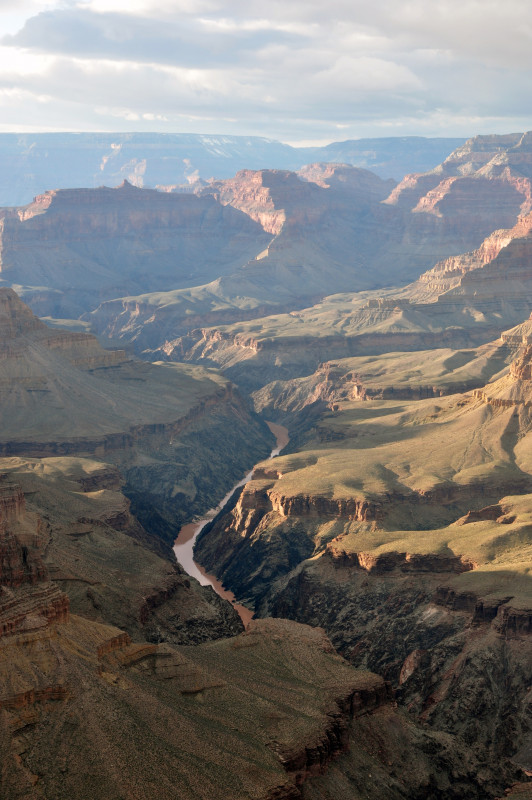
The Grand Canyon is a steep canyon in Arizona, United States, carved by the Colorado River. It stretches 277 miles (446 km) long, reaches up to 18 miles (29 km) wide, and plunges to depths exceeding a mile. It is a prominent landmark and a significant geological feature.
1902: Powell becomes first Director of the U.S. Bureau of Ethnology
In 1902, Powell served as the first Director of the U.S. Bureau of Ethnology of the Smithsonian Institution (1879–1902) and the second Director of the US Geological Survey (1881–1894).
1903: President Roosevelt Visits the Grand Canyon
In 1903, U.S. President Theodore Roosevelt, an avid outdoorsman and conservationist, visited the Grand Canyon.
1903: National Weather Service station established
Since 1903, the National Weather Service has had a cooperative station on the South Rim.
November 28, 1906: Grand Canyon Game Preserve established
On November 28, 1906, President Theodore Roosevelt established the Grand Canyon Game Preserve to protect the area's wildlife.
January 11, 1908: Grand Canyon redesignated as a U.S. National Monument
On January 11, 1908, adjacent national forest lands were added and the preserve was redesignated as a U.S. National Monument.
1908: Grand Canyon designated a National Monument
In 1908, the Grand Canyon became an official National Monument.
1916: Decrease in naturalized streamflow in the Upper Colorado River Basin
From 1916 to 2014, naturalized streamflow in the Upper Colorado River Basin decreased by 16.5%, in spite of a slight increase of +1.4% in annual precipitation over the same period.
January 1, 1919: Record low temperature on the South Rim
On January 1, 1919, the record low temperature on the South Rim was −20 °F (−29 °C).
February 26, 1919: Grand Canyon National Park Established
On February 26, 1919, Grand Canyon National Park was established as the 17th U.S. National Park by an Act of Congress signed into law by President Woodrow Wilson.
1919: Grand Canyon designated a National Park
In 1919, the Grand Canyon officially became a National Park.
1926: First dual distribution water system built
In 1926, the first dual distribution water system in the United States was built on the South Rim, treating and reclaiming wastewater for nonpotable reuse.
1950: Groundwater chemical composition studies
Studies of the Grand Canyon region's groundwater chemical composition indicate the groundwater contains a fraction of modern water (post-1950).
June 30, 1956: Mid-air collision
On the morning of June 30, 1956, a TWA Lockheed Super Constellation and a United Airlines Douglas DC-7 departed Los Angeles International Airport within three minutes of one another on eastbound transcontinental flights. Approximately 90 minutes later, the two propeller-driven airliners collided above the canyon while both were flying in unmonitored airspace.
1956: Deadliest Commercial Aviation Disaster
In 1956, the Grand Canyon was the site of the deadliest commercial aviation disaster in history at the time, accounting for 128 deaths.
1963: Glen Canyon Dam construction
In 1963, the construction of the Glen Canyon Dam permanently changed the Grand Canyon's ecosystem.
June 26, 1974: Record high temperature on the South Rim
On June 26, 1974, the record high temperature on the South Rim was 105 °F (41 °C).
September 1, 1981: Groundwater uranium study commenced
On September 1, 1981, a study examining samples of groundwater from 180 spring sites and 26 wells in the Grand Canyon region has assessed the presence of uranium in groundwater from September 1, 1981, to October 7, 2020.
1984: Last Aerial Video Footage Filmed Below the Rim
In 1984, the last aerial video footage from below the rim of the Grand Canyon was filmed.
February 1, 1985: Record low temperature on the South Rim
On February 1, 1985, the record low temperature on the South Rim was −20 °F (−29 °C).
December 23, 1990: Record low temperature on the South Rim
On December 23, 1990, the record low temperature on the South Rim was −20 °F (−29 °C).
1990: Grand Canyon Visibility Transport Commission Established
In 1990, amendments to the Clean Air Act established the Grand Canyon Visibility Transport Commission (GCVTC).
1992: Activity ceased at Pinyon Plain Mine
In 1992, activity ceased at the Pinyon Plain Mine (formerly Canyon Uranium Mine), ten years prior to the moratorium on new development in 2012.
1996: Federal officials started releasing floods in the Grand Canyon
Federal officials started releasing floods in the Grand Canyon in 1996 in hopes of restoring its ecosystem.
1996: Western Regional Air Partnership Initiated
In 1996 the GCVTC released its final report and initiated the Western Regional Air Partnership (WRAP).
1997: SO2 scrubbers added to Navajo Generating Station
