South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is composed of nine provinces. The country's southern border has 2,798 kilometres of coastline along the South Atlantic and Indian Ocean. It shares borders with Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe to the north, Mozambique and Eswatini to the east and northeast, and it encloses Lesotho.
1902: End of the Second Boer War
In 1902, the Second Boer War ended with a British victory, though they suffered heavy casualties due to Boer attrition warfare. Scorched earth tactics and concentration camps contributed to the deaths of 27,000 Boer civilians due to disease and neglect.
1909: South Africa Act
In 1909, the South Africa Act granted nominal independence while creating the Union of South Africa on 31 May 1910.
May 1910: Creation of the Union of South Africa
On 31 May 1910, the South Africa Act 1909 granted nominal independence creating the Union of South Africa.
1910: Unification of South Africa
After unification in 1910, South Africa had its own parliament which passed laws specific for South Africa, building on those previously passed for the individual member colonies.
1910: Union of South Africa created
In 1910, the Union of South Africa was created after the amalgamation of the Cape, Natal, Transvaal, and Orange River colonies.
1911: Percentage of whites in the population
The first census in 1911 showed that whites made up 22% of the population.
1913: Natives' Land Act restricted land ownership by blacks
In 1913, the Natives' Land Act severely restricted the ownership of land by blacks, limiting them to only 7% of the country's land.
1924: Discovery of the Taung Child
In 1924, Raymond Dart identified the Taung Child, the first hominin fossil discovered in Africa, near Taung.
1930: Publication of Mhudi
In 1930, Solomon Thekiso Plaatje's Mhudi, was written, one of the first novels written by a black author in an African language.
1931: Union becomes fully sovereign
In 1931, the union became fully sovereign from the United Kingdom with the passage of the Statute of Westminster.
1934: South African Party and National Party merge
In 1934, the South African Party and National Party merged to form the United Party, seeking reconciliation between Afrikaners and English-speaking whites.
1939: Party split over entry into World War II
In 1939, the United Party split over the entry of the union into World War II as an ally of the United Kingdom, opposed by National Party followers.
1945: Over 4,900 species of fungi recorded
By 1945, more than 4,900 species of fungi (including lichen-forming species) had been recorded in South Africa.
1948: Publication of Cry, the Beloved Country
In 1948, Alan Paton published the novel Cry, the Beloved Country.
1948: Unofficial record of hottest temperature near Upington
In 1948, an unofficial temperature of 51.7 °C (125.06 °F) was recorded in the Northern Cape Kalahari near Upington, though it was not recorded with standard equipment.
1948: National Party imposes apartheid
In 1948, the National Party imposed apartheid, institutionalising previous racial segregation.
1948: National Party elected and strengthens racial segregation
In 1948, the National Party was elected to power and strengthened the racial segregation, classifying people into three races and creating rights and limitations for each, leading to apartheid.
1950: South Africa population
According to the United Nations World Population Prospects, South Africa's total population was 13.6 million in 1950.
1955: Adoption of the Freedom Charter
In 1955, the Freedom Charter was adopted by the Congress Alliance, demanding a non-racial society and an end to discrimination.
May 1961: South Africa becomes a republic and withdraws from the Commonwealth
On 31 May 1961, the country became a republic following a referendum. Elizabeth II lost the title Queen of South Africa, and the last Governor-General, Charles Robberts Swart, became state president. South Africa withdrew from the Commonwealth of Nations in 1961.
1961: Republic of South Africa
Since 1961, the long formal name in English has been the "Republic of South Africa" and Republiek van Suid-Afrika in Afrikaans.
December 1967: First Human-to-Human Heart Transplant
In December 1967, cardiac surgeon Christiaan Barnard performed the first human-to-human heart transplant at Groote Schuur Hospital.
1970: Peak in gold production
In 1970, South Africa's gold production peaked at nearly 1,000 tonnes.
