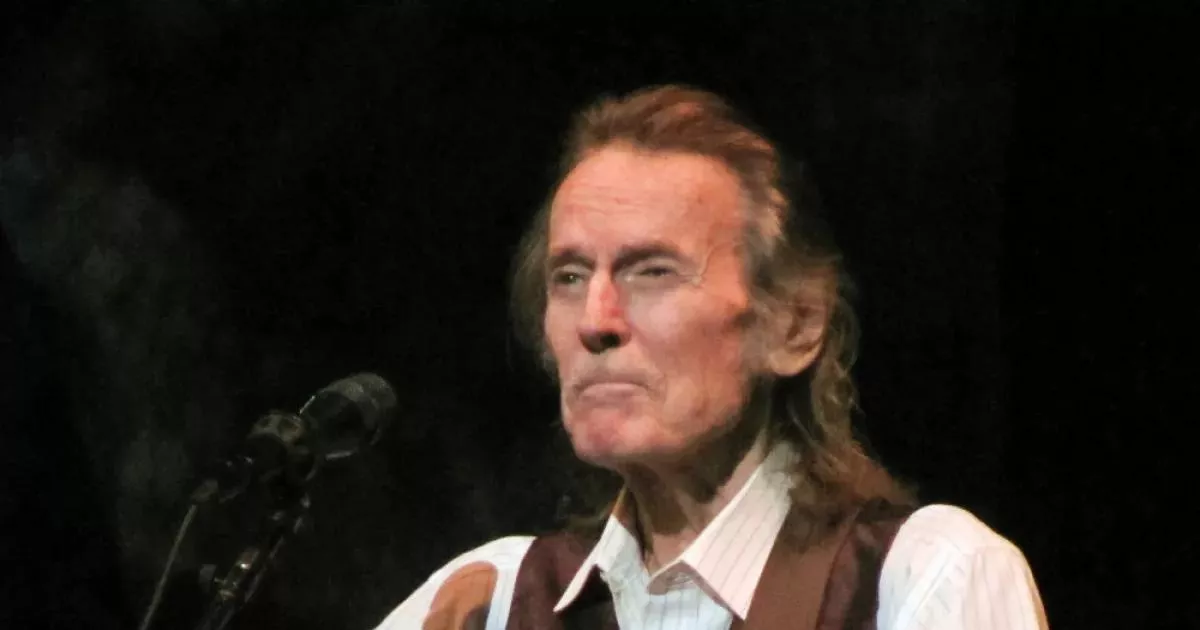
Gordon Lightfoot was a highly successful Canadian singer-songwriter and guitarist renowned for his contributions to folk, folk-rock, and country music. A defining figure in the folk-pop sound of the 60s and 70s, he is considered Canada's greatest songwriter. Lightfoot created numerous gold and multi-platinum albums, with his songs covered by many famous artists. His work often explored themes of trains, shipwrecks, nature, relationships, and solitude, securing his legacy as a storyteller through music.
1935: Birth of Sister, Beverley
In 1935, Beverley, Gordon Lightfoot's older sister, was born.
November 17, 1938: Gordon Lightfoot's Birth
On November 17, 1938, Gordon Meredith Lightfoot Jr. was born in Canada. He would become an internationally successful singer-songwriter and guitarist known for folk, folk-rock, and country music.
1958: Studies at Westlake College of Music
In 1958, Lightfoot moved to Los Angeles to study jazz composition and orchestration at Westlake College of Music.
1960: Return to Toronto
In 1960, after living in Los Angeles, Lightfoot returned to Toronto, where he continued to live in Canada thereafter.
1961: Release of first singles
In 1961, Gordon Lightfoot released two singles, recorded at RCA in Nashville, marking the start of his professional recording career.
July 1962: "(Remember Me) I'm the One" Reaches No. 3 in Toronto
In July 1962, Lightfoot's single "(Remember Me) I'm the One" reached No. 3 on CHUM radio in Toronto, marking a significant achievement.
1962: Canadian Chart Success Begins
In 1962, Lightfoot's Canadian chart success began with the No. 3 hit "(Remember Me) I'm the One".
April 1963: First Marriage to Brita Ingegerd Olaisson
In April 1963, Gordon Lightfoot married Brita Ingegerd Olaisson, a Swede, with whom he had two children.
1963: Travels in Europe and Hosts BBC Show
In 1963, Lightfoot travelled in Europe and hosted BBC TV's Country and Western Show in the UK for a year.
1964: Return to Canada and Mariposa Folk Festival
In 1964, Lightfoot returned to Canada and appeared at the Mariposa Folk Festival, enhancing his reputation as a songwriter.
December 1965: "Just Like Tom Thumb's Blues" Peak on Canadian Charts
In December 1965, Lightfoot's rendition of Bob Dylan's "Just Like Tom Thumb's Blues" peaked at No. 3 on the Canadian charts.
1965: Start of Red Shea Collaboration
From 1965, Red Shea was an important supporting player as lead guitarist in Lightfoot's sound.
1965: Juno Award for Top Folk Singer
In 1965, Gordon Lightfoot received a Juno Award for top folk singer, marking the beginning of a series of awards recognizing his talent and contributions to music.
1965: Management and Recording Contracts Signed
In 1965, Lightfoot signed a management contract with Albert Grossman and a recording contract with United Artists.
1965: Marty Robbins covers "Ribbon of Darkness"
In 1965, Marty Robbins's cover of Gordon Lightfoot's "Ribbon of Darkness" became a number one hit on the U.S. country chart, bringing Lightfoot wide recognition.
1966: Recording albums for United Artists
From 1966 to 1969, Gordon Lightfoot recorded albums for United Artists.
1966: Juno Award for Top Folk Singer
In 1966, Gordon Lightfoot received a Juno Award for top folk singer.
1966: Release of Debut Album Lightfoot!
In 1966, Gordon Lightfoot released his debut album, "Lightfoot!", which featured now-famous songs and increased his exposure as a singer and songwriter.
January 1, 1967: "Canadian Railroad Trilogy" Commissioned
On January 1, 1967, the CBC commissioned Lightfoot to write the "Canadian Railroad Trilogy" for a special broadcast to kick off Canada's Centennial year.
1967: Juno Award for Top Male Vocalist
In 1967, Gordon Lightfoot received a Juno Award for top male vocalist.
1967: First Canadian National Tour
In 1967, Lightfoot embarked on his first Canadian national tour and performed in New York City.
1967: "Black Day in July" Released
In 1967, Lightfoot released "Black Day in July," a song about the 1967 Detroit riot, which brought him recognition.
January 1968: Release of "Did She Mention My Name?"
In January 1968, Lightfoot released the album "Did She Mention My Name?", which included the song "Black Day in July" about the 1967 Detroit riot.
