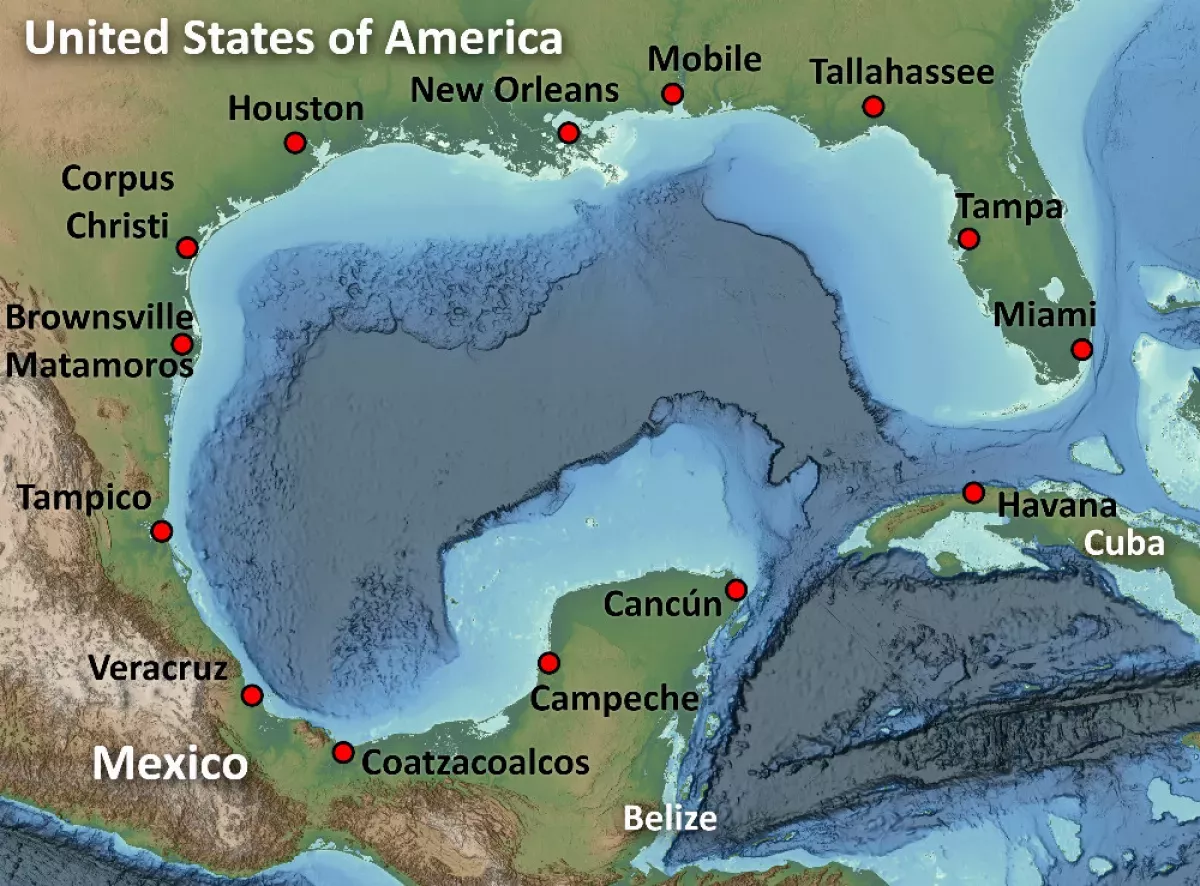
The Gulf of Mexico is a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely bordered by North America. It is bounded by the Gulf Coast of the United States to the north, the Mexican states to the southwest and south, and Cuba to the southeast. The U.S. states bordering the Gulf are occasionally called the "Third Coast" or the "Gulf Coast."
July 30, 1942: SS Robert E. Lee torpedoed by German submarine U-166
On July 30, 1942, the SS Robert E. Lee was torpedoed by the German submarine U-166. The explosion destroyed the No. 3 hold and damaged the engines, radio compartment, and steering gear. The ship sank within 15 minutes, resulting in the loss of one officer, nine crew members, and 15 passengers. The USS PC-566 dropped depth charges on a sonar contact, sinking U-166.
1952: Earthquake tremors felt in Florida
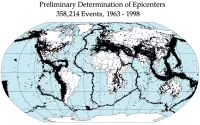
In 1952, earthquake tremors were last felt in Florida, recorded in Quincy, 32 km (20 miles) northwest of Tallahassee.
1970: Surface temperatures warmed at about twice the rate observed for the global ocean surface
From 1970 to 2020, surface temperatures warmed at about twice the rate observed for the global ocean surface.
1973: EPA prohibited the dumping of undiluted chemical waste
In 1973 the United States Environmental Protection Agency prohibited the dumping of undiluted chemical waste by manufacturing sediment interests into the gulf, and the military confessed to similar behavior in waters off Horn Island.
1975: 400 offshore drilling rigs host 10,000 workers
By 1975, the Gulf of Mexico hosted 400 offshore drilling rigs, accommodating a temporary population of more than 10,000 workers on any given day. These workers operated on a weekly staggered schedule.
December 1977: Maritime boundary agreement between United States and Cuba
In December 1977, the United States of America and the Republic of Cuba signed a maritime boundary agreement.
May 1978: Treaty on maritime boundaries between the United States of America and the United Mexican States (Caribbean Sea and Pacific Ocean)
In May 1978, a treaty on maritime boundaries between the United States of America and the United Mexican States (Caribbean Sea and Pacific Ocean) was signed.
June 1979: Ixtoc I oil platform explosion
In June 1979, the Ixtoc I oil platform in the Bay of Campeche suffered a blowout and a catastrophic explosion, initiating the largest oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico to date.
1979: Specimens deposited in the national collections of the National Museum of Natural History
Since 1979, specimens collected by the former Minerals Management Service were deposited in the national collections of the National Museum of Natural History.
April 1980: Ixtoc I oil well capped
In April 1980, the Ixtoc I oil well, which had been leaking since June 1979, was finally capped.
1985: Hypoxic dead zone reported in Gulf of Mexico
Between 1985 and 2008, researchers reported that the hypoxic dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico roughly doubled in size. The increase in nitrogen and phosphorus led to algae blooms and a lack of available oxygen.
1999: Volumetric flow rate through the Yucatan Channel
