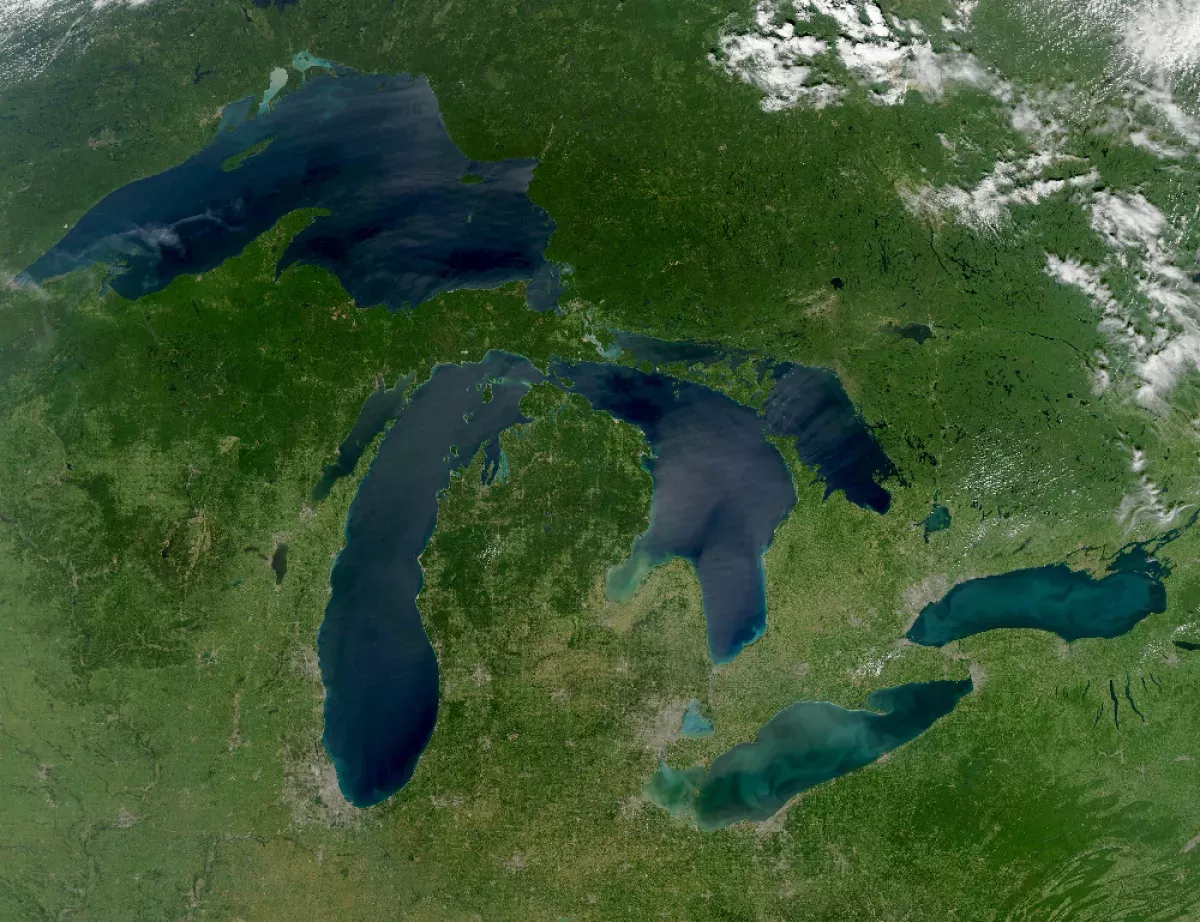
The Great Lakes are a chain of five large, interconnected freshwater lakes situated on the border between Canada and the United States. These lakes, named Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario, are connected by the Great Lakes Waterway, facilitating waterborne transportation. The primary outflow is the Saint Lawrence River, which connects to the Atlantic Ocean. The Illinois Waterway also provides a connection to the Mississippi River basin.
1900: Lake Michigan commercial fish harvests average 41 million pounds
By 1900, commercial fishermen on Lake Michigan were hauling in an average of 41 million pounds of fish annually.
October 11, 1907: Cyprus Sinks in Lake Superior Storm
On October 11, 1907, the ore carrier Cyprus sank during a Lake Superior storm, resulting in the drowning of 22 of its 23 crew members.
1909: International Joint Commission Established
In 1909, the International Joint Commission was established to help prevent and resolve disputes relating to the use and quality of boundary waters and to advise Canada and the United States on questions related to water resources.
1915: SS Eastland Disaster at Chicago Dock
In 1915, the SS Eastland rolled over while loading passengers at a Chicago dock, resulting in 844 deaths.
1918: Disappearance of French Minesweepers
In 1918, the French minesweepers Inkerman and Cerisoles vanished in Lake Superior during a blizzard, resulting in the loss of 78 lives.
1938: Wisconsin commercial fishing operations are motorized and mechanized
By 1938, Wisconsin's commercial fishing operations were motorized and mechanized, generating jobs for more than 2,000 workers, and hauling 14 million pounds per year.
1950: Common sight of self-unloader on the lakes
Since about 1950, one of the more common sights on the lakes has been the 1,000-by-105-foot (305 by 32 m), 78,850-long-ton (80,120-metric-ton) self-unloader.
1954: Intensification of Hurricane Hazel
In 1954, The Great Lakes helped intensify storms, such as Hurricane Hazel.
1970: Mercury not listed as harmful chemical
According to the United States Federal Water Quality Administration until 1970, mercury was not listed as a harmful chemical.
1972: Passage of U.S. Clean Water Act
In 1972, the first U.S. Clean Water Act was passed, which was an important piece of legislation designed to improve water quality.
1972: Great Lakes: An Environmental Atlas and Resource Book notes decline in commercial fishing
The 1972 Great Lakes: An Environmental Atlas and Resource Book noted that "Only pockets remain of the once large commercial fishery."
November 10, 1975: SS Edmund Fitzgerald Sinks
On November 10, 1975, the SS Edmund Fitzgerald, the largest and last major freighter wrecked on the Great Lakes, sank just over 17 miles offshore from Whitefish Point on Lake Superior.
1986: U.S. Water Resources Development Act
In 1986, the U.S. "Water Resources Development Act of 1986" stated that any diversion of water from the Great Lakes Basin requires the approval of all eight Great Lakes governors through the Great Lakes Commission.
1986: Detection of ruffe in Lake Superior
