Europe is a continent in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, bordered by the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, the Mediterranean Sea, and Asia. It shares the Eurasia landmass with Asia, and Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. The Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, Black Sea, and Turkish Straits are commonly considered its eastern boundary with Asia.
1900: European Population
By 1900, Europe's population had increased to approximately 400 million.
1906: Use of Kuma-Manych Depression boundary
As early as 1906, the boundary along the Kuma–Manych Depression was commonly used as the boundary between Europe and Asia in Russia and the Soviet Union.
1912: Balkan Wars Begin
The Balkan Wars in 1912 marked the end of Ottoman rule in the Balkans.
1913: Peak of European Share of World Population
Around the year 1913, the share of the world population living in Europe reached a peak of slightly above 25%.
1913: Balkan Wars End
The Balkan Wars ended in 1913 marking the end of Ottoman rule in the Balkans.
1918: End of World War I
World War I concluded in 1918, leaving more than 16 million civilians and military personnel dead and over 60 million European soldiers mobilized.
1919: Social Revolutions After The Great War
In 1919, social revolutions swept through Europe, including the establishment of the Weimar Republic in Germany and the First Austrian Republic.
1922: Rise of Fascism in Italy and the Turkish Republic
In 1922, Mussolini established a one-party fascist government in the Kingdom of Italy, and Atatürk established the Turkish Republic, adopting the Western alphabet and state secularism.
1929: Wall Street Crash
The Wall Street Crash of 1929 contributed to the worldwide Great Depression, impacting economic stability in Europe.
1932: Second Soviet Famine
In 1932, under Stalin's leadership, confiscations of grain by the Soviet authorities contributed to the second Soviet famine which caused millions of deaths.
1933: Hitler's Rise to Power in Germany
In 1933, Adolf Hitler became the leader of Germany and began to work towards building Greater Germany.
1933: Jewish population in Europe
In 1933, there were about 9.5 million Jewish people in Europe, representing 1.7% of the population.
1933: Soviet Famine
In 1933, under Stalin's leadership, confiscations of grain by the Soviet authorities contributed to the second Soviet famine which caused millions of deaths.
1937: The Great Purge
Between 1937 and 1938, Stalin was responsible for the Great Purge of 1937–38 in which the NKVD executed 681,692 people; millions of people were deported and exiled to remote areas of the Soviet Union.
September 1939: Invasion of Poland
In September 1939, Germany invaded Poland on September 1, prompting France and the United Kingdom to declare war on Germany on September 3, initiating the European theatre of World War II. The Soviet invasion of Poland started on September 17, leading to Poland's fall. The Soviet Union also attacked the Baltic countries.
1939: Division of Czechoslovakia
In early 1939, the remainder of Czechoslovakia was split into the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, controlled by Germany, and the Slovak Republic.
December 1941: United States Enters the War
On 7 December 1941, Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor drew the United States into the conflict as allies of the British Empire, and other allied forces.
1943: Battle of Stalingrad
After the Battle of Stalingrad in 1943, the German offensive in the Soviet Union turned into a continual fallback.
1945: Fall of Berlin and End of World War II in Europe
Berlin finally fell in 1945, ending the Second World War in Europe.
1947: Establishment of the Free Territory of Trieste
In 1947, the Free Territory of Trieste was founded with the UN.
1948: Founding of the Council of Europe
In 1948, European integration was institutionally advanced with the founding of the Council of Europe.
1948: Berlin Blockade
The Berlin blockade in 1948 and 1949 was one of the great international crises of the Cold War.
1949: Council of Europe founded
