El Salvador, officially the Republic of El Salvador, is a Central American country bordered by Honduras, Guatemala, and the Pacific Ocean. Its capital and largest city is San Salvador. In 2024, the estimated population of El Salvador is 6 million.
1903: End of General Tomás Regalado's Presidency
In 1903, General Tomás Regalado's term as president ended, after gaining power by force in 1898.
July 1906: Death of General Tomás Regalado
On July 11, 1906, General Tomás Regalado was killed at El Jicaro during a war against Guatemala.
1912: Creation of the National Guard
In 1912, the national guard was created as a rural police force.
1913: Assassination of President Manuel Enrique Araujo
In 1913, President Manuel Enrique Araujo was killed, leading to many hypotheses regarding the political motive of his murder.
1913: Start of the Meléndez–Quiñónez Dynasty
In 1913, the Meléndez–Quiñónez dynasty began, following the administration of Manuel Enrique Araujo.
1915: Official Name Change to El Salvador
In 1915, the Legislative Assembly passed a law that the country's name should be rendered as the definite form El Salvador.
1919: Earthquake in San Salvador
The capital, San Salvador, suffered heavy damage in the 1919 earthquake.
1927: End of the Meléndez–Quiñónez Dynasty
In 1927, the Meléndez–Quiñónez dynasty ended.
December 1930: Martí's Exile
In December 1930, Martí was once again exiled because of his popularity.
1930: Announcement of Free Elections
In 1930, Pío Romero Bosque announced free elections.
March 1931: Arturo Araujo Comes to Power
On March 1, 1931, Arturo Araujo came to power after winning what was considered the country's first freely contested election.
December 1931: Coup d'état led by Martínez
In December 1931, a coup d'état was organized by junior officers and led by Martínez, overthrowing President Araujo.
1931: Carlos Humberto Romero Becomes President
In 1931, Carlos Humberto Romero was the final president of the country's military dictatorship.
1931: Martí's Return
Once Araujo was elected president in 1931, Martí returned to El Salvador.
January 1932: Brutal Suppression of La Matanza
Beginning in January 1932, there was brutal suppression of a rural revolt known as La Matanza. Farabundo Martí helped found the Communist Party of Central America and led "International Red Aid."
January 1932: Peasant Revolt against the Government
On January 22, 1932, thousands of poorly armed peasants in the western part of El Salvador revolted against the government and Martínez.
1935: Martínez's Rule
In 1935, Martínez ruled as president of El Salvador.
1939: Martínez's Rule
In 1939, Martínez ruled as president of El Salvador.
1943: Martínez's Rule
In 1943, Martínez ruled as president of El Salvador.
1944: Martínez Resigned After A General Strike
In 1944, Martínez began a fourth term but resigned in May after a general strike.
November 1950: El Salvador Supports Tibetan Appeal
In November 1950, El Salvador was the only country to support the 14th Dalai Lama by backing his Tibetan Government's appeal to the United Nations to stop China's annexation of Tibet. However, the UN dropped the plea due to lack of support from other nations.
1950: El Salvador's Population in 1950
In 1950, El Salvador's population was 2,200,000.
1958: Reaffirmation of the Name El Salvador
In 1958, the legislature reaffirmed the country's name as El Salvador.
1960: Activity of PDC and PCN
From 1960, the Christian Democratic Party (PDC) and the National Conciliation Party (PCN) were active in Salvadoran politics.
1964: José Napoleón Duarte Becomes Mayor of San Salvador
From 1964, José Napoleón Duarte was the mayor of San Salvador.
1970: José Napoleón Duarte Ends Term as Mayor of San Salvador
Until 1970, José Napoleón Duarte was the mayor of San Salvador.
1972: Defeat of José Napoleón Duarte
In 1972, José Napoleón Duarte ran for president with UNO but was defeated in an election widely viewed as fraudulent.
1973: Hurricane Emily
In 1973, Hurricane Emily affected El Salvador. Hurricanes seldom affect El Salvador.
1976: Opening of Estadio Cuscatlán
The Estadio Cuscatlán in San Salvador opened in 1976, seating 53,400, making it the largest stadium in Central America and the Caribbean.
October 1979: US Calls For Regime Change
By October 1979, the Carter administration decided that El Salvador needed regime change.