In 1986, the ruffe, a small percid fish from Eurasia, was detected in Lake Superior's Saint Louis River. Within five years, it became the most abundant fish species there.
1988: Discovery of zebra mussel
The zebra mussel was first discovered in the Great Lakes in 1988, marking the introduction of an invasive species.
1989: Introduction of quagga mussel
The quagga mussel was introduced to the Great Lakes in 1989, further impacting the ecosystem as an invasive species.
1994: Collingwood Harbour delisted
In 1994, Ontario's Collingwood Harbour became the first of 43 "Great Lakes Areas of Concern" to be formally "de-listed" due to successful cleanup efforts.
1996: Formation of the 1996 Lake Huron cyclone
In 1996, a rare tropical or subtropical storm, dubbed the 1996 Lake Huron cyclone, was observed forming in Lake Huron.
March 6, 1998: Lake Champlain Declared Sixth Great Lake
On March 6, 1998, Lake Champlain was briefly declared the sixth Great Lake of the United States when President Clinton signed Senate Bill 927, which reauthorized the National Sea Grant Program and allowed neighboring states to apply for additional federal research and education funds.
1998: Nova Group Water Withdrawal Plan
In 1998, the Canadian company Nova Group won approval from the Province of Ontario to withdraw Lake Superior water for shipment to Asian countries, but the plan was later abandoned due to public outcry.
2000: Quagga mussel smothers Lake Michigan bottom
Since 2000, the invasive quagga mussel has covered the bottom of Lake Michigan, nearly from shore to shore, with an estimated population of 900 trillion.
2002: Dry Bulk Cargo Moved on the Lakes
In 2002, 162 million net tons of dry bulk cargo were moved on the Great Lakes, including iron ore, grain, and potash.
2003: Severn Sound delisted
In 2003, Ontario's Severn Sound was formally "de-listed" through successful cleanup.
2004: Possible Discovery of Le Griffon Wreck
In 2004, a wreck possibly belonging to Le Griffon, the first ship to sail the Great Lakes and which sank in 1679, was found.
2004: International Ferry Across Lake Ontario
In 2004, an international ferry service began operation across Lake Ontario, running from Rochester, New York, to Toronto.
December 13, 2005: Great Lakes Agreements Signed
On December 13, 2005, the Great Lakes Governors and the Premiers of Ontario and Quebec signed the Great Lakes-Saint Lawrence River Basin Sustainable Water Resources Agreement and the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence River Basin Water Resources Compact.
2005: International Ferry Across Lake Ontario
In 2005, the international ferry across Lake Ontario from Rochester, New York, to Toronto continued to operate, before ceasing operations.
2007: Car Ferry Services Operate on the Great Lakes
As of 2007, four car ferry services cross the Great Lakes, including services on Lake Michigan, Lake Erie, and Lake Huron, providing passenger transport to various islands.
2007: Wreckage of Cyprus Found
In 2007, the Great Lakes Shipwreck Historical Society announced that they had found the wreckage of Cyprus, which sank in 1907.
2007: Economic impact of zebra mussel