In 1949, the Council of Europe was founded following a speech by Sir Winston Churchill, with the aim of unifying Europe to achieve common goals.
1949: Berlin Blockade
The Berlin blockade in 1948 and 1949 was one of the great international crises of the Cold War.
1954: Dissolution of the Free Territory of Trieste
In 1954, the Free Territory of Trieste, founded in 1947 with the UN, was dissolved.
1957: Treaty of Rome establishes EEC
In 1957, the Treaty of Rome established the European Economic Community (EEC) between six Western European states, with the goal of a unified economic policy and common market.
1958: Soviet Geographical Society Recommendation
In 1958, the Soviet Geographical Society formally recommended the Europe-Asia boundary be drawn from Baydaratskaya Bay along the eastern foot of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Mugodzhar Hills, the Emba River, and the Kuma–Manych Depression.
1961: Construction of the Berlin Wall
The construction of the Berlin Wall in 1961 was one of the great international crises of the Cold War.
1975: Dissolution of the Free Territory of Trieste
In 1975, the Free Territory of Trieste, founded in 1947 with the UN, was dissolved.
1989: Increased trade after the Cold War
After 1989, trade between East and West, as well as towards Asia, which had been disrupted by the two world wars, new borders, and the Cold War, increased sharply.
1989: Fall of the Berlin Wall
In 1989, the symbolic fall of the Berlin Wall occurred, leading to the reunification of Germany and the redrawing of Central and Eastern Europe's maps.
1989: Revolutions of 1989 and the Fall of the Berlin Wall
The Revolutions of 1989, including the fall of the Berlin Wall, marked the end of the Cold War divide in Europe, allowing for significant advancement in European integration.
1990: Reunification and economic struggles
After East and West Germany were reunited in 1990, West Germany's economy struggled to support East Germany's rebuilding, while East Germany experienced mass unemployment and a decline in industrial production.
1991: Dissolution of the Soviet Union
In 1991, the dissolution of the Soviet Union enabled the eastward expansion of the European Union.
1991: Economic liberalization in Central and Eastern Europe
With the fall of communism in Central and Eastern Europe in 1991, the post-socialist states underwent shock therapy measures to liberalize their economies and implement free market reforms.
1993: European Union established
In 1993, the European Community was succeeded by the European Union (EU), which established a parliament, a court, and a central bank, and introduced the euro as a unified currency.
1993: Foundation of the European Union
In 1993, the European Union was established and has since been the focal point of economic integration in Europe.
1999: Introduction of the Euro
In 1999, 12 of the 15 members of the EU joined the Eurozone, replacing their national currencies with the euro.
2004: Peoples of Europe
In 2004, Pan and Pfeil counted 87 distinct "peoples of Europe", with 33 forming the majority in at least one sovereign state and the remaining 54 constituting ethnic minorities.
2004: Central European countries begin joining the EU
Starting in 2004, Central European countries began joining the EU, expanding it to 28 European countries.
2005: EU net immigration gain
In 2005, the EU had an overall net gain from immigration of 1.8 million people, accounting for almost 85% of Europe's total population growth.
2008: Europe's Wealth
In 2008, Europe's assets under management amounted to over $32.7 trillion, surpassing North America's $27.1 trillion, making it the richest region.
2009: Europe remains the wealthiest region
In 2009, Europe remained the wealthiest region, with $37.1 trillion in assets under management, representing one-third of the world's wealth, surpassing its pre-crisis year-end peak.
2009: Eurozone recession
In 2009, Eurostat confirmed that the Eurozone had entered a recession in 2008, affecting much of the region.
2012: High unemployment rate in the EU
In 2012, the EU-27 unemployment rate was 10.3%, with a rate of 22.4% for those aged 15–24.
2013: EU expansion continues