1968: Juno Award for Top Folk Singer
In 1968, Gordon Lightfoot received a Juno Award for top folk singer.
1968: Rick Haynes Joins Lightfoot's Band
In 1968, Rick Haynes joined Gordon Lightfoot's band as a bassist, becoming a core member.
1968: The Guess Who's "Lightfoot" track release
In 1968, The Guess Who celebrated Gordon Lightfoot in their song "Lightfoot" on the album "Wheatfield Soul," referencing his artistry and song titles.
1969: Juno Award for Top Folk Singer
In 1969, Gordon Lightfoot received a Juno Award for top folk singer.
1969: Live Recording "Sunday Concert"
In 1969, Gordon Lightfoot recorded the live album "Sunday Concert" for United Artists.
1970: Juno Award for Top Male Vocalist
In 1970, Gordon Lightfoot received a Juno Award for top male vocalist.
1970: "If You Could Read My Mind" Topped the Charts
In 1970, Gordon Lightfoot topped the US Hot 100 and Adult Contemporary charts with the hit "If You Could Read My Mind".
1970: Signs with Warner Bros./Reprise and Releases "If You Could Read My Mind"
In 1970, Lightfoot signed with Warner Bros./Reprise and released "If You Could Read My Mind", achieving major hit status in the United States.
1970: Terry Clements Joins and Red Shea leaves touring band
In 1970, Terry Clements joined Lightfoot's band as lead guitarist, and Red Shea left the touring band, but continued to record with Lightfoot until 1975.
1970: End of initial Red Shea Period
Until 1970, Red Shea was an important supporting player as lead guitarist in Lightfoot's sound.
1971: Juno Award for Top Male Vocalist
In 1971, Gordon Lightfoot received a Juno Award for top male vocalist.
1971: Release of "If You Could Read My Mind"
In 1971, Lightfoot originally released "If You Could Read My Mind", the melody of which became the subject of a lawsuit years later.
1971: Inspiration for "Alberta Bound"
In 1971, while travelling to Calgary, Lightfoot met a lonely teenaged girl named Grace on a bus, who inspired his song "Alberta Bound".
1971: "If You Could Read My Mind" Achieves Gold Status
In early 1971, "If You Could Read My Mind" sold over one million copies and was awarded a gold disc.
1971: First Major International Hit
In early 1971, Lightfoot scored his first major international hit with "If You Could Read My Mind" after defecting to Warner Bros. Records.
1972: Multiple Juno Awards
In 1972, Gordon Lightfoot received Juno Awards for top male vocalist and composer of the year, recognizing his vocal talent and songwriting abilities.
1972: Contracts Bell's Palsy
In 1972, Lightfoot contracted Bell's palsy, which temporarily paralyzed part of his face, curtailing his touring schedule.
1973: Multiple Juno Awards
In 1973, Gordon Lightfoot received Juno Awards for top folk singer and top male vocalist, further solidifying his status in Canadian music.
1973: Divorce from Brita Ingegerd Olaisson
In 1973, Lightfoot divorced Brita Ingegerd Olaisson. Lightfoot cited infidelity as a contributing factor to the end of the marriage.
June 1974: "Sundown" Reaches No. 1
In June 1974, Lightfoot's single "Sundown" from the album of the same name reached No. 1 on the American and Canadian charts.
1974: European and Australian Tours
Between 1967 and 1974, Lightfoot toured Europe and Australia, receiving positive reception.
1974: ASCAP Award for Songwriting
In 1974, Gordon Lightfoot received an ASCAP award for songwriting.
1974: "Sundown" and "Carefree Highway" Chart Success
In 1974, Gordon Lightfoot topped the charts with "Sundown" and had another hit with "Carefree Highway".
November 10, 1975: Sinking of the SS Edmund Fitzgerald
On November 10, 1975, the SS Edmund Fitzgerald sank on Lake Superior during a severe storm, with all 29 crew members lost.
November 1975: Inspiration for "The Wreck of the Edmund Fitzgerald"
In late November 1975, Lightfoot read a Newsweek article about the sinking of the SS Edmund Fitzgerald, which inspired his song about the event.
1975: "Rainy Day People" Hit Song
In 1975, Gordon Lightfoot had a hit song called "Rainy Day People" that appeared in the top 40.
1975: Juno Award for Top Folk Singer
In 1975, Gordon Lightfoot received a Juno Award for top folk singer.