In 2007, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service estimated that the economic impact of the zebra mussel could be about $5 billion over the next decade.
October 3, 2008: Great Lakes Compact Signed into Law
On October 3, 2008, the Great Lakes Compact, which had been approved by the state legislatures of all eight states that border the Great Lakes as well as the U.S. Congress, was signed into law by President George W. Bush.
2008: Discovery of HMS Ontario Wreck
In 2008, deep sea divers in Lake Ontario found the wreck of the 1780 Royal Navy warship HMS Ontario.
2009: International Joint Commission report on improved wastewater treatment
In 2009, the International Joint Commission summarized the change: "Since the early 1970s, the level of treatment to reduce pollution from waste water discharges to the Great Lakes has improved considerably.
2010: L.R. Doty Found in Lake Michigan
In 2010, the wreck of the L.R. Doty, which sank in October 1898, was found in Lake Michigan by an exploration diving team.
2011: Problematic blue-green algae blooms on Lake Erie
Blue-green algae, or cyanobacteria blooms, have been problematic on Lake Erie since 2011.
2011: Goderich, Ontario tornado
In 2011, the Goderich, Ontario tornado moved onshore as a tornadic waterspout after forming over the Great Lakes.
2011: Great Lakes Restoration Initiative Funding
In 2011, the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative was funded at $475 million in the U.S. federal government's Fiscal Year budget.
2011: Last commercial fisherman leaves Milwaukee
In 2011, the last commercial fisherman left Milwaukee due to overfishing and anthropogenic changes to the biosphere.
2011: Increased use of anti-depressant drugs
The number of American adults who take anti-depressant drugs rose from 7.7% of all American adults in 1999-2002 to 12.7% in 2011-2014.
2012: Great Lakes Restoration Initiative Funding
In 2012, the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative was funded at $300 million in the U.S. federal government's Fiscal Year budget.
2012: Beginning of long-term study of lake's micro-organisms
Only since 2012 has there been a long-term study of the lakes' micro-organisms.
2013: Cold winter resulted in high ice coverage
During the particularly cold winter of 2013-2014, ice coverage on the Great Lakes peaked at over 92% across the five lakes.
2013: Record low lake levels in Lakes Superior, Erie, and Michigan-Huron
In 2013, record low water levels were observed in Lakes Superior, Erie, and Michigan-Huron.
2014: Another Claimed Discovery of Le Griffon Wreck
In 2014, another wreck discovered in a different location was also claimed to be Le Griffon, the first ship to sail the Great Lakes which sank in 1679.
2014: Increased use of anti-depressant drugs
The number of American adults who take anti-depressant drugs rose from 7.7% of all American adults in 1999-2002 to 12.7% in 2011-2014.
2015: Largest Lake Erie algae bloom to date
In 2015, the largest Lake Erie bloom to date occurred, exceeding the severity index at 10.5.
August 2019: Satellite images depict large algae bloom on Lake Erie
In early August 2019, satellite images depicted a bloom stretching up to 1,300 square kilometers on Lake Erie, with the heaviest concentration near Toledo, Ohio.