October 1979: Coup d'état Brings Revolutionary Government Junta to Power
On October 15, 1979, a coup d'état brought the Revolutionary Government Junta (JRG) to power.
1979: Duarte Returns to Politics
In 1979, Duarte returned to the country to enter politics after working on projects in Venezuela.
1979: Start of the Salvadoran Civil War
In 1979, the Salvadoran Civil War began, fought between the military-led government and left-wing guerrilla groups, stemming from socioeconomic inequality and civil unrest.
March 1980: Assassination of Óscar Romero
On March 24, 1980, Óscar Romero was assassinated while saying Mass.
October 1980: Formation of the FMLN
In October 1980, several major guerrilla groups of the Salvadoran left had formed the Farabundo Martí National Liberation Front, or FMLN.
1980: Salvadoran Emigration to the United States
From 1980, a large number of Salvadorans began emigrating to the United States.
1980: Investigation of Violence
In 1980, the Chapultepec Peace Accords established a Commission on the Truth for El Salvador to investigate serious acts of violence occurring since 1980, including the nature and effects of the violence, and to recommend methods for promoting national reconciliation.
1982: El Salvador National Football Team Qualified for FIFA World Cup
The El Salvador national football team qualified for the FIFA World Cup in 1982.
1982: Earthquake in San Salvador
The capital, San Salvador, suffered heavy damage in the 1982 earthquake.
1983: Constitution
The 1983 constitution has the highest legal authority in El Salvador.
1986: Earthquake in San Salvador
In 1986, a 5.7 Mw earthquake resulted in 1,500 deaths, 10,000 injuries, and 100,000 people left homeless.
1989: ARENA Dominance Begins
From 1989, the Nationalist Republican Alliance (ARENA) began a period of dominance in El Salvador, winning every presidential election until 2009.
1989: Murder of Jesuit Priests
In 1989, during the height of the civil war, Jesuit priests and professors Ignacio Ellacuría, Ignacio Martín-Baró, and Segundo Montes were murdered by the Salvadoran Army.
January 1992: Signing of Peace Agreements
On January 16, 1992, the government of El Salvador and the FMLN signed peace agreements brokered by the United Nations, ending the 12-year civil war.
September 1992: Implementation of Value-Added Tax (IVA)
In September 1992, El Salvador implemented a 10% value-added tax (IVA).
1992: End of the Salvadoran Civil War
In 1992, the Salvadoran Civil War concluded with the Chapultepec Peace Accords, establishing a multiparty constitutional republic.
1993: Commission on Truth Findings and Amnesty Law
In 1993, the Commission on the Truth delivered its findings, reporting human rights violations by both sides during the conflict. Five days later, in 1993, the Salvadoran legislature passed an amnesty law for all acts of violence that occurred during the conflict period.
July 1995: Increase in Value-Added Tax (IVA)
In July 1995, El Salvador raised the value-added tax (IVA) from 10% to 13%.
1996: GDP Growth Rate
After 1996, El Salvador's GDP grew at an average annual rate of 3.2%.
1997: Establishment of the Ministry of Environment
In 1997, the government established the Ministry of the Environment and Natural Resources.
1998: Hurricane Mitch
In 1998, Hurricane Mitch affected El Salvador, although hurricanes seldom do so. Mitch formed over the Atlantic Basin.
1999: Approval of Environmental Framework Law
In 1999, a general environmental framework law was approved by the National Assembly.
2000: Total Exports and Imports
From 2000 to 2006, total exports from El Salvador grew 19% from $2.94 billion to $3.51 billion, and total imports rose 54% from $4.95 billion to $7.63 billion.
January 2001: Earthquake and Landslide
On 13 January 2001, a magnitude 7.7 earthquake caused a landslide that killed more than 800 people.
January 2001: Adoption of the US Dollar
On January 1, 2001, El Salvador adopted the United States dollar as its currency.
February 2001: Another Earthquake
On 13 February 2001, another earthquake killed 255 people and damaged about 20% of the country's housing.
2001: Adoption of the United States dollar
In 2001, El Salvador replaced the colón with the United States dollar as its currency.
2001: Severe Drought
In the summer of 2001, a severe drought destroyed 80% of El Salvador's crops, causing famine in the countryside.
