas Reduction Baseline
Cleveland's climate action plan, updated in December 2018, aims to reduce greenhouse gases to 80% below the 2010 level by 2050.
2010: Population Growth in Downtown Cleveland Since 2010
Since 2010, Cleveland's downtown and several neighborhoods have experienced significant population growth, while overall population decline has slowed.
2010: Increase in Condominiums, Lofts, and Apartments Since 2010
The number of condominiums, lofts, and apartments in downtown Cleveland has been on the increase since 2000 and especially 2010, reflecting downtown's growing population.
2011: Kill the Irishman Film Release
In 2011, Kill the Irishman depicted the 1970s turf war between Danny Greene and the Cleveland crime family.
2012: The Avengers Doubles for Manhattan
In 2012, Downtown Cleveland doubled for Manhattan in The Avengers.
2013: Global Center for Health Innovation Opens
In 2013, Cleveland's Global Center for Health Innovation opened with 235,000 square feet of display space for healthcare companies worldwide.
2013: Belt Magazine Founded
The digital Belt Magazine was founded in Cleveland in 2013.
2014: Cleveland Hosts Gay Games Ceremony
In 2014, Cleveland hosted the ninth official Gay Games ceremony.
June 3, 2015: Hot in Cleveland Finale
Hot in Cleveland, a comedy that aired on TV Land, premiered on June 16, 2010, and ran for six seasons until its finale on June 3, 2015.
2015: Cavaliers Win Eastern Conference
In 2015, the Cleveland Cavaliers won the Eastern Conference, but were defeated in the NBA Finals by the Golden State Warriors.
2015: Renovation of Cleveland Trust Company Building in 2015
In 2015, the Cleveland Trust Company Building was renovated as a downtown Heinen's supermarket.
June 22, 2016: Cavs Victory Parade
On June 22, 2016, over 1.3 million people attended a parade held in the Cavs' honor in downtown Cleveland after their NBA Championship win.
2016: Republican National Convention Hosted
Cleveland hosted a Republican National Convention in 2016.
2016: Car Ownership Statistics
In 2016, 23.7% of Cleveland households lacked a car, while the national average was 8.7%. Cleveland averaged 1.19 cars per household in 2016, compared to a national average of 1.8.
2016: Cavaliers Win NBA Championship and Host Parade
In 2016, the Cavaliers won the Eastern Conference and won their first NBA Championship defeating the Golden State Warriors. On June 22, 2016, over 1.3 million people attended a parade held in the Cavs' honor in downtown Cleveland.
2016: Cleveland Indians Win American League Pennant
In 2016, the Cleveland Indians won the American League pennant, making the World Series.
2016: Cleveland Monsters Win Calder Cup
In 2016, the Cleveland Monsters of the American Hockey League won the Calder Cup.
2017: The Fate of the Furious Doubles for Manhattan
In 2017, Downtown Cleveland doubled for Manhattan in The Fate of the Furious.
2017: Cavaliers Win Eastern Conference
In 2017, the Cleveland Cavaliers won the Eastern Conference, but were defeated in the NBA Finals by the Golden State Warriors.
December 2018: Climate Action Plan Update
In December 2018, Cleveland updated its climate action plan, setting a 2050 target of 100% renewable power and an 80% reduction in greenhouse gases below the 2010 level.
2018: Cavaliers Win Eastern Conference
In 2018, the Cleveland Cavaliers won the Eastern Conference, but were defeated in the NBA Finals by the Golden State Warriors.
2019: Immigration Processing Time
A 2019 study found Cleveland to be the city with the shortest average processing time in the nation for immigrants to become U.S. citizens.
2020: Ethnic and Racial Diversity
A 2020 analysis found Cleveland to be the most ethnically and racially diverse major city in Ohio.
2020: Racial and Ethnic Composition of Cleveland
As of 2020, the racial and ethnic composition of Cleveland was 47.5% African American, 32.1% non-Hispanic white, 13.1% Hispanic or Latino, 2.8% Asian, 0% Pacific Islander, 0.2% Native American, and 3.8% from two or more races.
2020: First 2020 U.S. Presidential Debate Hosted
Cleveland hosted the first 2020 U.S. presidential debate.
2020: Cleveland Population in 2020
In 2020, Cleveland had a population of 372,624, making it the most populous city on Lake Erie, the second-most populous city in Ohio, and the 53rd-most populous city in the U.S.
2020: Rise in Crime Rate
In 2020, crime in Cleveland saw an abrupt rise.
2020: 2020 Census Data
In 2020, the census recorded Cleveland's population as 372,624 people in 170,549 households, with a population density of 4,901.51 inhabitants per square mile. The median household income was $30,907, and the per capita income was $21,223; 32.7% of the population was living below the poverty line.
2020: Normal Yearly Precipitation in Cleveland from 1991-2020
Normal yearly precipitation based on the 30-year average from 1991 to 2020 is 41.03 inches (1,042 mm).
2021: Cleveland Television Market Size
As of 2021, the Cleveland television market, including Akron and Canton, was the 19th-largest in the country.
2021: Judas and the Black Messiah Filming Location
In 2021, Judas and the Black Messiah, set in Chicago, was filmed in Cleveland.
2021: Walk Score Ranking
In 2021, Walk Score ranked Cleveland the 17th most walkable of the 50 largest cities in the U.S.
2021: Cleveland Indians Name Change
In 2021, the Cleveland Guardians were renamed.
2022: Cleveland Clinic Employment
As of 2022, the Cleveland Clinic is the largest private employer in the state of Ohio, with a workforce of over 55,000.
2022: Justin Bibb Becomes Mayor
In 2022, Justin Bibb became the mayor of Cleveland.
2022: Cleveland Silent Film Festival Established
In 2022, the Cleveland Silent Film Festival was established and has been held in the city since then.
2022: Greater Cleveland MSA GDP in 2022
In 2022, the GDP for the Greater Cleveland MSA was US$138.3 billion. Combined with the Akron MSA, the eight-county Cleveland–Akron metropolitan economy was $176 billion in 2022, the largest in Ohio.
2023: Cleveland Public Library Collection Size
In 2023, the Cleveland Public Library had a collection of over 13 million materials.
July 2024: Cleveland Hosts Pan American Masters Games
In July 2024, Cleveland hosted the Pan American Masters Games.
2024: Cleveland Division of Police Size
As of 2024, the Cleveland Division of Police has roughly 1,100 sworn officers.
2025: Superman Doubles for Metropolis
In 2025, Downtown Cleveland will double for Metropolis in James Gunn's Superman.
2050: Renewable Power Target
Cleveland's climate action plan, updated in December 2018, sets a 2050 target of 100% renewable power, along with reduction of greenhouse gases to 80% below the 2010 level.
Mentioned in this timeline

