The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union comprised of 27 member states primarily located in Europe. It covers a total area of 4,233,255 km2 and has a population of over 450 million. The EU is characterized as a sui generis political entity, exhibiting traits of both a federation and a confederation. It represents a unique form of international cooperation and integration among its member states, aiming for economic and political cohesion.
1920: Keynes proposes a European customs union
In 1920, John Maynard Keynes proposed a European customs union for the struggling post-war European economies.
1923: Paneuropean Union was founded
In 1923, the Paneuropean Union was founded, led by Richard von Coudenhove-Kalergi.
September 1929: Briand speech at the League of Nations
On September 5, 1929, Aristide Briand delivered a speech at the League of Nations in Geneva advocating for a federal Europe.
1930: Churchill's first calls for a European Union
Since 1930 Winston Churchill had been calling for a European Union.
1941: Declaration of St James's Palace and Atlantic Charter
In 1941, the Declaration of St James's Palace and the Atlantic Charter established the Allies' common goals.
1944: Yalta Conference decision to form a European Advisory Commission
In 1944, at the Yalta Conference, a decision was made to form a European Advisory Commission.
1944: Bretton Woods System
In 1944, the Bretton Woods System was established.
1945: Potsdam Agreement
In 1945, following the German surrender, the Allied Control Council was established, following the Potsdam Agreement.
1945: Founding of the United Nations
In 1945, the United Nations was founded as a new wave of global international institutions.
September 1946: Churchill calls for a European Union and Council of Europe
On September 19, 1946, Winston Churchill called for a "European Union" and "Council of Europe" in a speech at the University of Zürich.
June 1947: European Parliamentary Union founded
In June 1947 Richard von Coudenhove-Kalergi founded the European Parliamentary Union (EPU).
1947: Treaty of Dunkirk and Truman Doctrine
In 1947, the Treaty of Dunkirk was signed between France and the United Kingdom, and the Truman Doctrine was announced, pledging American support for democracies to counter the Soviets.
March 1948: Treaty of Brussels signed
In March 1948, the Treaty of Brussels was signed, establishing the Western Union (WU), followed by the International Authority for the Ruhr.
May 1948: Hague Congress
In May 1948, the Hague Congress led to the creation of the European Movement International and the College of Europe.
1948: Marshall Plan
Since 1948, the Marshall Plan backed the ECSC with large funds coming from the United States.
1948: Beginnings of modern European integration
The beginnings of modern European integration can be traced back to 1948 with the Inner Six states.
May 1949: Foundation of the Council of Europe
On May 5, 1949, the Council of Europe was founded, now celebrated as Europe Day.
1949: International Authority for the Ruhr installed
In 1949 the International Authority for the Ruhr was installed by the Western Allies.
1949: Institution of the Charlemagne Prize
Since 1949, the city of Aachen has awarded the Charlemagne Prize to champions of European unification.
May 1950: Schuman Declaration
On May 9, 1950, the Schuman Declaration was made, leading to six nations drafting the Treaty of Paris.
1950: European Convention on Human Rights
In 1950 the European Convention on Human Rights was achieved.
1950: Schuman Declaration Date
In 1950, the Schuman declaration happened on May 9.
1951: Pleven Plan
In 1951, the Pleven Plan tried but failed to tie the institutions of the developing European community under the European Political Community.
1952: Establishment of the Court of Justice
In 1952, the Court of Justice of the European Union was established, based in Luxembourg, to interpret EU law and ensure its uniform application.
1954: Modified Brussels Treaty
In 1954, the Modified Brussels Treaty transformed the Western Union into the Western European Union (WEU).
1955: West Germany joins WEU and NATO, Warsaw Pact formed
In 1955, West Germany joined both the WEU and NATO, prompting the Soviet Union to form the Warsaw Pact.
1955: Design of the Flag of Europe
In 1955, the flag of Europe, consisting of a circle of 12 golden stars on a blue background, was originally designed for the Council of Europe.
