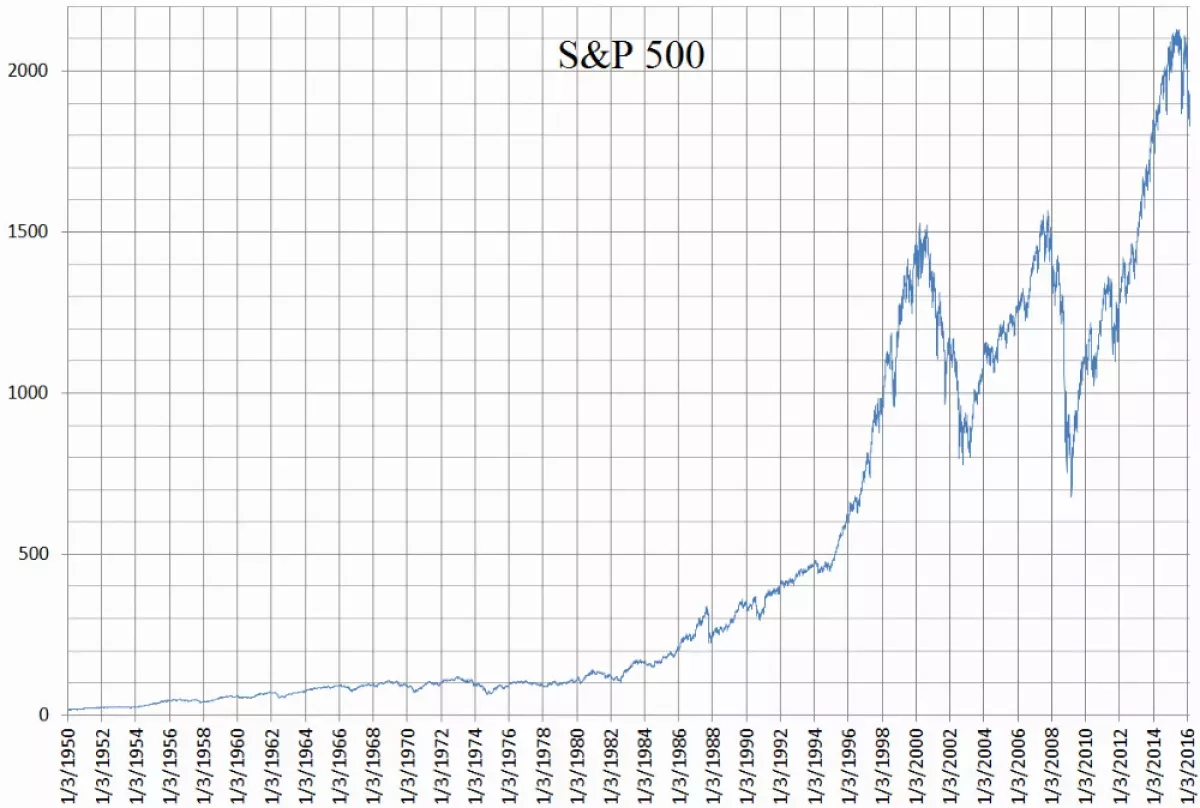
The S&P 500 is a stock market index that tracks the performance of 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States. Representing approximately 80% of the total U.S. market capitalization, it serves as a benchmark for the overall health and performance of the U.S. equity market. The S&P 500's aggregate market capitalization was over $57.401 trillion as of August 29, 2025, making it a widely followed indicator of the U.S. economy.
1860: Poor's Publishing Formed
In 1860, Henry Varnum Poor created Poor's Publishing, which was created to publish an investor's guide to the railroad industry.
1906: Standard Statistics Bureau Founded
In 1906, the Standard Statistics Bureau, which later became the Standard Statistics Company, was founded.
1923: Standard Statistics Company's First Stock Market Index
In 1923, the Standard Statistics Company started rating mortgage bonds and created its first stock market index, which consisted of stocks from 233 U.S. companies and was computed weekly.
1926: S&P 500 Inception
Since its inception in 1926, the S&P 500 index has demonstrated a compound annual growth rate of approximately 9.8% including dividends (6% after inflation).
1941: Formation of Standard & Poor's
In 1941, Poor's Publishing merged with Standard Statistics Company, leading to the establishment of Standard & Poor's.
March 4, 1957: S&P 500 Expansion
On March 4, 1957, the index expanded to 500 companies and was renamed the S&P 500 Stock Composite Index.
1962: Ultronic Systems Becomes Compiler
In 1962, Ultronic Systems became the compiler of the S&P indices, including the S&P 500 Stock Composite Index, the 425 Stock Industrial Index, the 50 Stock Utility Index, and the 25 Stock Rail Index.
August 31, 1976: First Mutual Fund Tracking the Index
On August 31, 1976, The Vanguard Group introduced the first mutual fund to retail investors that tracked the S&P 500 index.
April 21, 1982: Futures Trading on the Index
On April 21, 1982, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange started trading futures based on the S&P 500 index.
1982: Original SP big contract began trading
In 1982, original SP big contract began trading.
July 1, 1983: Options Trading on the Index
On July 1, 1983, the Chicago Board Options Exchange began trading options based on the S&P 500 index.
1986: Index Value Update Frequency Increase
Beginning in 1986, the S&P 500 index value was updated every 15 seconds, disseminated by Reuters, a significant increase from the previous update frequency of once per minute.