2004: Salvadorans Living Outside El Salvador in 2004
As of 2004, approximately 3.2 million Salvadorans were living outside El Salvador, with the United States being the primary destination for economic migrants.
2004: Temporary success of "Super Mano Dura" gang reform
In 2004, the government's gang reform called "Super Mano Dura" experienced temporary success.
2004: Intentional Homicides in 2004
In 2004, there were 41 intentional homicides per 100,000 citizens in El Salvador, with 60% being gang-related.
2004: 2004 Election in El Salvador
In the 2004 election, Antonio Saca, of Palestinian descent, was elected President of El Salvador. His opponent, Schafik Handal, was also of Palestinian descent.
2004: Failure to Win Enough Votes
The PDC and PCN failed to win enough votes in the 2004 presidential election.
2004: ARENA Presidential Election Wins
Until 2004, El Salvadorans favored the Nationalist Republican Alliance (ARENA), voting in ARENA presidents in every election.
October 2005: Santa Ana Volcano Eruption
On 1 October 2005, the Santa Ana Volcano spewed a cloud of ash, hot mud and rocks that fell on nearby villages and caused two deaths.
October 2005: Severe Rains and Flooding
On 4 October 2005, severe rains resulted in dangerous flooding and landslides, which caused at least 50 deaths.
2005: Rise in crime after 2005
After 2005, there was a rise in crime after the temporary success of "Super Mano Dura" gang reform.
2005: Epicenter of a Gang Crisis in 2005
In 2005, El Salvador was considered an epicenter of a gang crisis, along with Guatemala and Honduras.
2005: Expiration of Multi Fibre Arrangement
In 2005, the Multi Fibre Arrangement expired, leading El Salvador to anticipate declines in the apparel sector's competitiveness and to seek diversification of the economy.
2006: Total Exports and Imports
From 2000 to 2006, total exports from El Salvador grew 19% from $2.94 billion to $3.51 billion, and total imports rose 54% from $4.95 billion to $7.63 billion.
2006: El Salvador Ratifies CAFTA
In 2006, El Salvador was the first country to ratify the Central America-Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA) with the United States.
2006: Gay Marriage Proposal Rejected
In 2006, a proposal to legally recognize gay marriage was rejected in El Salvador.
2006: Remittances as Percentage of GDP
In 2006, remittances to El Salvador from Salvadorans living in the United States were approximately $3.32 billion, or approximately 16.2% of GDP.
2007: GDP Real Growth Rate
In 2007, El Salvador's GDP real growth rate hit 4.7%.
2008: Salvadorans in the United States
By 2008, nearly one million Salvadorans had emigrated to the United States, becoming the sixth largest immigrant group in the US.
2008: Service Sector Component of GDP
In 2008 (est.), the service sector was the largest component of El Salvador's GDP at 64.1%.
2008: International Arbitration Against Enel Green Power
In 2008, El Salvador sought international arbitration against Italy's Enel Green Power, on behalf of Salvadoran state-owned electric companies, regarding a geothermal project.
March 2009: Funes of the FMLN Won Election
ARENA candidates won four consecutive presidential elections until the election of Mauricio Funes of the FMLN in March 2009.
March 2009: Mauricio Funes Elected President
On March 15, 2009, Mauricio Funes, a television figure, was elected as the first president from the FMLN.
June 2009: Funes Inauguration and Corruption Focus
On June 1, 2009, Mauricio Funes was inaugurated as president. One focus of the Funes government was revealing alleged corruption from past governments.
December 2009: Saca Expelled and Forms GANA
In December 2009, ARENA formally expelled Saca from the party. With 12 loyalists in the National Assembly, Saca established his own party, the Grand Alliance for National Unity (GANA), and entered into a tactical legislative alliance with the FMLN.
2009: Gay Marriage Proposal Rejected Again
In 2009, a proposal to legally recognize gay marriage was once again rejected in El Salvador.
2009: Analysis of ARENA's Electoral Defeat
In 2009, the U.S. Embassy in San Salvador pointed to official corruption under the Saca administration as a significant reason for public rejection of continued ARENA government.