1956: Spaak report recommends next steps of European integration
In 1956, the Spaak report recommended the next significant steps of European integration.
1957: Treaty of Rome signed
In 1957, Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany signed the Treaty of Rome, creating the European Economic Community (EEC) and the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom).
1957: Foreign policy co-operation begins
In 1957, member states began foreign policy cooperation by negotiating as a bloc in international trade negotiations under the EU's common commercial policy.
1957: No Environmental Policy
In 1957, when the European Economic Community was founded, it initially had no environmental policy.
1958: Treaties come into force
In 1958, both the Treaty of Rome and the pact creating Euratom came into force.
1961: OEEC reformed into the OECD
In 1961, the OEEC was reformed into the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), with its membership extended to states outside of Europe, the United States and Canada.
1962: Introduction of the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP)
In 1962, the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) was introduced in the European Union, implementing a system of agricultural subsidies and other programs.
1965: Agreement Reached in France
In 1965 an agreement was reached, leading to the Merger Treaty.
July 1967: Merger Treaty creates single set of institutions
On July 1, 1967, the Merger Treaty created a single set of institutions for the three communities, referred to as the European Communities.
1969: Creation of a European Single Currency objective
In 1969, the creation of a European single currency became an official objective of the European Economic Community.
1970: Establishment of European Political Cooperation
In 1970, European Political Cooperation was established, creating an informal consultation process between member states aimed at forming common foreign policies.
1973: Accessions of further states to the EU
From 1973, the EU grew in size through the accessions of further states.
1973: Start of Analyzed Period for Economic Integration Study
In 1973, the start of analyzed period for economic integration study by the EU began.
1975: Establishment of the European Court of Auditors
In 1975, the European Court of Auditors (ECA) was established in Luxembourg to improve EU financial management.
1979: First direct elections to the European Parliament
In 1979, the first direct elections to the European Parliament were held.
1984: Start of EU's Framework Programmes for Scientific Development
In 1984, the EU's Framework Programmes for scientific development were initiated to coordinate and stimulate research in areas such as energy, aiming to develop renewable energy sources and reduce dependence on imported fuels.
1985: Greenland leaves and Schengen Agreement
In 1985, Greenland left the Communities and the Schengen Agreement paved the way for open borders.
1985: EEC Budget Cost Reduction for CAP
In 1985, the EEC budget cost for the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) reduced to 73%.
1985: Schengen Agreement Signed
In 1985, the Schengen Agreement was signed in Schengen, Luxembourg, laying the foundation for the creation of the Schengen Area.
1985: Establishment of Europe Day
Since 1985, Europe Day, commemorating the Schuman declaration of 1950, has been observed on 9 May as the flag day of the union. In 1985, the leaders of the European Community adopted an instrumental version of the prelude to the Ode to Joy from Beethoven's ninth symphony as the anthem of the European Union.
1986: Adoption of the Flag by the European Communities
In 1986, the European Communities, the predecessors of the present European Union, adopted the flag of Europe.
1987: Launch of the Erasmus Programme
In 1987, the Erasmus Programme, a university exchange program, was launched to support exchanges and mobility in higher education. It facilitated international exchange opportunities for over 1.5 million students in its first 20 years.
1987: Introduction of the Single European Act
In 1987, the Single European Act established the legal basis for EU environmental policy, formally recognizing the environment as a policy area.
1987: Formal Introduction of European Political Cooperation
In 1987, the Single European Act formally introduced the European Political Cooperation (EPC), solidifying the cooperation process among member states.
1990: Reference year for emissions reduction
1990 is the year used as reference to calculate carbon dioxide emissions reduction for the EU's 2020 target.
1990: East Germany becomes part of the communities
In 1990, after the fall of the Eastern Bloc, the former East Germany became part of the communities as part of a reunified Germany.
1990: Schengen Convention Signed
In 1990, the Schengen Convention was signed in Schengen, Luxembourg, further developing the principles of the Schengen Agreement.
1990: Creation of the Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T)
In 1990, the Trans-European Transport Network (TEN-T) was created to manage cross-border road, railway, airport and water infrastructure within the European Union.