1974: Signing of the Mahlabatini Declaration of Faith
In 1974, the Mahlabatini Declaration of Faith was signed by Mangosuthu Buthelezi and Harry Schwarz, enshrining the principles of peaceful transition of power and equality for all.
1979: Jody Scheckter wins Formula One World Championship
In 1979, Jody Scheckter won the Formula One motor racing World Championship.
1979: Vela incident
In 1979, the "Vela incident", a suspected nuclear test, occurred over the Atlantic, although South Africa officially denies any involvement.
1980: Percentage of whites in the population
By 1980, the percentage of whites in the population had declined to 16%.
1980: Completion of first operational nuclear device
In 1980, South Africa completed its first operational nuclear device as part of its weapons of mass destruction program.
1983: Constitution Act eliminates prime minister role
In 1983, P. W. Botha's Constitution Act eliminated the office of prime minister and instated a "strong presidency".
1987: Founding of Nando's
In 1987, Nando's was founded in Johannesburg, specializing in flame-grilled peri-peri chicken.
1990: Water Access Increase
From 1990 to 2010, water access increased from 66% to 79% in South Africa.
1990: Completion of sixth operational nuclear device
In 1990, South Africa completed its sixth operational nuclear device as part of its weapons of mass destruction program.
1990: Ban lifted on ANC and Nelson Mandela released
In 1990, the National Party government lifted the ban on the ANC and other political organizations, and Nelson Mandela was released from prison.
1991: Estimates of English speakers
Estimates based on the 1991 census suggest just under half of South Africans could speak English.
1991: Nadine Gordimer Wins Nobel Prize
In 1991, Nadine Gordimer became the first South African to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature.
1991: Dismantling of nuclear arsenal
In 1991, South Africa voluntarily dismantled its nuclear arsenal and joined the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT).
1992: Referendum approves ending apartheid
In 1992, with approval from the white electorate in a referendum, the government continued negotiations to end apartheid.
1992: South African life expectancy at a high
The fall is in large part attributable to the South African HIV/AIDS pandemic which saw South African life expectancy fall from a high point of 62 years in 1992 to a low of 53 in 2005, and the failure of the government to take steps to address the pandemic in its early years.
January 1993: Official hottest temperature recorded at Vioolsdrif
In January 1993, the official highest temperature of 48.8 °C (119.84 °F) was recorded at Vioolsdrif.
1993: Discussions between F.W. de Klerk and Nelson Mandela
In 1993, F.W. de Klerk opened bilateral discussions with Nelson Mandela for a transition of policies and government.
June 1994: South Africa signs the Rio Convention on Biological Diversity
On June 4, 1994, South Africa signed the Rio Convention on Biological Diversity.
1994: First universal elections and ANC victory
In 1994, South Africa held its first universal elections, which the ANC won by an overwhelming majority. The country rejoined the Commonwealth of Nations and became a member of the Southern African Development Community.
1994: South Africa rejoins the Commonwealth
In 1994, South Africa rejoined the Commonwealth of Nations after the end of apartheid.
1994: Electricity Access
In 1994, about 36% of South Africans had access to electricity.
1994: Establishment of the SANDF
In 1994, the South African National Defence Force (SANDF) was established as a volunteer military through the integration of the former South African Defence Force (SADF) and various liberation movement forces.
1994: Constitutional Court based in Johannesburg
In 1994, the highest court, the Constitutional Court of South Africa, was based in Johannesburg.
1994: Black South Africans enfranchised
In 1994, the vast majority of Black South Africans were enfranchised.
1994: Universal elections take place
In 1994, universal elections took place, following which all racial groups have held political representation.
1994: Unemployment skyrockets in post-apartheid South Africa
In post-apartheid ANC-governed South Africa, unemployment skyrocketed to over 30% since 1994 and income inequality increased.
1994: Start of high murder rates
More than 526,000 South Africans were murdered from 1994.
November 1995: South Africa becomes a party to the Rio Convention
On November 2, 1995, South Africa became a party to the Rio Convention on Biological Diversity.