January 22, 1993: Standard & Poor's Depositary Receipts exchange-traded fund
On January 22, 1993, the Standard & Poor's Depositary Receipts exchange-traded fund issued by State Street Corporation began trading.
September 9, 1997: Introduction of S&P E-mini Futures Contract
On September 9, 1997, the CME Group introduced the S&P E-mini futures contract.
2005: Transition to Public Float-Adjusted Capitalization-Weighting
In 2005, the S&P 500 index transitioned to a public float-adjusted capitalization-weighting.
September 17, 2021: Final Trading Date for SP Big Contract
Friday, September 17, 2021, was the final trading date for the original SP big contract which began trading in 1982.
October 2021: Study on S&P Global Ratings Services
In October 2021, a study by the National Bureau of Economic Research suggested that companies purchasing ratings services from S&P Global may improve their chances of entering the S&P 500.
August 29, 2025: S&P 500 Market Cap
On August 29, 2025, the S&P 500 had an aggregate market capitalization of more than $57.401 trillion.
October 27, 2025: S&P 500 Record Closing High
On October 27, 2025, the S&P 500 set a record closing high of 6,875.16, following an intra-year correction to a low of 4,982.77 on April 8.
Mentioned in this timeline

Nvidia is a prominent American technology company specializing in the...

The stock market is where buyers and sellers trade stocks...

Microsoft an American multinational technology corporation headquartered in Redmond Washington...

An apple is a widely cultivated round edible fruit originating...

News encompasses information about current events disseminated through various media...

Chicago is the most populous city in Illinois and the...
Trending
14 minutes ago Rugby Property Assets acquires Cavendish Walk Shopping Centre in Merseyside for £1.5m.
1 hour ago Medvedev, Bublik, and Rublev advanced; Medvedev seeks rankings change in Dubai.

1 hour ago Lauren Chapin, 'Father Knows Best' Child Star, Passes Away at 80
2 hours ago Tim NeCastro Announces Retirement as Erie Insurance CEO After 10 Years

1 hour ago Scientists speculate on insights from government's UFO files release directed by Trump.

4 hours ago Apple MacBook Pro: Touchscreen, Dynamic Island, and New Interface Coming Soon.
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Susan Rice is an American diplomat and public official prominent...

Barack Obama the th U S President - was the...

Michael Joseph Jackson the King of Pop was a highly...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Bernie Sanders is a prominent American politician currently serving as...