1991: Launch of the MEDIA Programme
Since 1991, the MEDIA Programme of the European Union has supported the European popular film and audiovisual industries by providing support for the development, promotion, and distribution of European works within Europe and beyond.
1992: Signing of the Maastricht Treaty
In 1992, member states signed the Maastricht Treaty, legally binding them to fulfill agreed-on rules for a currency union, including convergence criteria.
1992: UN Conference on Environment and Development
In 1992, the UN Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) took place in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, recognizing sustainable development as a key element.
June 1993: Copenhagen criteria agreed upon
In June 1993, the Copenhagen criteria for candidate members to join the EU were agreed upon.
November 1993: Maastricht Treaty comes into force
In November 1993, the Maastricht Treaty came into force, formally establishing the European Union.
1993: Definition of Copenhagen Criteria
In 1993, the Copenhagen criteria were defined at the European Council meeting in Copenhagen, setting the requirements for countries to become EU members, including a stable democracy, a functioning market economy, and acceptance of EU law.
1993: Creation of the European Union
In 1993, the European Union was created, leading to the development of competencies in justice and home affairs, initially at an intergovernmental level and later through supranationalism, resulting in legislation in areas such as extradition, family law, asylum law, and criminal justice.
1993: Maastricht Treaty comes into force
In 1993, the Maastricht Treaty came into force, formally establishing the European Union and its citizenship.
1996: Idea of a European-level Aviation Safety Authority
In 1996, the idea of a European-level aviation safety authority was conceived.
December 1999: Helsinki European Council Decisions
The Helsinki European Council in December 1999 called for the establishment of permanent political-military institutions, leading to the creation of the European Union Military Staff.
1999: Start of the Currency Union
In 1999, the currency union started to materialise through introducing a common accounting (virtual) currency in eleven of the member states.
2000: Adoption of "United in Diversity" as the EU Motto
In 2000, "United in Diversity" was adopted as the motto of the European Union after being selected from proposals by school pupils.
2000: EU Services Trade Surplus Rises
In 2000, the European Union's services trade surplus was recorded at $16 billion.
2000: EU Cultural Initiatives
Since its inclusion as a community competency in the Maastricht Treaty, the European Union has had an interest in cultural co-operation between member states. Actions taken in the cultural area by the EU include the Culture 2000 seven-year programme, the European Cultural Month event, and orchestras such as the European Union Youth Orchestra. The European Capital of Culture programme selects one or more cities in every year to assist the cultural development of that city.
2001: EU Prevents Merger Between General Electric and Honeywell
In 2001, the EU commission blocked a merger between General Electric and Honeywell, two United States based companies, even after it had been approved by US authorities. This was the first time the EU prevented a merger between two companies based in the United States.
2002: Introduction of Euro Banknotes and Coins
In 2002, euro banknotes and coins were introduced, replacing national currencies in 12 of the member states, marking a significant step in economic integration.
2002: Founding of the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA)
In 2002, the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) was founded in Lisbon, Portugal, with the aim of reducing maritime accidents, marine pollution from ships, and loss of life at sea.
2002: Legal Establishment of the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA)
In 2002, the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) was legally established.
2002: World Summit on Sustainable Development
In 2002, the World Summit on Sustainable Development (WSSD) was held in Johannesburg, South Africa, reinforcing the international recognition of sustainable development.
2003: EASA Begins Operating
In 2003, the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) began its operations.
2003: Adoption of Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics
In 2003, the Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS), a geocode standard for statistical purposes, was adopted by the European Union.
2004: End of Analyzed Period for Economic Integration Study
In 2004, the end of analyzed period for economic integration study by the EU ended.
October 2005: Introduction of a Mandatory and Comprehensive European Energy Policy Approved
In October 2005, the introduction of a mandatory and comprehensive European energy policy was approved at the meeting of the European Council.