1995: United Nations Human Development Index falls
From 1995 to 2005, The United Nations Human Development Index fell before recovering its 1995 peak in 2013. The fall is in large part attributable to the South African HIV/AIDS pandemic
1995: South Africa wins 1995 Rugby World Cup
In 1995, South Africa won the Rugby World Cup for the first time, hosting the event.
1996: Penny Heyns wins Olympic Gold at the Atlanta Olympic Games
Penny Heyns won Olympic Gold in the 1996 Atlanta Olympic Games.
1998: Proteas win ICC KnockOut Trophy and South Africa wins Blind Cricket World Cup
In 1998, South Africa's national cricket team, the Proteas, won the inaugural edition of the ICC KnockOut Trophy. Also in 1998, South Africa's national blind cricket team won the Blind Cricket World Cup.
1998: Land claims settled
Since 1998, the South African government has settled 80,000 land claims from people who had been evicted from land by the previous government.
1999: Financial aid scheme
In 1999, a financial aid scheme was promulgated.
2001: Eskom Recognized as World's Best
In 2001, Eskom was recognized as the world's best electricity company.
2001: Christian denominations according to census
Per the 2001 census, the Christian category included Zion Christian (11.1%), Pentecostal (Charismatic) (8.2%), Catholic (7.1%), Methodist (6.8%), Dutch Reformed (6.7%), and Anglican (3.8%).
2002: Sydney Brenner wins Nobel Prize
In 2002, Sydney Brenner won the Nobel Prize for his pioneering work in molecular biology.
2003: J.M. Coetzee Wins Nobel Prize
J.M. Coetzee won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 2003.
2003: Worsening of black unemployment rate
The overall unemployment rate of black people worsened between 1994 and 2003 by official metrics but declined significantly using expanded definitions.
2004: Start of tertiary education system reform
In 2004, South Africa started reforming its tertiary education system.
2004: South African swimming team wins Olympic gold in Athens
In 2004, the South African swimming team of Roland Schoeman, Lyndon Ferns, Darian Townsend, and Ryk Neethling won the gold medal at the Olympic Games in Athens, breaking the world record in the 4×100 Freestyle Relay.
2004: Increase in popular protests
Since 2004, South Africa experienced a surge in popular protests, some of which were violent, leading to the country being described as the "most protest-rich country in the world".
2005: U-Carmen e-Khayelitsha wins Golden Bear
In 2005, U-Carmen e-Khayelitsha won the Golden Bear at the Berlin International Film Festival.
2005: South African life expectancy at a low
The fall is in large part attributable to the South African HIV/AIDS pandemic which saw South African life expectancy fall from a high point of 62 years in 1992 to a low of 53 in 2005, and the failure of the government to take steps to address the pandemic in its early years.
June 2006: National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan received
On June 7, 2006, South Africa's National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan was received by the Rio Convention.
2006: Legalisation of same-sex marriage
In 2006, South Africa became one of the first jurisdictions in the world to legalise same-sex marriage.
2006: Tsotsi wins Academy Award
In 2006, the film Tsotsi won the Academy Award for Foreign Language Film at the 78th Academy Awards.
2006: Estimated number of fungi species in South Africa
In 2006, the number of fungi species in South Africa was estimated at 200,000, not taking into account fungi associated with insects.
2006: Survey on immigration
In a 2006 survey, the South African Migration Project concluded that South Africans are more opposed to immigration than any other national group.
2006: Zuma Indictment
On 16 March 2018, just over a month after President Jacob Zuma resigned from the presidency, National Director of Public Prosecutions Shaun Abrahams announced that Zuma would again face prosecution on 16 criminal charges – 12 charges of fraud, two of corruption, and one each of racketeering and money laundering, just as in the 2006 indictment.