1975: Pee Wee Charles Joins the Band
In 1975, Pee Wee Charles added pedal steel guitar to Lightfoot's songs.
1975: Red Shea Stops Recording with Lightfoot
In 1975, Red Shea stopped recording with Lightfoot, having continued recording with him since leaving the touring band in 1970.
1976: Multiple Juno and ASCAP Awards
In 1976, Gordon Lightfoot received Juno Awards for top folk singer and composer of the year, along with an ASCAP award for songwriting.
1976: "The Wreck of the Edmund Fitzgerald" Success
In 1976, Gordon Lightfoot released "The Wreck of the Edmund Fitzgerald" which topped the US Hot 100 and Adult Contemporary charts.
1977: "The Greatest Love of All" First Release
In 1977, George Benson recorded and released a version of "The Greatest Love of All", prior to Whitney Houston's later version.
1977: Multiple Juno and ASCAP Awards
In 1977, Gordon Lightfoot received Juno Awards for top folk singer and an ASCAP award for songwriting.
1977: Received the Vanier Award
In 1977, Gordon Lightfoot received the Vanier Award from the Canadian Jaycees.
1978: Top 40 Hit with "The Circle Is Small"
In 1978, Lightfoot had another top 40 hit on the United States Hot 100 with a re-recorded version of "The Circle Is Small (I Can See It in Your Eyes)", which reached number 33.
1979: Honorary Doctor of Laws degree from Trent University
In spring 1979, Gordon Lightfoot received an honorary Doctor of Laws degree from Trent University.
1980: Canadian Male Recording Artist of the Decade
In 1980, Gordon Lightfoot was named Canadian male recording artist of the decade for his work during the 1970s, highlighting his significant impact on Canadian music.
1981: Mike Heffernan Completes the Ensemble
In 1981, keyboardist Mike Heffernan completed the five-piece backup band that would remain intact until 1987.
1982: Release of Shadows album
In 1982, Lightfoot released the Shadows album.
1982: "Baby Step Back" Last Top 50 Hit in US
In 1982, the single "Baby Step Back" marked Lightfoot's last time in the top 50 in the US.
1983: Release of Salute album
In 1983, Lightfoot released the Salute album.
1985: Whitney Houston Releases "The Greatest Love of All"
In 1985, Whitney Houston recorded and released a version of "The Greatest Love of All".
1986: Ken Danby begins painting Lightfoot's portrait
Between 1986 and 1988, Ken Danby worked on a portrait of Gordon Lightfoot dressed in the white suit he wore on the cover of the album East of Midnight.
1986: Induction into Canadian Music Hall of Fame
In 1986, Gordon Lightfoot was inducted into the Canadian Music Hall of Fame.
1986: Release of East of Midnight album
In 1986, Lightfoot released the East of Midnight album.
April 1987: Lawsuit Filed Against Michael Masser
In April 1987, Lightfoot filed a lawsuit against Michael Masser, claiming Masser's "The Greatest Love of All" stole from Lightfoot's "If You Could Read My Mind".
1987: Pee Wee Charles Leaves the Band
In 1987, Pee Wee Charles left Lightfoot's band to operate a radio station in Southern Ontario.
1988: Ken Danby completes painting Lightfoot's portrait
Between 1986 and 1988, Ken Danby completed a portrait of Gordon Lightfoot dressed in the white suit he wore on the cover of the album East of Midnight.
1988: Winter Olympics Performance
In 1988, Gordon Lightfoot was a featured musical performer at the opening ceremonies of the Winter Olympic Games in Calgary, Alberta.
1988: Performance at Winter Olympics Opening Ceremony
In 1988, Lightfoot performed with Ian Tyson at the opening ceremonies of the Winter Olympics in Calgary.
1988: Release of Gord's Gold Volume II compilation
In 1988, Lightfoot released the compilation Gord's Gold Volume II.
1989: Second Marriage to Elizabeth Moon
In 1989, Lightfoot married Elizabeth Moon, with whom he had two children.
1991: Celebrity Captain for Toronto Maple Leafs
In 1991, Gordon Lightfoot was chosen as the celebrity captain of the Toronto Maple Leafs for the NHL's 75th anniversary season.
1992: Celebrity Captain for Toronto Maple Leafs
In 1992, Gordon Lightfoot continued his role as the celebrity captain of the Toronto Maple Leafs during the NHL's 75th anniversary season.
1993: Release of Waiting for You album