2009: U.S. Embassy Warns of Populist Policies
In 2009, the U.S. Embassy warned that the Salvadoran government's populist policies of mandating artificially low electricity prices were damaging private sector profitability, including the interests of American investors in the energy sector.
2010: Metallic Mining Contribution to GDP
Between 2010 and 2015, the contribution of metallic mining was a minuscule 0.3% of El Salvador's GDP.
2010: Agriculture Component of GDP
In 2010 (est.), agriculture represented 11.2% of El Salvador's GDP.
2010: El Salvador's Population Demographics in 2010
In 2010, 32.1% of El Salvador's population was below 15 years of age, 61% were between 15 and 65 years of age, and 6.9% were 65 years or older.
2011: Disbanding of PDC and PCN
In 2011, the PDC and PCN were disbanded by the Supreme Court.
2011: Gang Members in 2011
In 2011, there were an estimated 25,000 gang members at large in El Salvador, with another 9,000 in prison.
April 2012: IMF Suspends Loan to El Salvador
In April 2012, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) suspended a $750 million loan to the central government of El Salvador due to problems with economic subsidies.
2012: Salvadoran Immigrants in the U.S. in 2012
By 2012, there were about 2.0 million Salvadoran immigrants and Americans of Salvadoran descent in the U.S., making them the sixth largest immigrant group in the country.
2012: Highest Murder Rate in the World in 2012
In 2012, El Salvador had the highest murder rate in the world.
2012: Homicide Rate in 2012
In 2012, the homicide rate in El Salvador had increased to 66 per 100,000 inhabitants.
2013: Increased Foreign Direct Investment
According to Santander Trade, in 2013, the influx of Foreign Direct Investment into El Salvador increased.
2013: Survey on Homosexuality Acceptance
In 2013, a survey by Pew Research indicated that 53% of Salvadorans believed that homosexuality should not be accepted by society.
2013: Tourism Directly Supported Jobs
In 2013, tourism directly supported 80,500 jobs in El Salvador. This represented 3.1% of total employment in El Salvador.
March 2014: Cerén Wins Election
In March 2014, former FMLN guerrilla leader Cerén narrowly won the election.
May 2014: Cerén Sworn in as President
On May 31, 2014, Cerén was sworn in as president, becoming the first former guerrilla to hold the office in El Salvador.
December 2014: Settlement of Dispute with Enel
In December 2014, El Salvador and Enel reached a settlement regarding the geothermal project dispute, the details of which were not released.
2014: Corruption Perceptions Index Ranking
In 2014, El Salvador ranked 80 out of 175 countries in terms of perceived levels of public corruption, as per the Corruption Perceptions Index.
2014: International Tourist Visits
In 2014, it was estimated that 1,394,000 international tourists visited El Salvador.
2014: World Bank's Ease of Doing Business Index
In 2014, the World Bank rated El Salvador 109 in the World Bank's annual "Ease of doing business" index.
2014: Political Ideology
The FMLN Party is leftist in ideology, and is split between the dominant Marxist-Leninist faction in the legislature, and the social liberal wing led by Mauricio Funes until 2014.
2015: Progress in Water Supply and Sanitation
A 2015 study by the University of North Carolina recognized El Salvador for achieving the greatest progress worldwide in increasing access to water supply and sanitation, and reducing inequity in access between urban and rural areas.
2015: Metallic Mining Contribution to GDP
Between 2010 and 2015, the contribution of metallic mining was a minuscule 0.3% of El Salvador's GDP.
2015: Homicides Recorded in 2015
In 2015, 6,650 homicides were recorded in El Salvador.
2016: Murders Recorded in 2016
In 2016, at least 5,728 people were murdered in El Salvador.
2016: Funes Seeks Asylum
In 2016, former president Funes sought asylum in Nicaragua.
October 2017: Court Ruling Against Funes
In October 2017, an El Salvador court ruled that former president Funes and one of his sons had illegally enriched themselves.
December 2017: Net International Reserves
As of December 2017, El Salvador's net international reserves stood at $3.57 billion.
2017: Homicides Recorded in 2017
In 2017, there were 3,962 recorded homicides in El Salvador.
September 2018: Saca Sentenced to Prison
In September 2018, former president Saca was sentenced to 10 years in prison after pleading guilty to diverting more than US$300 million in state funds.