2007: World Refugee Survey
According to the World Refugee Survey 2008, published by the U.S. Committee for Refugees and Immigrants, South Africa's refugee and asylum seeker population numbered approximately 144,700 in 2007.
2007: Introduction of Load Shedding
Eskom introduced rolling blackouts (load shedding) in 2007 to prevent grid collapse.
2007: South Africa hosts 2007 World Twenty20 Championship
In 2007, South Africa hosted the World Twenty20 Championship.
2007: Government efforts to fight AIDS
In 2007, in response to international pressure, the South African government made efforts to fight AIDS.
2007: Energy crisis begins
Since 2007, South Africa has been undergoing an energy crisis, resulting in routine rolling electricity blackouts due to loadshedding.
May 2008: Anti-immigrant riots
A series of anti-immigrant riots occurred in South Africa beginning in May 2008.
May 2008: Riots leave over 60 people dead
In May 2008, riots in South Africa left over 60 people dead and drove over 100,000 people from their homes. The targets were mainly migrants and refugees, but a third of the victims were South African citizens.
2008: HIV/AIDS infection along racial lines
A 2008 study revealed that HIV/AIDS infection is distinctly divided along racial lines: 13.6% of blacks are HIV-positive, whereas only 0.3% of whites have the virus.
2008: World Refugee Survey
According to the World Refugee Survey 2008, published by the U.S. Committee for Refugees and Immigrants, South Africa's refugee and asylum seeker population numbered approximately 144,700 in 2007.
2009: Life expectancy and healthcare spending
According to the South African Institute of Race Relations, the life expectancy in 2009 was 71 years for a white South African and 48 years for a black South African. The healthcare spending in the country is about 9% of GDP.
2009: Appointment of new health minister
After the 2009 general elections, President Jacob Zuma appointed Aaron Motsoaledi as the health minister and committed his government to increasing funding for HIV treatment.
2010: Sanitation Access Increase
From 1990 to 2010, sanitation access increased from 71% to 79% in South Africa.
2010: Jordy Smith wins Billabong J-Bay Open
In 2010, Durban surfer Jordy Smith won the Billabong J-Bay Open, becoming the highest-ranked surfer in the world.
2011: Publication of first national climate change report
In 2011, South Africa published its first national climate change report.
2011: UNHCR reports on violence
In 2011, the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees reported that recent violence had not been as widespread as initially feared.
2012: Oscar Pistorius competes at the Olympic Games in London
In 2012, Oscar Pistorius became the first double amputee sprinter to compete at the Olympic Games in London.
August 2013: Ranked top African "Country of the Future"
In August 2013, South Africa was ranked as the top African "Country of the Future" by fDi Intelligence.
2013: The United Nations Human Development Index recovers
From 1995 to 2005, The United Nations Human Development Index fell before recovering its 1995 peak in 2013. The fall is in large part attributable to the South African HIV/AIDS pandemic
2013: Coldest temperature recorded in Buffelsfontein
In 2013, the coldest temperature on mainland South Africa was recorded in Buffelsfontein in the Eastern Cape, reaching −20.1 °C (−4.2 °F).
2014: Poverty rate in South Africa
In 2014, approximately 56% of South Africans lived below the poverty line.
2014: Record number of rhinos killed
Statistics from the Department of Environmental Affairs show a record 1,215 rhinos were killed in 2014.
2015: Number of people living with HIV
According to the 2015 UNAIDS medical report, South Africa has an estimated seven million people living with HIV, more than any other country in the world.
2015: South Africa population
According to the United Nations World Population Prospects, South Africa's total population was 55.3 million in 2015.
2015: Wealth Inequality
As of 2015, the wealthiest 10% held 71% of national wealth, while the poorest 60% held just 7% in South Africa, illustrating high inequality.
2015: Number of students aided by financial aid scheme
By 2015, 1.4 million students in higher education have been aided by a financial aid scheme.
2015: Progress in HIV treatment
By 2015, South Africa had made significant progress in HIV treatment, with the widespread availability of antiretroviral drugs resulting in an increase in life expectancy.