In 1993, Lightfoot released the Waiting for You album.
November 1997: Governor General's Performing Arts Award
In November 1997, Gordon Lightfoot was bestowed the Governor General's Performing Arts Award, Canada's highest honour in the performing arts.
1998: Induction into Canada's Walk of Fame
In 1998, Gordon Lightfoot was inducted into Canada's Walk of Fame.
1998: Release of A Painter Passing Through album
In 1998, Lightfoot released the A Painter Passing Through album.
1999: Purchase of Bridle Path Home
In 1999, Lightfoot purchased his final home in the Bridle Path neighbourhood of Toronto.
1999: Rhino Records Release "Songbook"
In 1999, Rhino Records released "Songbook", a four-CD boxed set of Gordon Lightfoot recordings that included rare and unreleased tracks from the 1960s, 1970s, 1980s, and 1990s, along with a booklet describing his songwriting process and career facts.
April 2000: Taping Live Concert in Reno
In April 2000, Lightfoot taped a live concert in Reno, Nevada, which was later broadcast by CBC in October and as a PBS special across the United States.
April 2001: Performance at Tin Pan South Legends Concert
In April 2001, Lightfoot performed at the Tin Pan South Legends concert at Ryman Auditorium in Nashville, closing the show.
2001: Induction into Canadian Country Music Hall of Fame
In 2001, Gordon Lightfoot was inducted into the Canadian Country Music Hall of Fame.
January 2002: Writing New Songs for Studio Album
By January 2002, Lightfoot had written 30 new songs for his next studio album and recorded guitar and vocal demos of some of these songs.
May 2003: Made a Companion of the Order of Canada
In May 2003, Gordon Lightfoot was made a Companion of the Order of Canada.
2003: Follow-up Surgery and New Recording Contract
In 2003, Lightfoot underwent follow-up surgery for his abdominal condition, signed a new recording contract with Linus Entertainment, and began rehearsing with his band.
January 2004: Completion of "Harmony" Album
In January 2004, Lightfoot completed work on the album "Harmony", which was mostly recorded before his illness.
July 2004: Surprise Comeback Performance
In July 2004, Lightfoot made a surprise comeback performance at Mariposa in Orillia, his first since falling ill, performing "I'll Tag Along" solo.
2005: Better Late Than Never Tour
In 2005, Lightfoot embarked on the 'Better Late Than Never Tour', marking his return to touring after his illness.
September 14, 2006: Minor Stroke During Performance
On September 14, 2006, while performing in Harris, Michigan, Lightfoot suffered a minor stroke that temporarily affected the use of fingers on his right hand.
December 4, 2007: Death of Manager Barry Harvey
On December 4, 2007, Lightfoot's manager, Barry Harvey, died at age 56.
2007: Honored with Canada Post postage stamp
In 2007, Canada Post honoured Gordon Lightfoot with a postage stamp highlighting his name and image.
2008: Death of Red Shea
In 2008, Red Shea, a former lead guitarist for Lightfoot, passed away.
2009: 26-City Tour
In 2009, Lightfoot undertook a 26-city tour.
February 2010: Death Hoax on Twitter
In February 2010, Lightfoot was the victim of a death hoax originating from Twitter. He dispelled the rumours by phoning a radio station and doing an interview, confirming he was alive and well.
2011: Carter Lancaster Replaces Terry Clements
In 2011, Carter Lancaster replaced Terry Clements in Lightfoot's band after Clements' death. Lightfoot commended him as a "great player".
2011: Divorce from Elizabeth Moon
In 2011, Lightfoot divorced Elizabeth Moon after a separation that had lasted nine years.
2011: Death of Terry Clements
In 2011, Terry Clements, Lightfoot's lead guitarist, died at the age of 63.
February 6, 2012: Presented with the Queen Elizabeth II Diamond Jubilee Medal
On February 6, 2012, Gordon Lightfoot was presented with the Queen Elizabeth II Diamond Jubilee Medal by the Lieutenant Governor of Ontario.
June 24, 2012: Induction into the Songwriters Hall of Fame
On June 24, 2012, Gordon Lightfoot was inducted into the Songwriters Hall of Fame in a New York City ceremony.
November 2012: Performance at 100th Grey Cup
In November 2012, Lightfoot performed "Canadian Railroad Trilogy" at the 100th Grey Cup at Rogers Centre, receiving an enthusiastic reception.
