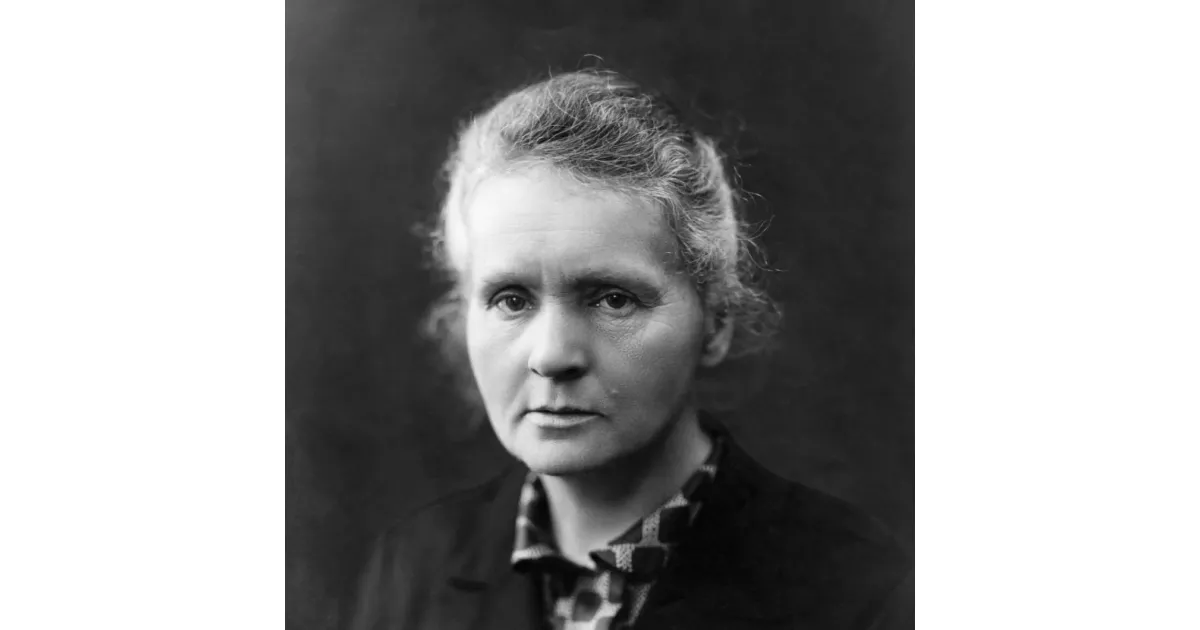
Discover the defining moments in the early life of Marie Curie. From birth to education, explore key events.
Marie Curie, born Maria Skłodowska in Poland, was a pioneering physicist and chemist renowned for her groundbreaking research on radioactivity. Working primarily in France, she was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize, the first person and only woman to win the Nobel Prize twice, and the only person to win the Nobel Prize in two different scientific fields (Physics and Chemistry). Curie's work led to the discovery of polonium and radium, and she developed techniques for isolating radioactive isotopes. Her research was crucial in developing treatments for cancer. She died in 1934 from aplastic anemia likely caused by her long-term exposure to radiation.
June 1903: Curie Awarded Doctorate from University of Paris
In June 1903, Marie Curie was awarded her doctorate from the University of Paris, supervised by Gabriel Lippmann.
December 1904: Birth of Ève Curie
In December 1904, Marie Curie gave birth to her second daughter, Ève Curie. She hired Polish governesses to teach her daughters her native language, and sent or took them on visits to Poland.
1906: Death of Pierre Curie
In 1906, Pierre Curie died in a Paris street accident. Following his death, Marie took over his professorship at the University of Paris.
1911: After her 1911 Nobel Prize victory
Lauren Gunderson's 2019 play The Half-Life of Marie Curie portrays Curie during the summer after her 1911 Nobel Prize victory, when she was grappling with depression and facing public scorn over the revelation of her affair with Paul Langevin.
1912: Avoided public life
For most of 1912, Marie Curie avoided public life, but did spend time in England with her friend and fellow physicist Hertha Ayrton.
1913: Visit to Poland
In 1913, Marie Curie visited Poland and was welcomed in Warsaw, but the visit was mostly ignored by the Russian authorities.
1921: Fundraising tour of the United States
In 1921, Marie Curie toured the United States to raise funds for research on radium. Marie Mattingly Meloney helped publicise her trip.
1921: Received radium at the White House
In 1921, U.S. President Warren G. Harding presented Marie Curie with 1 gram of radium at the White House.
1922: Fellow of the French Academy of Medicine
In 1922, Marie Curie became a fellow of the French Academy of Medicine. She also travelled to other countries.
1929: Second American tour
In 1929, Marie Curie's second American tour succeeded in equipping the Warsaw Radium Institute with radium.
1979: Women Eligible for Académie des Sciences
In 1979, women became eligible for membership of the Académie des Sciences. Before 1979 all presentations had to be made for her by male colleagues.
Mentioned in this timeline

The White House located at Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington...
Albert Einstein - was a German-born theoretical physicist renowned for...
France officially the French Republic is primarily located in Western...

Books are a means of storing information as text or...
Spain officially the Kingdom of Spain is located in Southern...

The horse scientifically known as Equus ferus caballus is a...
Trending

42 minutes ago US, Israel launch military operation against Iran, airstrikes kill leader, Gulf earthquake follows.

42 minutes ago Kaitlan Collins covers Bill Clinton's Epstein testimony and calls out Trump allies.

42 minutes ago Adam Levine and Behati Prinsloo: Navigating Cheating Allegations and Maintaining Relationship

42 minutes ago Brandi Carlile Honored as Time's 2026 Woman of the Year, Other News Emerge
Gabe Perreault is a Canadian-born American professional ice hockey player currently playing for the New York Rangers in the NHL...

43 minutes ago Steve Witkoff involved in tense Geneva meeting before US-Iran conflict escalation.
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton is a prominent American politician lawyer...

Jim Carrey is a Canadian-American actor and comedian celebrated for...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Kashyap Pramod Patel is an American lawyer who became the...

Michael Joseph Jackson the King of Pop was a highly...