By 2013, the EU had expanded to include 28 European countries, solidifying its position as a major economic and political center of power.
2014: Russo-Ukrainian War begins
In 2014, the Russo-Ukrainian War began, which later escalated into a full-scale invasion in February 2022.
June 2016: Referendum on EU membership
In June 2016, a referendum on EU membership was held, which eventually led to the United Kingdom withdrawing from the EU in January 2020.
2016: Europe's GDP per capita
According to a 2016 International Monetary Fund assessment, Europe's GDP per capita was US$21,767.
2016: Income inequality in Europe
In 2016, the richest 20% of households in Europe earned over five times more than the poorest 20%, indicating rising income inequality since the 1980s.
2018: Richest country in Europe
In 2018, Monaco was the richest country in Europe in terms of nominal GDP, with US$185,829 per capita.
2019: Poorest country in Europe
In 2019, Ukraine was the poorest country in Europe in terms of nominal GDP, with US$3,659 per capita.
January 2020: United Kingdom withdraws from the EU
In January 2020, the United Kingdom withdrew from the European Union as a result of the June 2016 referendum on EU membership.
2020: Migrant population in Europe
In 2020, Europe hosted the highest number of migrants of all global regions, with nearly 87 million people, according to the International Organisation for Migration.
2021: Citizenship granted by EU member states
In 2021, 827,000 persons were given citizenship of an EU member state, an increase of about 14% compared with 2020. 2.3 million immigrants from non-EU countries entered the EU in 2021.
2021: European Population in 2021
In 2021, Europe had a total population of approximately 745 million, which constitutes about 10% of the world population, making it the third-largest continent in terms of population after Asia and Africa.
2021: Percentage of elderly population in Europe
In 2021, the percentage of people over 65 years old was 21% in Western Europe and Southern Europe, compared to 19% in all of Europe and 10% in the world.
2022: Projected population decline
The United Nations predicts that Europe will decline in population between 2022 and 2050 by −7 per cent, without changing immigration movements.
2023: Europe's population
In 2023, the population of Europe was estimated to be about 742 million people, slightly more than one-ninth of the world's population, according to UN estimates.
2050: Projected population of Europe
According to a population projection by the UN Population Division, by 2050 Europe's population may fall to between 680 and 720 million people, which would be 7% of the world population at that time.
Mentioned in this timeline
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe the second-largest on...
The United States of America is a federal republic located...
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics USSR existed from to...
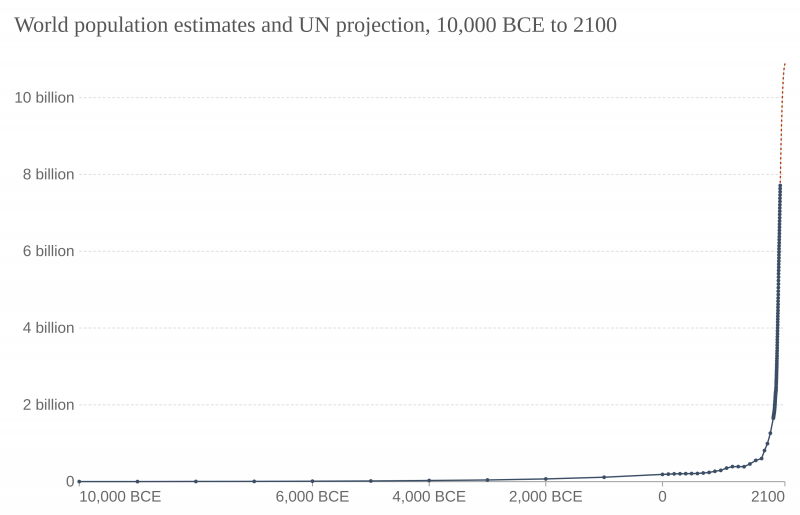
The world population the total number of living humans surpassed...
The Cold War - was a geopolitical rivalry between the...
Germany officially the Federal Republic of Germany is a nation...
Trending

44 minutes ago Jon Jones and Daniel Cormier Engage in Heated Exchange During Reality TV Taping.

2 hours ago Lewis Hamilton Urges African Grand Prix Before Retirement, Calls for Continent's Reclamation.

2 hours ago Cody Garbrandt finds peace, eyes Sean O'Malley fight after Xiao Long journey.

2 hours ago Red Bull Welcomes Isack Hadjar to F1 Hot Seat Ahead of First Race

2 hours ago Bryan Cranston Celebrates 70th Birthday, Plans Acting Hiatus After Illustrious Career.
2 hours ago DC local news evolves: Theater Arts doubles down after Washington Post cuts.
Popular

Ken Paxton is an American politician and lawyer serving as...

Markwayne Mullin is an American politician and businessman serving as...

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton is a prominent American politician lawyer...

Jim Carrey is a Canadian-American actor and comedian celebrated for...

Corey Lewandowski is an American political operative lobbyist commentator and...