December 2005: Endorsement of the European Consensus on Development
On December 20, 2005, the European Consensus on Development was endorsed by EU Member States, the council, the European Parliament, and the commission, providing a basis for EU development action.
2005: Eurobarometer Opinion Poll on Religious Beliefs
In 2005, a Eurostat's Eurobarometer opinion poll showed that 52% of EU citizens believed in a god, 27% in "some sort of spirit or life force", and 18% had no form of belief.
2006: Services in the Internal Market Directive 2006
In 2006, the Services in the Internal Market Directive 2006 aimed to liberalise the cross-border provision of services within the EU single market, addressing the legislative gap in the service sector which accounts for a significant portion of GDP.
January 2007: First Draft of European Energy Policy Published
In January 2007, the first draft of the European energy policy was published, following the approval of its introduction in October 2005.
May 2007: Establishment of the European Space Policy
On May 22, 2007, the European Space Policy was established between the EU and the European Space Agency (ESA), marking the first common political framework for space activities by the EU.
2007: EU Import Dependence on Energy Sources in 2007
In 2007, EU countries as a whole imported 82 per cent of their oil, 57 per cent of their natural gas and 97.48 per cent of their uranium demands.
2007: Member States Agreement on Renewable Energy
In 2007, member states agreed that 20% of the energy used across the EU must be renewable in the future.
2007: Establishment of the European Institute for Gender Equality
In 2007, the European Institute for Gender Equality was established to promote gender equality within the EU.
2007: Lifelong Learning Programme
In 2007, the Lifelong Learning Programme was introduced, offering similar programmes for school pupils, teachers, trainees in vocational education, and adult learners to encourage knowledge of other countries and spread good practices in education and training.
2007: Development Cooperation Instrument
The Development Cooperation Instrument (DCI) was established in 2007 with a budget of €16.9 billion for the period 2007-2013.
2008: European Development Fund Budget
In 2008, the European Development Fund (EDF) was allocated €22.7 billion for the period 2008–2013, consisting of voluntary contributions from member states.
2008: EU Largest Importer of Goods and Services
In 2008, the European Union held the position of the largest importer of goods and services globally.
2008: End of Analysis for Greece in Economic Integration Study
In 2008, the end of analysis for Greece in economic integration study by the EU ended.
2008: Inauguration of the Charlemagne Youth Prize
Since 2008, the Charlemagne Youth Prize has been awarded by the organisers of the Charlemagne Prize in conjunction with the European Parliament, recognizing similar efforts led by young people.
December 2009: Lisbon Treaty Entry into Force
In December 2009, the Lisbon Treaty came into effect, reforming various aspects of the EU, including its legal structure and the creation of a permanent president of the European Council.
December 2009: Court of First Instance Renamed to General Court
On December 1, 2009, with the coming into force of the Lisbon Treaty, the Court of First Instance was renamed to the General Court.
2009: Thomas Risse's assessment of EU's impact on Eastern European democracies
In 2009, scholar Thomas Risse stated that there was a consensus that the EU membership perspective had a huge anchoring effect for the new democracies in Eastern Europe.
2009: Introduction of the Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) with the Treaty of Lisbon
In 2009, the Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) was introduced with the Treaty of Lisbon, formally enshrining fisheries conservation policy as one of the "exclusive competences" reserved for the European Union.
2009: Religious Demographics in the EU
In 2009, the EU had an estimated Muslim population of 13 million and a Jewish population of over 1 million. Other world religions like Buddhism, Hinduism, and Sikhism were also represented. The Christian population includes Catholics, Protestants, and Eastern Orthodox.
2009: Lisbon Treaty and Charter of Fundamental Rights
In 2009, the Lisbon Treaty gave legal effect to the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union, which consolidates fundamental rights and serves as a benchmark for evaluating EU legal acts.
2009: Treaty of Lisbon comes into force
In 2009, the Treaty of Lisbon came into force, incorporating the EU as an international legal juridical person.
December 2010: Implementation of the European External Action Service
On December 1, 2010, the European External Action Service (EEAS) was officially implemented and became operational, marking the first anniversary of the Treaty of Lisbon's entry into force; the EEAS serves as a foreign ministry and diplomatic corps for the European Union.