2015: The Endless River at Venice Film Festival
In 2015, the Oliver Hermanus film The Endless River became the first South African film selected for the Venice Film Festival.
2016: Publication of second national climate change report
In 2016, South Africa published its second national climate change report.
2016: Wayde van Niekerk becomes world record holder in 400 metres
Since 2016, Wayde van Niekerk has been the world record holder in the 400 metres.
April 2017: Start of high murder rate period
From April 2017, South Africa experienced a period where an average of 57 murders were committed each day.
2017: Signing the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons
In 2017, South Africa reaffirmed its disarmament stance by signing the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
February 2018: Jacob Zuma resigns, Cyril Ramaphosa becomes president
On 14 February 2018, Jacob Zuma resigned the presidency. On 15 February, ANC president Cyril Ramaphosa became President of South Africa.
March 2018: Zuma to face prosecution
On 16 March 2018, Zuma would again face prosecution on 16 criminal charges.
March 2018: End of high murder rate period
Until March 2018, South Africa experienced a period where an average of 57 murders were committed each day.
2018: HIV prevalence and AIDS-related deaths
In 2018, HIV prevalence among adults (15–49 years) was 20.4%, and 71,000 people died from an AIDS-related illness.
2018: Establishment of the Zondo Commission
In 2018, the Zondo Commission was established to investigate allegations of corruption and state capture.
2018: Cape Town Water Crisis
In early 2018, Cape Town faced a water crisis with the city's water supply predicted to run dry before the end of June. Water-saving measures were in effect, limiting citizens to 50 litres per day.
2019: André de Ruyter attempts to reform Eskom
During 2019–2023, Eskom CEO André de Ruyter attempted to reform the utility but faced fierce internal resistance and assassination threats from criminal elements within the company.
2019: Forest Landscape Integrity Index ranking
In 2019, South Africa had a Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 4.94/10, ranking it 112th globally out of 172 countries.
2019: Ratification of the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons
In 2019, South Africa ratified the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
2019: Port of Durban Container Handling
In 2019, the Port of Durban handled approximately 4.5 million TEUs, making it the largest and busiest container port in sub-Saharan Africa.
2019: End of high murder rates
More than 526,000 South Africans were murdered until 2019.
February 2020: Warrant issued for Zuma's arrest
A warrant was issued for Jacob Zuma's arrest in February 2020 after he failed to appear in court.
2020: South Africa pledge to peak emissions
As part of its international commitments, South Africa has pledged to peak emissions between 2020 and 2025.
2020: Political and economic crisis
Since 2020, South Africa experienced a period of political and economic crisis.
2021: Zuma found guilty of contempt of court
In 2021, Jacob Zuma was found guilty of contempt of court and sentenced to 15 months' imprisonment, leading to protests and riots that resulted in 354 deaths.
December 2022: André de Ruyter's Resignation and Sabotage
Following André de Ruyter's resignation as Eskom CEO in December 2022, multiple coal-fired generating units were sabotaged.
December 2022: MTN User Base
In December 2022, the MTN Group reportedly reached around 290 million users.
2022: Religious affiliations according to census
According to the 2022 census, Christians accounted for 85.3% of the population, Muslims 1.6%, Hindus 1.1%, traditional African religions 7.8%, 3.1% had no religious affiliation, and 1.1% were "other".
2022: Most spoken languages according to census
According to the 2022 census, the three most spoken first languages are Zulu (24.4%), Xhosa (16.6%), and Afrikaans (10.6%). English is the fifth most common home language, spoken by 8.7% of South Africans.
2022: South Africa population
As of 2022, South Africa's population is about 62 million. The last census was held in 2022.
2022: South Africa's ranking on the Ibrahim Index of African Governance
In 2022, South Africa was ranked sixth out of 48 sub-Saharan African countries on the Ibrahim Index of African Governance.