In 1999, the average volumetric flow rate through the Yucatan Channel varied between 15.8 and 28.1 Sverdrups (hectometers per second).
June 2000: Treaty on the delimitation of the continental shelf in the western Gulf of Mexico beyond 200 nautical miles
In June 2000, a treaty on the delimitation of the continental shelf in the western Gulf of Mexico beyond 200 nautical miles (370 km; 230 mi) was signed between Mexico and the United States.
2001: Wrecks of U-166 and Robert E. Lee found
In 2001, the wrecks of U-166 and Robert E. Lee were found during the C & C Marine survey. The submarine was located in 5,000 feet (1,500 m) of water, about three km (1.9 miles) from where it had attacked the liner.
2002: Shipwreck discovered off the coast of Louisiana
In 2002, an oilfield inspection crew working for the Okeanos Gas Gathering Company (OGGC) discovered a shipwreck, later named the Mardi Gras, dating back to the early 19th century, approximately 56 km (35 mi) off the coast of Louisiana in 1,200 m (3,900 feet) of water.
2005: Hurricane Katrina
In 2005, the gulf's warm sea surface temperatures fed powerful, deadly, and destructive Atlantic hurricanes such as Hurricane Katrina.
September 10, 2006: Magnitude 6.0 earthquake occurs west-southwest of Anna Maria, Florida
On September 10, 2006, a magnitude 6.0 earthquake occurred about 400 km (250 miles) west-southwest of Anna Maria, Florida, as reported by the U.S. Geological Survey National Earthquake Information Center. The quake was felt from Louisiana to Florida, with items knocked from shelves and seiches observed in swimming pools, though no damage or injuries were reported.
December 2007: Mexico submits information to the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS)
In December 2007, Mexico submitted information to the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf (CLCS) regarding the extension of Mexico's continental shelf beyond 200 nautical miles.
2007: Study finds disproportioned sex ratio of Atlantic croaker
A 2007 study of the Atlantic croaker found a disproportioned sex ratio of 61% males to 39% females in hypoxic sites. This was compared with a 52% to 48% male-female ratio found in reference sites, showing impaired reproductive output for fish populations inhabiting hypoxic coastal zones.
2007: Expedition launched to study the Mardi Gras shipwreck
In 2007, an expedition led by Texas A&M University and funded by OGGC was launched to study the Mardi Gras shipwreck site on the seafloor. Artifacts were recovered for public display in the Louisiana State Museum.
July 2008: Hypoxic dead zone doubles in size
In July 2008, researchers reported that between 1985 and 2008, the hypoxic dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico roughly doubled in size.
March 2009: CLCS accepts Mexico's arguments for extending its continental shelf
In March 2009, the CLCS accepted Mexico's arguments for extending its continental shelf up to 350 nautical miles (650 km; 400 mi) into the Western Polygon, requiring a bilateral agreement with the United States.
April 20, 2010: Deepwater Horizon oil platform explosion
On April 20, 2010, the Deepwater Horizon oil platform, operated by BP, suffered a catastrophic explosion and later sank, leading to a major oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. The spill threatened marine life, coastal wetlands, and Gulf Coast livelihoods.