2011: Estonia adopts the Euro
In 2011, Estonia adopted the euro as its official currency, further integrating into the Eurozone.
2011: Closure of the Western European Union
In 2011, the Western European Union, a military alliance, closed as its role had been transferred to the EU.
2012: EU Awarded Nobel Peace Prize
In 2012, the EU was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for its contributions to peace, reconciliation, democracy, and human rights in Europe.
2012: ECHO's Humanitarian Aid Budget
In 2012, the European Commission's Humanitarian Aid and Civil Protection department (ECHO) had a budget of €874 million for providing humanitarian aid from the EU to developing countries.
2012: UN Conference on Sustainable Development
In 2012, the UN Conference on Sustainable Development (UNCSD) took place in Rio de Janeiro, further emphasizing the role of sustainable development.
2013: Croatia becomes 28th EU Member
In 2013, Croatia joined the European Union, becoming its 28th member state.
2013: Depiction of Europa on Euro Banknotes
In 2013, a portrait of Europa was featured on the euro banknotes series.
2013: Continuation of Lifelong Learning Programme
In 2013, the Lifelong Learning Programme 2007-2013 continued to provide opportunities for school pupils, teachers, trainees in vocational education, and adult learners to promote knowledge of other countries and spread good practices in education and training.
2013: End of DCI Budget Period
In 2013, the budget period for the Development Cooperation Instrument (DCI), which started in 2007 with €16.9 billion, came to an end.
2013: Accessions of further states to the EU
Until 2013, the EU grew in size through the accessions of further states.
2014: Latvia adopts the Euro
In 2014, Latvia adopted the euro as its official currency, further integrating into the Eurozone.
2014: New EDF Budget
In 2014, the European Development Fund (EDF) was allocated €30.5 billion for the period 2014–2020, consisting of voluntary contributions from member states.
2015: Koen Lenaerts Becomes President of the Court of Justice
In 2015, Koen Lenaerts became the President of the Court of Justice of the European Union.
2015: Lithuania adopts the Euro
In 2015, Lithuania adopted the euro as its official currency, further integrating into the Eurozone.
2015: Surge in Asylum Seekers
In 2015, the European Union faced a significant challenge with a surge in asylum seekers, testing the cohesion of the union.
2015: United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
In 2015, the United Nations established the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
2016: Language Usage in the EU
In 2016, English was the most widely spoken language in the EU, used by 44% of the population and studied by 95% of students. German and French were spoken by 36% and 30% of the population, respectively. Over half (56%) of EU citizens could converse in a language other than their native tongue.
2016: UK Referendum to Leave the EU
In 2016, a referendum was held in the UK regarding its membership in the European Union, with 51.9% voting to leave.
2016: Galileo Global Navigation Satellite System Went Live
In 2016, the Galileo global navigation satellite system (GNSS), created by the EU through the ESA, went live, providing an independent high-precision positioning system.
2016: EU Countries Achieve 0.7% Target
In 2016, the average ODA among EU countries was 0.4%, with five countries (Denmark, Germany, Luxembourg, Sweden, and the United Kingdom) meeting or exceeding the 0.7% target.
2016: Unemployment in the EU
In 2016, unemployment in the EU stood at 8.9 per cent while inflation was at 2.2 per cent, and the account balance at −0.9 per cent of GDP.
March 2017: UK Formally Notifies Decision to Leave EU
On March 29, 2017, the UK formally notified the European Council of its decision to leave the EU, initiating the formal withdrawal procedure.
2017: EEC Budget Cost Reduction for CAP
In 2017, the EEC budget cost for the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) reduced to 37%.
2017: EU Global Greenhouse-Gas Emissions
In 2017, the EU emitted 9.1 per cent of global greenhouse-gas emissions.
2017: United Kingdom Invokes Article 50
In 2017, the United Kingdom formally invoked Article 50 of the Consolidated Treaty on European Union, initiating the process to withdraw from the EU.