From 1997 through 1999 scrubbers were added to the Navajo Generating Station's three units to reduce SO2 emissions by 90%.
1999: Grand Canyon Area Has Some of the Cleanest Air in the United States
As of 1999 the Grand Canyon area had some of the cleanest air in the United States.
1999: SO2 scrubbers added to Navajo Generating Station
From 1997 through 1999 scrubbers were added to the Navajo Generating Station's three units to reduce SO2 emissions by 90%.
1999: Regional Haze Rule Established
In 1999, the Regional Haze Rule established a goal of restoring visibility in national parks and wilderness areas to natural background levels by 2064.
2001: Fatalities in Grand Canyon
From 1869 to 2001, airplane and helicopter crashes were the most common cause of death in the Grand Canyon, with 242 deaths. 53 deaths resulted from falls, 65 were due to environmental causes, 7 were due to flash floods, 79 drowned in the Colorado River, 25 died in freak errors and accidents, and 23 were victims of homicides.
2003: Mining claims requested near the Grand Canyon
Between 2003 and 2011, 2,215 mining claims had been requested that are adjacent to the canyon, including claims for uranium mines.
August 2004: Visitor Survey Results
In August 2004, a survey of visitors to the Grand Canyon, conducted between September 2003 and August 2004, indicated that 83% were from the United States, with California, Arizona, Texas, Florida, and New York being the top domestic states. Seventeen percent were international visitors, with the United Kingdom, Canada, Japan, Germany, and the Netherlands being the most represented nations.
2004: Federal officials release floods in the Grand Canyon
In 2004, federal officials continued to release floods in the Grand Canyon in hopes of restoring its ecosystem.
2005: Mohave Generating Station shut down
In 2005, the Mohave Generating Station was shut down, completely eliminating its emissions.
2007: Grand Canyon Skywalk Opening
In 2007, the Hualapai tribe opened the glass-bottomed Grand Canyon Skywalk at Grand Canyon West, attracting thousands of visitors a year, mostly from Las Vegas.
2008: Rebecca Flowers' apatite thermochronometry results
In 2008, Rebecca Flowers reported on apatite (U-Th)/He thermochronometry results suggesting that parts of the Grand Canyon had reached a depth near to the modern depth around 20 million years ago.
2008: Victor Polyak's cave origin study
In 2008, a study by Victor Polyak, which was published in the journal Science, examined caves near the Grand Canyon and placed their origins approximately 17 million years ago using uranium-lead dating to analyze calcite deposits.
2008: Federal officials release floods in the Grand Canyon
In 2008, federal officials continued to release floods in the Grand Canyon in hopes of restoring its ecosystem.
2009: Suspension of new uranium mining approvals
In 2009, U.S. Interior Secretary Ken Salazar published a Notice of Intent to suspend approvals for new uranium mining in the area.
2009: Low-NOx SOFA burners installed at Navajo Generating Station
In 2009–2011 low-NOx SOFA burners were installed at the Navajo Generating Station, reducing emissions of NOx by 40%.
2011: Mining claims requested near the Grand Canyon
Between 2003 and 2011, 2,215 mining claims had been requested that are adjacent to the canyon, including claims for uranium mines.
2011: Low-NOx SOFA burners installed at Navajo Generating Station
In 2009–2011 low-NOx SOFA burners were installed at the Navajo Generating Station, reducing emissions of NOx by 40%.
2012: Moratorium on new development
Activity at the mine had ceased in 1992, ten years prior to the moratorium on new development in 2012.
2012: Salazar establishes a 20-year moratorium on uranium mining
In 2012, Interior Secretary Ken Salazar established a 20-year moratorium (known as the "Northern Arizona Withdrawal") withdrawing 1 million acres from the permitting process for uranium and hardrock mining.
2012: Rebecca Flowers' Grand Canyon age study
In 2012, Rebecca Flowers suggested in a study published in the journal Science that the western part of the Grand Canyon could be as old as 70 million years.
2012: Federal government moratorium on uranium mining
In 2012, the federal government's moratorium on uranium mining was challenged in court.
November 2014: Moratorium Appealed in National Mining Association v. Jewell
In November 2014, the federal government's 2012 moratorium was appealed in National Mining Association v. Jewell (No. 14-17350).
2014: Decrease in naturalized streamflow in the Upper Colorado River Basin
From 1916 to 2014, naturalized streamflow in the Upper Colorado River Basin decreased by 16.5%, in spite of a slight increase of +1.4% in annual precipitation over the same period.