2013: Volumetric flow rate through the Yucatan Channel
In 2013, the average volumetric flow rate through the Yucatan Channel varied between 15.8 and 28.1 Sverdrups (hectometers per second).
2014: Brine pool discovered on the sea floor
In 2014, a brine pool was discovered on the Gulf of Mexico sea floor at a depth of 3,300 feet (1,000 m). This pool, with a circumference of 100 feet (30 m) and a depth of 12 feet (4 m), is four to five times saltier than the surrounding water and has been named the "Jacuzzi of Despair" due to its warmer temperature of 18 °C (65 °F) compared to the surrounding water at 4 °C (39 °F).
2015: BP had spent $54 billion on cleanup, penalties, and to repair environmental and economic damage
As of 2015, BP had spent $54 billion on cleanup, penalties, and to repair environmental and economic damage.
May 12, 2016: Oil released from Shell's Brutus oil rig
On May 12, 2016, 2,100 barrels of oil were released from subsea infrastructure on Shell's Brutus oil rig. This leak created a 5 to 34 km (3.1 to 21.1 mi) oil slick in the sea about 156 km (97 miles) south of Port Fourchon, Louisiana.
2017: Largest hypoxic dead zone recorded
In 2017, the hypoxic dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico reached 22,730 km (8,780 square miles), the largest ever recorded.
2020: Surface temperatures warmed at about twice the rate observed for the global ocean surface
From 1970 to 2020, surface temperatures warmed at about twice the rate observed for the global ocean surface.
January 2025: Donald Trump directs federal agencies to adopt the name Gulf of America
In January 2025, United States president Donald Trump directed federal agencies to adopt the name Gulf of America for the waters bounded by the U.S. This decision led to controversy, including objections from Mexican president Claudia Sheinbaum, despite major online map platforms and several U.S.-based media outlets voluntarily adopting the change.
Mentioned in this timeline

Donald John Trump is an American politician media personality and...

A submarine is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater...

Claudia Sheinbaum Pardo is a Mexican politician scientist and academic...
An earthquake is a sudden shaking of the Earth's surface...
Florida a state in the Southeastern United States is largely...

New Orleans is the most populous city in Louisiana and...
Trending

27 minutes ago Peyton Stearns, Texas Longhorn, triumphs at ATX Open, securing second WTA title.

1 hour ago Tom Steyer's California plan faces criticism while he spends millions on governor's race.

1 hour ago Darius Garland Prepares for Clippers Debut Against Warriors After Trade

1 hour ago Mark Stoops Hired by Texas as Special Assistant to Steve Sarkisian

1 hour ago Tyus Jones Joins Denver Nuggets: Bolstering Depth Before Jazz Game.

3 days ago Katie Boulter faces Jasmine Paolini in WTA Merida Quarterfinals; Hon Prediction
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton is a prominent American politician lawyer...

Jim Carrey is a Canadian-American actor and comedian celebrated for...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Kashyap Pramod Patel is an American lawyer who became the...

Barack Obama the th U S President - was the...