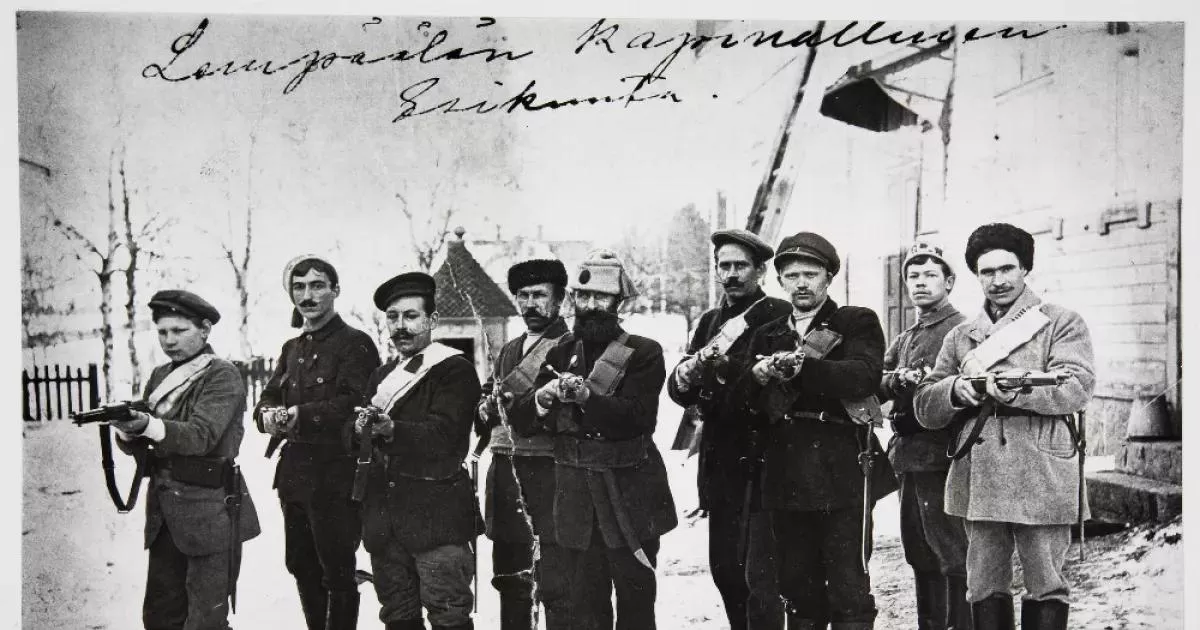
A civil war is an armed conflict between organized groups within the same country. The objectives of a side may include seizing control of the nation or a specific region, achieving regional independence, or altering government policies. The term originates from the Latin "bellum civile," referencing the Roman Republic's civil wars in the 1st century BC. The phrase "civil" denotes a conflict among citizens rather than against an external enemy.
1900: Civil War Duration Between 1900 and 1944
Between 1900 and 1944, civil wars lasted on average one and a half years, reflecting the trend of shorter conflicts compared to later periods.
1939: End of the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ended in 1939 after 3 years of fighting between the Republicans and Nationalists, with the Nationalists winning and establishing the Franco dictatorship.
1944: Civil War Duration Between 1900 and 1944
Between 1900 and 1944, civil wars lasted on average one and a half years, reflecting the trend of shorter conflicts compared to later periods.
1944: Civil War Statistics
From 1944 to 1997, there were 104 civil wars based on the 1,000-casualties-per-year criterion.
1945: Sovereignty Norms Post WWII
After World War II in 1945, international norms towards sovereignty changed, maintaining the existence of weak states by granting de jure sovereignty and offering development aid.
1945: Civil War Statistics Post 1945
Between 1945 and 2007, there were over 90 civil wars based on the 1,000 casualties total criterion.
1945: Post-WWII Decolonization
Following World War II in 1945, major European powers rapidly divested themselves of colonies, increasing ex-colonial states from approximately 30 to almost 120.
1945: Post WWII Rise in Ongoing Civil Wars
Following World War II in 1945, the number of ongoing civil wars rose drastically due to the tripling of their average duration, linked to increased states, fragility of post-1945 states, decline in interstate war, and the Cold War rivalry.
1945: International intervention in civil wars after World War II
Since 1945, there has been a significant increase in international intervention in civil wars, with some arguing that it prolonged conflicts. According to Patrick M. Regan, about two-thirds of intrastate conflicts between the end of World War II and 2000 experienced international intervention.
1946: Start of the Greek Civil War
In 1946, the Greek Civil War erupted shortly after World War II, pitting the communist-dominated Democratic Army of Greece, backed by Yugoslavia and the Soviet Union, against the Kingdom of Greece, supported by the United Kingdom and the United States under the Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan.
1947: Start of the Cold War
In 1947, the Cold War began, establishing a global support network that often perpetuated civil wars, primarily in weaker, post-colonial states rather than stronger states aligned with the Warsaw Pact and NATO.
1960: Belgium Grants Independence to its Colonies
In 1960, Belgium granted independence to its colonies without prior preparation for self-government.
1960: World Bank Civil War Study Begins
In 1960, The World Bank started a study of civil war, called the Collier–Hoeffler Model, which examined 78 five-year increments from 1960 to 1999 and 1,167 five-year increments of "no civil war".
1960: Start of the Guatemalan Civil War
In 1960, the Guatemalan Civil War began, a lengthy conflict associated with the Cold War.
1970: Start of the Nicaraguan Civil War
In 1970, the Nicaraguan Civil War began. This was another lengthy conflict.
1979: Start of the El Salvador Civil War
In 1979, the El Salvador Civil War began, another conflict related to the Cold War.
1989: Fall of the Berlin Wall and its Impact on Civil Wars
In 1989, the fall of the Berlin Wall marked the end of the Cold War, leading to a 92% reduction in the duration of Cold War civil wars, signifying a roughly ten-fold increase in their rate of resolution.
1990: Iraq's Invasion of Kuwait
In 1990, Iraq's invasion of Kuwait prompted international military intervention to reverse the territorial aggression, showcasing the international community's response to territorial annexation.
1990: End of the Nicaraguan Civil War
In 1990, the Nicaraguan Civil War ended. The civil war had been ongoing since 1970.
1991: End of the Cold War
In 1991, the Cold War ended, concluding a period where civil wars were often fueled by ideological and material support from global powers.
1991: End of the El Salvador Civil War
In 1991, the El Salvador Civil War ended. It had been ongoing since 1979.
1996: End of the Guatemalan Civil War
In 1996, the Guatemalan Civil War ended. It had been ongoing since 1960.
1997: Civil War Statistics
From 1816 to 1997, there were 213 civil wars based on the 1,000-casualties-per-year criterion, 104 of which occurred from 1944 to 1997.
1997: Civil War declaration Post 1945
From 1945 to 1997 major international anti-secessionist declarations increased the number of ongoing civil wars by +114%.
1999: World Bank Civil War Study Data Collection Ends
In 1999, the World Bank's civil war study concluded its data collection, having examined 78 five-year increments when civil war occurred from 1960 to 1999, and 1,167 five-year increments of "no civil war" for comparison.
2000: Civil Wars and Foreign Powers Publication
In 2000, Patrick M. Regan published "Civil Wars and Foreign Powers", noting that approximately two-thirds of intrastate conflicts post-World War II involved international intervention.