2012: Death of John Stockfish
In 2012, John Stockfish, a bassist who played with Lightfoot, passed away.
2012: Continued Touring
In 2012, Lightfoot continued to tour, performing approximately sixty times a year, including two shows at Ottawa's National Arts Centre after his induction into the Songwriters Hall of Fame.
2012: Comments on Mortality and Health
In 2012, Lightfoot discussed his health regimen and his perspective on mortality, stating he was prepared to go whenever he was taken, feeling he was on borrowed time.
June 16, 2014: SOCAN Lifetime Achievement Award
On June 16, 2014, Gordon Lightfoot was awarded a Lifetime Achievement Award by SOCAN at the 2014 SOCAN Awards in Toronto.
December 19, 2014: Third Marriage to Kim Hasse
On December 19, 2014, Lightfoot married Kim Hasse at Rosedale United Church.
June 6, 2015: Honorary doctorate of music from Lakehead University
On June 6, 2015, Gordon Lightfoot received an honorary doctorate of music in his hometown of Orillia from Lakehead University.
October 23, 2015: Bronze sculpture unveiled in Orillia
On October 23, 2015, Gordon Lightfoot was honoured with a bronze sculpture in his hometown of Orillia, Ontario.
2016: Royal Albert Hall Concert
Gordon Lightfoot performed a concert at Royal Albert Hall, which was later released as a live album in July 2023.
2016: UK Tour and Interview
In 2016, Lightfoot made his first tour of the United Kingdom in more than 35 years, with 11 dates. In an interview that year, he said his challenge was doing the best show he could.
2016: Comments on Songwriting
In 2016, Lightfoot stated he did not plan to return to songwriting, citing its isolating effect on his family life.
July 1, 2017: Performance at Canada's 150th Birthday Celebration
On July 1, 2017, Lightfoot performed at Canada's 150th birthday celebration on Parliament Hill, introduced by Prime Minister Justin Trudeau, noting that Lightfoot had also played the same stage for Canada's 100th birthday.
2017: Death of Sister, Beverley
In 2017, Beverley, Gordon Lightfoot's older sister, passed away.
2017: Ranked among best Canadian songwriters
In 2017, Gordon Lightfoot was rated fifth in the CBC's list of the 25 best Canadian songwriters ever.
2018: Tours in Canada and the US
Lightfoot's 2017 and 2018 tours included dozens of dates in Canada and the United States.
2019: Documentary release: Gordon Lightfoot: If You Could Read My Mind
In 2019, the documentary "Gordon Lightfoot: If You Could Read My Mind" was released.
2019: Gym Injury
Lightfoot's 2019 tour was interrupted when he was injured while working out in a gym.
March 2020: Concert Schedule Interrupted by Pandemic
In March 2020, Lightfoot's concert schedule was interrupted by governmental restrictions during the coronavirus pandemic.
2020: Release of "Solo" Album
In 2020, Lightfoot released his 20th studio album, "Solo", unaccompanied by other musicians, marking his return to Warner Music Canada.
October 30, 2022: Final Concert Performance
On October 30, 2022, Lightfoot played what turned out to be his final concert in Winnipeg. Remaining dates were postponed and eventually cancelled due to his declining health.
2022: Golden Plate Award of the American Academy of Achievement
In 2022, Gordon Lightfoot received the Golden Plate Award of the American Academy of Achievement.
May 1, 2023: Gordon Lightfoot's Death
On May 1, 2023, Gordon Meredith Lightfoot Jr. passed away, marking the end of a significant era in folk, folk-rock and country music.
May 8, 2023: Private Funeral Held
On May 8, 2023, a private funeral was held for Lightfoot at St. Paul's United Church. His body was later cremated, and his ashes were buried next to his parents.
July 2023: Release of "At Royal Albert Hall" Live Album
Two weeks after his death, it was announced that his 2016 concert performance at Royal Albert Hall would be released in July 2023 as the live album "At Royal Albert Hall".
May 23, 2024: Tribute Concert at Massey Hall
On May 23, 2024, a tribute concert took place at Massey Hall, featuring performances of Lightfoot songs by his band, The Lightfoot Band, and other artists.
Mentioned in this timeline