October 2018: Canonization of Óscar Romero
On 14 October 2018, Óscar Romero, the first Salvadoran saint, was canonized by Pope Francis.
2018: Forest Landscape Integrity Index Score
In 2018, El Salvador had a Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 4.06/10, ranking it 136th globally out of 172 countries.
2018: Transition to Digital TV/Radio
In 2018, El Salvador transitioned to digital transmission of TV/radio networks, adopting the ISDB-T standard.
2018: Deaths Recorded in 2018
In 2018, there were 3,348 recorded deaths in El Salvador.
February 2019: Bukele Wins Presidential Election
In February 2019, Nayib Bukele won the presidential election representing GANA after being denied participation with the Nuevas Ideas party.
June 2019: Homicide Rate Drops
According to a report by the International Crisis Group (ICG), the homicide rate in El Salvador had dropped by as much as 60% since Bukele became president in June 2019.
June 2019: Bukele Becomes President
On June 1, 2019, Nayib Bukele became the new president of El Salvador.
2019: Lowest Income Inequality
As of 2019, economic improvements in El Salvador led to the lowest level of income inequality among nearby countries.
2019: Decline in Murder Rate in 2019
In 2019, El Salvador experienced a sharp decline in the murder rate with a new conservative government in power.
2019: Remittances from Salvadorans in the U.S.
In 2019, El Salvador led the region in remittances per capita, equivalent to nearly all export income. 2.35 million Salvadorans lived in the U.S., and about a third of all households received remittances.
2019: Global Innovation Index Ranking
In 2019, El Salvador was ranked 108th in the Global Innovation Index.
2019: Nayib Bukele Wins Presidential Election
In 2019, Nayib Bukele, a candidate from GANA, won the Salvadoran presidential election, breaking the two-party dominance.
2019: Tourism Contribution to GDP
In 2019, Tourism contributed US$2970.1 million to El Salvador's GDP, representing 11% of the total GDP.
2019: Homicides Recorded in 2019
In 2019, authorities reported a total of 2,365 homicides in El Salvador.
2019: Reference Point for Homicide-Free Year
President Bukele stated on Twitter that El Salvador had completed one full year or 365 days since 2019 without a single homicide occurring.
June 2020: Inauguration of Hospital El Salvador
In June 2020, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the main convention center in El Salvador was converted into Hospital El Salvador, the largest hospital in Latin America. The president inaugurated the facility in June 2020 and announced that the hospital conversion would be permanent, costing $75 million with a capacity of 1,083 ICU beds and 2,000 beds total.
2020: Report on Homicide Rate Drop
In 2020, a report by the International Crisis Group (ICG) noted a significant drop in El Salvador's homicide rate following Bukele's presidency, while press reports suggested a "non-aggression deal" between the government and gangs, which was officially denied.
2020: 5G Testing
In 2020, testing of 5G coverage began in El Salvador.
2020: Homicides Recorded in 2020
In 2020, there were only 1,322 reported homicides in El Salvador.
January 2021: Energy Injections from Renewable Sources
During January 2021, 94.4% of total energy injections in El Salvador came from hydroelectric plants (28.5%), geothermal (27.3%), biomass (24.4%), photovoltaic solar (10.6%), and wind (3.6%).
February 2021: Nuevas Ideas Wins Congressional Majority
In February 2021, legislative election results led to a major shift in El Salvador's politics, with Nuevas Ideas (New Ideas), the allied party of President Nayib Bukele, securing the largest congressional majority in the country's history.
February 2021: Nuevas Ideas Wins Legislative Elections
In the February 2021 legislative elections, the Nuevas Ideas party, founded by Bukele, and its ally GANA won around 63% of the vote, securing a supermajority in the parliament.
February 2021: Certification for Elimination of Malaria
On 25 February 2021, El Salvador became the first Central American country to be awarded certification for the elimination of malaria by the WHO.
June 2021: President Bukele Announces Bitcoin Legislation
In June 2021, President Nayib Bukele announced plans to introduce legislation to make Bitcoin legal tender in El Salvador.
June 2021: Bitcoin Legal Tender Legislation
On 8 June 2021, at the initiative of President Bukele, pro-government deputies in the Legislative Assembly voted legislation to make bitcoin legal tender in El Salvador.