2022: Women's Africa Cup of Nations Win
In 2022, South Africa's women's team won the Women's Africa Cup of Nations.
2022: Release of the Zondo Commission findings
In 2022, the Zondo Commission released its findings, documenting evidence of systemic corruption, fraud, racketeering, bribery, money laundering, and state capture at every level of government.
2022: Racial population groups census
The 2022 census figures for racial groups were: Black African at 81%, Coloured at 8.2%, White at 7.3%, Indian or Asian at 2.7%, and Other/Unspecified at 0.5%.
2023: South African Sign Language recognised as an official language
In 2023, South African Sign Language was recognised as an official language.
2023: South Africa hosts ICC Women's T20 World Cup
In 2023, the ICC Women's T20 World Cup was hosted in South Africa and the women's team won silver.
2023: Market capitalization of the JSE
In 2023, the Johannesburg Stock Exchange (JSE) had a market capitalization of approximately US$1.36 trillion.
2023: Special Task Force ranked 9th in SWAT competition
In the 2023 International SWAT Competition, the Special Task Force (STF) ranked 9th out of 55 international law enforcement teams.
March 2024: Stable Electricity Supply Achieved
By March 2024, interventions helped South Africa achieve a stable electricity supply for the first time in over a decade, with load shedding suspended.
May 2024: ANC loses majority in election
In May 2024, the ANC lost its majority for the first time since the end of Apartheid, winning only 40% of the vote and 159 seats. The Democratic Alliance (DA) won 22% of the vote and 87 seats. uMkhonto weSizwe won 14.6% of the vote and 58 seats, while the Economic Freedom Fighters won 9.5% of the vote and 39 seats. The ANC formed a Government of National Unity with the DA and several smaller parties after the May 2024 election.
2024: Unemployment rate in South Africa
As of 2024, about 32% of the population is unemployed in South Africa.
2024: Mobile Subscriptions and Internet Usage
By 2024, mobile subscriptions exceeded the population in South Africa, and internet usage reached over 72%.
2024: Increase in Tourism Numbers
In 2024, South Africa experienced a growth in tourism, with combined passenger arrivals increasing to 8.92 million people.
2024: Global Innovation Index Ranking
In 2024, South Africa was ranked 69th in the Global Innovation Index.
2024: ANC vote share falls below 50% for the first time since Apartheid
In 2024, the African National Congress's share of the national vote fell below 50% for the first time since the end of Apartheid. Despite this, it remained the single largest party in the South African Parliament. President Ramaphosa announced a national unity government and was reelected for a second term.
2024: Men's Cricket team wins silver at ICC T20 World Cup
In 2024, the men's cricket team won silver at the ICC T20 World Cup.
May 2025: Tourism Industry Contribution to GDP
As of May 2025, the tourism industry accounted for 3.3% of South Africa's GDP, according to Statistics South Africa (Stats SA).
August 2025: Approval of New Nuclear Power Plant
In August 2025, South Africa approved the construction of a new 4,000-MW nuclear power plant near Cape Town.
2025: Number of Airports and Airport Ranking
As of 2025, South Africa has 573 airports, the most in Africa and 13th globally. Cape Town International Airport was also ranked the best airport in the world by the AirHelp Score index in 2025.
2025: Railway Network Size
As of 2025, South Africa has the largest railway network in Africa and the 9th-largest in the world, with a total track length of approximately 31,000 km.
2025: South Africa's defence spending
As of 2025, South Africa spends approximately R57 billion (around US$3.25 billion), which amounts to roughly 0.8% of GDP, on defence.
2025: Electricity Access
As of 2025, approximately 94% of South Africans have access to electricity.
2025: SANDF consists of around 75,000 professional soldiers
As of 2025, the SANDF consists of around 75,000 professional soldiers and operates under the authority of the President of South Africa.
2025: Purchasing power parity (PPP)
As of 2025, the purchasing power parity (PPP) in South Africa of around US$16,000 ranks among the highest on the continent.