2000: Publication of Civil Wars and Foreign Powers
In 2000, Patrick M. Regan published "Civil Wars and Foreign Powers", noting that approximately two-thirds of the 138 intrastate conflicts between the end of World War II and 2000 involved international intervention, with the United States intervening in 35 of these conflicts.

2003: Changes in post-2003 Civil Wars
According to Barbara F. Walter, civil wars after 2003 differ from previous ones, with most occurring in Muslim-majority countries, involving rebel groups espousing radical Islamist ideas with transnational goals, a shift attributed to changes in information technology, notably Web 2.0 in the early 2000s.
2003: Fearon and Laitin's Opportunity-Based Explanation
In 2003, James Fearon and David Laitin published an article in the American Political Science Review presenting an opportunity-based explanation for civil war onset, which became the most influential explanation according to a 2017 review.
2006: Systematic Review Highlights Rough Terrain
In 2006, a systematic review highlighted rough terrain as one of the more important factors in civil wars.
2007: Ongoing Civil Wars in 2007
As of 2007, there were 20 ongoing civil wars, using the less-stringent 1,000 casualties total criterion since 1945.
2007: Cederman's Criticism of ELF
In 2007, Lars-Erik Cederman criticized the ethno-linguistic fractionalization index (ELF) used by Fearon, Laitin, and other political scientists, arguing that it does not adequately measure ethnic groups' power within a state.
2009: Bleaney's Review of Civil War Evidence
In 2009, Michael Bleaney published a paper titled "Incidence, Onset and Duration of Civil Wars: A Review of the Evidence", concluding that neither ethnoreligious diversity nor ethnic polarization were sufficient measures of diversity as it affects the probability of conflict.
2011: Cederman's Research on Inequality and Conflict
In 2011, Cederman and fellow researchers found that in highly unequal societies, both rich and poor groups fight more often than those groups whose wealth lies closer to the country average, challenging the opportunity-based explanation for civil war outbreak.
2017: Review Study of Civil War Research
A 2017 review study identified three prominent explanations for civil war: greed-based, grievance-based, and opportunity-based, citing Fearon and Laitin's 2003 article as the most influential.
Mentioned in this timeline
The United States of America is a federal republic located...
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics USSR existed from to...
Myanmar also known as Burma is a Southeast Asian country...
Germany officially the Federal Republic of Germany is a nation...
World War II - was a global conflict between the...
Iraq officially the Republic of Iraq is a West Asian...
Trending
30 minutes ago Gregory Bovino Faces DHS Investigation Over Remarks and Operation Metro Surge Actions.
30 minutes ago Scottie Scheffler Favored at 2026 Arnold Palmer Invitational: Expert Predictions and Purse Details

30 minutes ago Seth MacFarlane reveals 'The Orville' Season 4 scripts are complete, teasing a new life.
30 minutes ago Apple's MacBook prices rise with M5 chips, new displays, and AI focus.

31 minutes ago Hegseth and Caine Briefed on Iran War Operations; Pentagon Discussed Iran Conflict.

1 hour ago Tennis star Aryna Sabalenka announces engagement to Georgios Frangulis before Indian Wells tournament.
Popular

Ken Paxton is an American politician and lawyer serving as...

Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton is a prominent American politician lawyer...

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Jim Carrey is a Canadian-American actor and comedian celebrated for...

Bill Clinton served as the nd U S President from...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...