September 2021: Supreme Court Allows Bukele to Run Again
In September 2021, El Salvador's Supreme Court ruled to allow Bukele to run for a second term in 2024, despite constitutional prohibitions.
September 2021: Bitcoin Becomes Legal Tender
On September 7, 2021, Bitcoin officially became a legal tender in El Salvador. The law also allowed foreigners to gain permanent residence by investing 3 Bitcoin into the country.
September 2021: Bitcoin Mining Using Geothermal Energy
Since September 2021, nearly 474 bitcoin (approx $29 million circa May 2024) mined using geothermal energy from the Tecapa volcano.
2021: GDP Estimate for 2021
In 2021, El Salvador's gross domestic product (GDP) in purchasing power parity was estimated at US$57.95 billion, with a real GDP growth of 4.2%.
2021: El Salvador's Population in 2021
In 2021, El Salvador's population was recorded at 6,314,167.
2021: Homicides Recorded in 2021
In 2021, the country recorded 1,140 homicides, marking the lowest number of recorded murders since the end of the civil war.
2021: Least Complex Economies
In a 2021 study, El Salvador had one of the least complex economies for doing business among 77 countries.
January 2022: IMF Urges Reversal of Bitcoin Decision
In January 2022, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) urged El Salvador to reverse its decision to make cryptocurrency legal tender. Bukele announced plans to build Bitcoin City.
March 2022: Bitcoin Transaction Usage Among Merchants
According to a survey conducted by the Salvadoran Chamber of Commerce, as of March 2022 only 14% of merchants in the country processed at least one Bitcoin transaction.
March 2022: Gang-Related Violence and State of Emergency
Beginning on 25 March 2022, three days of gang-related violence occurred that left 87 people dead. In response, President Bukele asked the Salvadoran parliament to ratify a state of emergency. On 26 March, Bukele also ordered mass arrests.
May 2022: Sovereign Default Prospect
As of May 2022, El Salvador government bonds trading at 40% of their original value, indicating the prospect of a looming sovereign default.
2022: Homicide Rate in 2022
In 2022, El Salvador had a homicide rate of 7.8 per 100,000 individuals.
2022: Gang Membership Estimate in 2022
In 2022, it was estimated that the Mara Salvatrucha (MS-13) and Barrio 18 gangs, among others, had around some 70,000 members.
2022: Crackdown on Criminal Gangs
In 2022, the Salvadoran government initiated a massive fight against criminal gangs, leading to the arrest of over 53,000 suspected gang members and precipitating the highest reported incarceration rate in the world.
May 2023: One Year Without Homicides
On 10 May 2023, President Bukele stated on Twitter that El Salvador had completed one full year or 365 days since 2019 without a single homicide occurring.
August 2023: Government Crackdown on Gangs
As of August 2023, around 72,000 suspected gang members have been sent to prison as a part of the government crackdown on the gangs.
November 2023: Bukele Takes Leave for Re-Election Campaign
On 30 November 2023, the Legislative Assembly granted Bukele and Vice President Felix Ulloa a leave of absence for their 2024 re-election campaign. Claudia Rodríguez de Guevara became acting president.
2023: Democracy Ranking
El Salvador was ranked the 5th least electoral democratic country in Latin America and the Caribbean in 2023 by V-Dem Democracy Report.
January 2024: Homicide rate decrease announcement
In January 2024, it was announced that the homicide rate dropped nearly 70% year over year, with 154 in 2023 compared to 495 homicides in 2022.
February 2024: Bukele Wins Re-Election
On 4 February 2024, Bukele won re-election with 84% of the vote in the presidential election. His party Nuevas Ideas won 58 of the parliament's 60 seats.
May 2024: Government Bitcoin Holdings
Since May 2024, the Bitcoin Office of El Salvador reports that the government holds 5,750 bitcoin (approximately $354 million circa May 2024) -- with nearly 474 bitcoin (approx $29 million circa May 2024) mined since September 2021 using geothermal energy from the Tecapa volcano.
June 2024: Bukele Sworn In For Second Term
On 1 June 2024, Bukele was sworn in for his second five-year term.
December 2024: Government Purchase of Bitcoin
In December 2024, Nayib Bukele's government purchased 11 new BTC for over a million dollars, thus strengthening its strategic reserves.