2017: Richest and Poorest Regions in EU
In 2017, the difference between the richest (Luxembourg) and poorest regions (Severozapaden, Bulgaria) in the EU ranged from 31% to 253% of the EU28 average.
July 2018: EU-Japan Economic Partnership Agreement Signed
On July 17, 2018, the EU-Japan Economic Partnership Agreement was officially signed, marking a significant step towards creating the world's largest bilateral free trade deal.
September 2018: EU Unemployment Rate in September 2018
In September 2018, the EU seasonally adjusted unemployment rate was reported at 6.7 per cent, while the euro area unemployment rate was 8.1 per cent.
2018: EU Zero Carbon Economy Proposals
Proposals to reach a zero carbon economy in the European Union by 2050 were suggested in 2018–2019.
2018: EU GHG emissions reduction
The European Union claims that already in 2018, its GHG emissions were 23% lower than in 1990.
February 2019: EU-Japan Economic Partnership Agreement Went Into Effect
On February 1, 2019, the EU-Japan Economic Partnership Agreement came into effect, establishing an open trade zone covering nearly one-third of global GDP.
June 2019: EU Summit on Zero Carbon Economy
At an EU summit in June 2019, almost all member states supported the goal of reaching a zero carbon economy in the European Union by 2050, with the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, and Poland disagreeing.
2019: Study on Economic Effects of European Integration
According to a 2019 study, without European integration, per capita incomes would have been approximately 10% lower in the first ten years after joining the EU for member states who joined from 1973 to 2004.
2019: Ursula von der Leyen Nominated as President of the European Commission
In 2019, Ursula von der Leyen was nominated as the President of the European Commission for the 2019–2024 term, and oversees the commission's civil service.
2019: Establishment of European Commissioner for Equality
In 2019, the role of European Commissioner for Equality was created, signifying the EU's commitment to gender equality and related issues.
2019: EU Energy Supply Data for 2019
In 2019, the total energy supply of the EU was 59 billion GJ, which was about 10.2 per cent of the world total. Renewable energy contributed 18.1 per cent of the EU's total energy supply in 2019.
January 2020: UK Leaves the European Union
On January 31, 2020, the United Kingdom officially left the European Union, marking a significant event in the history of the EU.
July 2020: Agreement on Next Generation EU
In July 2020, the European Council agreed in principle to create common debt to finance the European Recovery Program called Next Generation EU (NGEU) to support EU member states recovering from the COVID-19 pandemic.
October 2020: EU Plans to Act Against Human Rights Violations Worldwide
On 19 October 2020, the European Union revealed new plans to create a legal structure to act against human rights violations worldwide, providing greater flexibility to target and sanction those responsible for serious human rights abuses.
November 2020: Hungary and Poland Block EU Budget Approval
In November 2020, Hungary and Poland blocked the approval of the EU's budget, citing a proposal that linked funding with adherence to the rule of law.
December 2020: Adoption of Next Generation EU Instrument
On December 14, 2020, the Next Generation EU (NGEU) instrument, worth €750 billion, was adopted to help EU member states recover from the COVID-19 pandemic.
December 2020: End of UK Transition Period
On December 31, 2020, the transition period following the UK's departure from the European Union ended, concluding the application of most areas of EU law to the UK.
2020: Urban Population Distribution
In 2020, 68.2% of EU inhabitants lived in urban areas, slightly less than the world average. The EU has approximately 40 urban areas with populations exceeding 1 million. Paris, with over 13 million residents, is the largest metropolitan area and the only megacity in the EU.
2020: Immigration and Emigration Statistics
In 2020, approximately 1.9 million people immigrated to EU member states from non-EU countries, while around 956,000 people emigrated from EU member states to non-EU countries. 5.3% of EU residents were not EU citizens, with Moroccan, Turkish, Syrian, and Chinese being the largest non-EU citizenships.
2020: China Becomes EU's Largest Trading Partner
In 2020, partially due to the COVID-19 pandemic, China surpassed the United States to become the European Union's largest trading partner.