2014: Grand Canyon Escalade Announced
In 2014, a developer announced plans to build a multimedia complex on the canyon's rim called the Grand Canyon Escalade.
2015: Death Toll Estimate
As of 2015, about 770 deaths had occurred in the Grand Canyon between the mid-1800s and 2015.
2016: Grand Canyon Skydiving Operation Opens
In 2016, skydiving at the Grand Canyon became possible with the first Grand Canyon Skydiving operation opening at the Grand Canyon National Park Airport on the South Rim.
October 31, 2017: Navajo Nation Council Voted Against Grand Canyon Escalade
On October 31, 2017, the Navajo Nation Council voted against the Grand Canyon Escalade project.
2017: Moratorium upheld by 9th Circuit Court of Appeals
In 2017, the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals upheld the moratorium, stating that the Secretary of the Interior held valid withdrawal authority.
2018: Department of Interior experiments with adaptive management of Glen Canyon Dam
In 2018, the Department of Interior started experimenting with “adaptive management” of the Glen Canyon Dam, using a High-Flow Experiment (HFE) water release.
2019: Plans to replace aging Transcanyon Pipeline proposed
As of 2019, plans to replace the aging 16-mile aluminum Transcanyon Pipeline were proposed.
2019: Navajo Generating Station shut down
In 2019 the Navajo Generating Station shut down completely.
October 3, 2020: Charlie Haeger Found Dead
On October 3, 2020, former Major League Baseball player Charlie Haeger was found dead from a self-inflicted gunshot wound on a canyon trail, following an investigation into the murder of his ex-girlfriend.
October 7, 2020: Groundwater uranium study concluded
To October 7, 2020, a study examining samples of groundwater from 180 spring sites and 26 wells in the Grand Canyon region concluded, assessing the presence of uranium in groundwater from September 1, 1981, to October 7, 2020.
2020: Climate Action Plan goals
By 2020, The National Park Service's "Climate Action Plan" set goals to reduce greenhouse gases 30 percent below 2008 levels and plan and implement measures that best allow the park to adapt to the impacts of climate change.
February 22, 2022: 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals rejects arguments in Havasupai Tribe v. Provencio
On February 22, 2022, the 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals rejected the arguments in No. 20-16401, concluding that the Forest Service had not acted arbitrarily in making its decision in Havasupai Tribe v. Provencio.
2022: Planned water release delayed due to extreme drought
As of 2022, extreme drought has caused water levels in Lake Powell to drop so much that a planned release of water has been delayed, to ensure that the Glen Canyon Dam can continue to generate hydropower.
August 8, 2023: Biden to designate Baaj Nwaavjo I’tah Kukveni – Ancestral Footprints of the Grand Canyon National Monument
On August 8, 2023, it was announced that U.S. President Joe Biden will designate Baaj Nwaavjo I’tah Kukveni – Ancestral Footprints of the Grand Canyon National Monument, a move aimed at conserving nearly 1 million acres of greater Grand Canyon landscape.
2064: Visibility in national parks and wilderness areas to natural background levels goal
In 1999, the Regional Haze Rule established a goal of restoring visibility in national parks and wilderness areas to natural background levels by 2064.
Mentioned in this timeline
IMAX is a proprietary system utilizing high-resolution cameras film formats...
The United States of America is a federal republic located...

Joe Biden is an American politician who served as the...
The National Weather Service NWS is a United States federal...
Colorado a Mountain and Southwestern U S state is the...

Woodrow Wilson the th U S president - was a...
Trending
14 minutes ago Pokemon Celebrates 30 Years: A Cultural Phenomenon with Multimillion-Dollar Cards
15 minutes ago Daylight Saving Time 2026: Prepare to set your clocks forward and lose sleep.

15 minutes ago Indiana Investigates CenterPoint Energy Amid Bill Concerns and New Utility Law.

15 minutes ago Galatasaray's Champions League opponent revealed; Liverpool legend comments on Juventus match; Real Madrid faces Man City.

2 hours ago Google Maps to fully function in South Korea after data agreement.

3 hours ago CDC Panel to Discuss COVID-19 Vaccine Injuries Following RFK Jr.'s Meeting
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Barack Obama the th U S President - was the...

Susan Rice is an American diplomat and public official prominent...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Michael Joseph Jackson the King of Pop was a highly...

Kashyap Pramod Patel is an American lawyer who became the...