2024: Homicide Rate in 2024
In 2024, El Salvador reported a homicide rate of 1.9 per 100,000 people, a figure lower than any other Latin American country. This rate represents a 98% decrease in nine years.
2024: El Salvador Population Estimate
In 2024, El Salvador's population was estimated to be 6 million.
2024: Bukele Takes Leave for Re-Election Campaign
In November 2023, the Legislative Assembly granted Bukele and Vice President Felix Ulloa a leave of absence for their 2024 re-election campaign.
2024: Bukele Allowed to Run Again
In September 2021, El Salvador's Supreme Court ruled to allow Bukele to run for a second term in 2024, despite constitutional prohibitions.
2024: Global Hunger Index Ranking
In the 2024 Global Hunger Index, El Salvador ranked 43rd out of 127 countries, with a low level of hunger and a score of 8.0.
February 2025: Highest Prisoner Rate Worldwide
As of February 2025, El Salvador had the highest prisoner rate worldwide, with over 1,600 prisoners per 100,000 of the national population.
February 2025: Congress Agrees to Remove Bitcoin's Legal Tender Status
In February 2025, El Salvador’s Congress agreed to remove Bitcoin's legal tender status, following pressure from the International Monetary Fund.
March 2025: US Transfers Immigrants to El Salvador Prison
In March 2025, the United States transferred more than 200 immigrants, alleged to be members of a Venezuelan gang, to be imprisoned in El Salvador, violating court orders. These incarcerations were part of President Bukele’s efforts to reduce high crime rates and gang violence.
April 2025: Bitcoin value increases
As of April 2025, the value of Bitcoin in El Salvador is trading twice the price that it was when El Salvador made it legal tender.
July 2025: Legislative Assembly Approves Constitutional Changes
In late-July 2025, the Legislative Assembly approved of changes to the Constitution of El Salvador, which would remove presidential term-limits, and extend individual terms from 5 years to 6.
2025: Global Innovation Index Ranking
In 2025, El Salvador was ranked 98th in the Global Innovation Index.
2027: Legislative Assembly Moves Presidential Election
In late-July 2025, the Legislative Assembly approved of changes to the Constitution of El Salvador, which would remove presidential term-limits, and extend individual terms from 5 years to 6. The Legislative Assembly also moved the next presidential election from 2029 to 2027 (making it coterminous with the legislative elections that year), after which the constitutional changes would take effect.
2029: Legislative Assembly Moves Presidential Election
In late-July 2025, the Legislative Assembly approved of changes to the Constitution of El Salvador, which would remove presidential term-limits, and extend individual terms from 5 years to 6. The Legislative Assembly also moved the next presidential election from 2029 to 2027 (making it coterminous with the legislative elections that year), after which the constitutional changes would take effect.
Mentioned in this timeline

Pope Francis served as the head of the Catholic Church...
Cryptocurrency is a digital currency operating on a decentralized network...
China officially the People's Republic of China is an East...
The Dominican Republic is a Caribbean nation sharing the island...

The World Bank is an international financial institution offering loans...
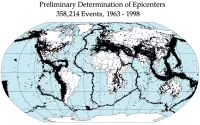
An earthquake is a sudden shaking of the Earth's surface...
Trending
23 minutes ago Jaelan Phillips and Eagles growing optimism for deal during free agency.
23 minutes ago Panthers' Free Agency: Tracking Signings, Extensions, and Roster Moves for 2026

24 minutes ago Tommy DeCarlo, Boston's Lead Singer, Dies at 60; Remembered on Brad Delp Anniversary
25 minutes ago Colts Pursued Daniel Jones, Tracker Reveals Pittman's Contract, Transition Tag Used

25 minutes ago NFL Offseason: McDuffie's Extension, Trade Grades & League Deals Analyzed.

25 minutes ago Travis Etienne free agency rumors: Broncos, Chiefs, and Seahawks may battle
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Ken Paxton is an American politician and lawyer serving as...

Markwayne Mullin is an American politician and businessman serving as...

Corey Lewandowski is an American political operative lobbyist commentator and...

Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton is a prominent American politician lawyer...

Kristi Lynn Arnold Noem is an American politician She was...