2019: Discovery of new species
Between 2012 and 2019 more than 160 new species have been discovered in the Great Lakes.
2019: Great Lakes Restoration Initiative Act of 2019
In 2019, The Great Lakes Restoration Initiative Act of 2019 passed as Pub. L. 116–294.
2020: Record high lake levels in Lakes Superior, Erie, and Michigan-Huron
In 2020, record high water levels were recorded in the Great Lakes. Lakes Superior, Erie, and Michigan-Huron reached record high levels, while Lake Ontario remained relatively constant.
2020: Implementation of Great Lakes Plastic Cleanup project
In 2020, self-operating floating devices called Seabin were put in the Great Lakes to capture plastic trash as part of the Great Lakes Plastic Cleanup project.
January 5, 2021: Great Lakes Restoration Initiative Act Reauthorization
On January 5, 2021, the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative Act of 2019 was passed, reauthorizing the program through Fiscal Year 2026.
2021: Great Lakes Plastic Cleanup project captured 74,000 pieces of trash
In 2021, The Great Lakes Plastic Cleanup project captured 74,000 pieces of trash.
2021: Wisconsin Shipwreck Coast National Marine Sanctuary Established
In 2021, the Wisconsin Shipwreck Coast National Marine Sanctuary was established in the waters of Lake Michigan off Wisconsin.
2023: Milder winter resulted in low ice coverage
During the milder winter of 2023-2024, ice coverage on the Great Lakes remained below 20%.
2024: Milder winter resulted in low ice coverage
During the milder winter of 2023-2024, ice coverage on the Great Lakes remained below 20%.
2026: End of Great Lakes Restoration Initiative Reauthorization
Fiscal Year 2026 marks the end of the reauthorization period for the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative program.
Mentioned in this timeline

George W Bush the rd U S President - is...

Chicago is the most populous city in Illinois and the...

A tornado is a violently rotating column of air extending...

A car also known as an automobile is a wheeled...
Canada is a North American country the second largest in...

Books are a means of storing information as text or...
Trending
52 minutes ago Knicks vs Pacers: Injury Updates and Game Notes for March 13, 2026

52 minutes ago Photograph of Andrew Anderson, Peter Mandelson, and Jeffrey Epstein surfaces, sparking controversy and raising questions.

53 minutes ago James Fishback aims to win Florida after seizing the Gen Z right online.

53 minutes ago Mars Mission: Mice Study Reveals Muscle Loss Challenges for Human Space Travel

53 minutes ago Tony Finau comments on Akshay Bhatia; Bhatia faces cheating claims at The Players.
2 hours ago Geno Stone Signs One-Year Deal with Buffalo Bills After Free Agency Move
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Victoria MacKenzie-Childs is a ceramic artist and co-founder with her...

Paula White-Cain is a prominent American televangelist and key figure...

Markwayne Mullin is an American politician and businessman serving as...

William Franklin Graham III commonly known as Franklin Graham is...