Basketball is a team sport played on a rectangular court...
California is a U S state on the Pacific Coast...

Amelia Earhart was a groundbreaking American aviation pioneer who vanished...

Christmas is an annual festival celebrated on December th commemorating...

Los Angeles is the most populous city in California and...
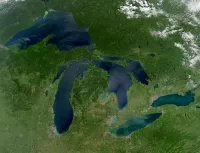
The Great Lakes are a chain of five large interconnected...
Trending
45 minutes ago Diego Garcia: Britain's Chagos deal faces opposition amid military base concerns and global implications.

45 minutes ago Charles Leclerc and Alexandra Saint Mleux Spark Marriage Rumors in Monaco

2 hours ago Fetterman Discussed Amid Trump's Iran Actions and Lawmaker Support Debate.
2 hours ago Citigroup integrates Bitcoin into $30T asset management, boosting institutional crypto adoption.

2 hours ago Greg Abel's first letter signals Berkshire Hathaway's future post-Buffett, watched by Wall Street.
2 hours ago Ali Larter Celebrates Her 50th Birthday: A Look Back at Her Career
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton is a prominent American politician lawyer...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Michael Joseph Jackson the King of Pop was a highly...

Barack Obama the th U S President - was the...

Susan Rice is an American diplomat and public official prominent...