Justin Trudeau served as the rd Prime Minister of Canada...

Elizabeth II reigned as Queen of the United Kingdom and...

Whitney Houston nicknamed The Voice was a highly acclaimed American...

Bob Dylan is a highly influential American singer-songwriter renowned as...
The Winter Olympic Games a major international multi-sport event held...
Coronaviruses are a family of RNA viruses affecting mammals and...
Trending

56 minutes ago Kate Hudson Discusses Goldie Hawn, Kurt Russell, and Her Privileged Upbringing
56 minutes ago Philip Rosenthal's 'Somebody Feed Phil' moves to YouTube in 2027 with Banijay deal.

56 minutes ago Giants Secure Greg Newsome II with $10 Million Deal Amid Free Agency

2 hours ago Michelle Pfeiffer and David E. Kelley's Rare Red Carpet Appearance: A Loving Display

2 hours ago Silo Season 3: Production Update and Series Acclaim on Apple TV+

2 hours ago Jalen Hurts Reflects on Career Doubts and Releases Children's Book
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Ken Paxton is an American politician and lawyer serving as...

Markwayne Mullin is an American politician and businessman serving as...

Corey Lewandowski is an American political operative lobbyist commentator and...

Kristi Lynn Arnold Noem is an American politician She was...

Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton is a prominent American politician lawyer...