2025: South Africa pledge to peak emissions
As part of its international commitments, South Africa has pledged to peak emissions between 2020 and 2025.
2025: Tourism Ranking by The Telegraph
In 2025, South Africa was rated as the 4th best country in the world for tourism, and the best in the Africa and Indian Ocean region, by The Telegraph.
2025: Adult literacy rate
In 2025, the adult literacy rate in South Africa was 95%, the second-highest in Africa.
2025: Men's Cricket team wins the ICC World Test Championship
In 2025, the men's team won the 2023–2025 ICC World Test Championship, beating Australia in the final.
2025: Tourism Sector Employment
In early 2025, 1.8 million people were employed in South Africa's tourism sector.
2025: Men's U-20 Africa Cup of Nations win
South Africa's men's U-20 team also won the 2025 U-20 Africa Cup of Nations.
2030: Expected Launch of High-Speed Train Line
South Africa is exploring the development of future high-speed bullet trains, with the first line expected to launch in 2030.
2050: Projected temperature increase in southern Africa
By 2050, computer models project that parts of southern Africa will experience a temperature increase of about 1 °C (1.8 °F) along the coast to more than 4 °C (7.2 °F) in the hinterland, such as the Northern Cape, during late spring and summertime.
Mentioned in this timeline
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe the second-largest on...

Elizabeth II reigned as Queen of the United Kingdom and...
India officially the Republic of India is a South Asian...
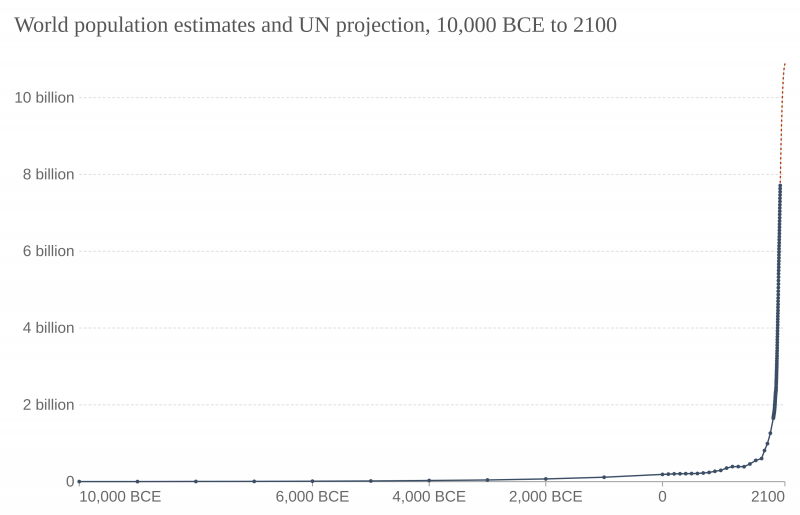
The world population the total number of living humans surpassed...
China officially the People's Republic of China is an East...
Africa is the second-largest and second-most populous continent home to...
Trending

Alessandra Mussolini is an Italian politician television personality model and former actress and singer A member of the Mussolini family...
41 minutes ago Puerto Rico faces challenges for WBC 2026 as MLB stars withdraw.
41 minutes ago Kurdistan: Israel backs Kurdish plans against Iran; US support sought, family hopes.

42 minutes ago Colombia aims for deep WBC run led by Quintana and Teheran.

2 hours ago Katie Couric Interviewed Gavin Newsom on California Economy and His Appearance.

2 hours ago Marlon Wayans aims to 'cancel cancel culture' with new 'Scary Movie' trailer.
Popular

Ken Paxton is an American politician and lawyer serving as...

Markwayne Mullin is an American politician and businessman serving as...

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton is a prominent American politician lawyer...

Jim Carrey is a Canadian-American actor and comedian celebrated for...

Corey Lewandowski is an American political operative lobbyist commentator and...