2020: United Kingdom leaves the EU
In 2020, the United Kingdom became the first and only member state to leave the EU.
2020: United Kingdom Withdraws from the EU
In 2020, the United Kingdom officially withdrew from the European Union, becoming the only sovereign state to have left the EU.
2020: End of EDF Budget Period
In 2020, the budget period for the European Development Fund (EDF), which started in 2014 with €30.5 billion, came to an end.
2020: Approval of First European Union Strategy on LGBTIQ Equality
In 2020, the first ever European Union Strategy on LGBTIQ equality was approved under Helena Dalli mandate.
2020: EU Carbon Dioxide Emissions Target
The EU aimed to have carbon dioxide emissions lower in 2020 by at least 20 percent compared to 1990 levels.
June 2021: European Climate Law Passed
In June 2021, the European Union passed a European Climate Law with targets of 55% GHG emissions reduction by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2050.
December 2021: Commission Announces Intention of Codifying Union-Wide Law Against LGBT Hate Crimes
In December 2021, the European Commission announced its intention to codify a union-wide law against LGBT hate crimes.
2021: Study on Economic Effects of the 2004 Enlargement
A 2021 study in the Journal of Political Economy found that the 2004 enlargement had aggregate beneficial economic effects on all groups in both the old and new member states, with the largest winners being the new member states, particularly unskilled labor.
2021: Population Decrease and Birth Rates
In 2021, the EU population decreased by 0.04% due to a low birth rate of about 1.5 children per woman, which is less than the world average. There were 4.1 million babies born in the EU in 2021.
2021: Establishment of the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA)
In 2021, the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) was established in Prague, Czech Republic, to manage the European Union Space Programme and implement the pre-existing European Space Policy.
2021: Next Generation EU Implementation
In 2021, the Next Generation EU (NGEU) instrument began operating, running alongside the EU's Multiannual Financial Framework (MFF) for the period 2021-2027.
2021: Average Annual Net Earnings
In 2021, the average annual net earnings in the European Union was around €25,000.
2021: Life Expectancy in the EU
In 2021, the average life expectancy at birth in the EU was 80.1 years, which is among the highest in the world. Life expectancy is generally lower in Eastern Europe compared to Western Europe.
May 2022: EU Prepares New Sanctions Against Russia and Publishes RePowerEU Initiative
In May 2022, the European Union was preparing another sanction against Russia over its invasion of Ukraine. The European Commission published the RePowerEU initiative, a €300 billion plan outlining the path towards the end of EU dependence on Russian fossil fuels by 2030.
September 2022: Approval of European Care Strategy
In September 2022, the European Care Strategy was approved to provide "quality, affordable and accessible care services".
September 2022: European Parliament Approves Directive About Minimum Wage
In September 2022, the European Parliament approved the European Directive about Minimum Wage, aimed at lifting minimum wages and strengthening collective bargaining.
2022: Adoption of the EU Strategic Compass
In 2022, the EU Strategic Compass reaffirmed the bloc's partnership with NATO, committing to increased military mobility and the formation of a 5,000-strong EU Rapid Deployment Capacity.
2022: EU Budget
In 2022, the European Union had an agreed budget of €170.6 billion.
2022: EU Member States GDP
In 2022, the gross domestic product (GDP) of EU member states was US$16.64 trillion, around 16.6 per cent of the world GDP.
2023: Croatia adopts the Euro
In 2023, Croatia adopted the euro as its official currency, further integrating into the Eurozone.
2023: EU member states contain 5.5% of world population
In 2023, EU member states accounted for 5.5% of the world population.
May 2024: Concerns Rise Over EU Policies After Elections
In May 2024, concerns arose that the outcome of the elections in June could undermine crucial EU policies related to the environment, diplomacy, and economy, particularly due to the war in Ukraine.
November 2024: Report on Czech Republic Emissions
A research report from November 2024 declared that the Czech Republic is the EU's most toxic country in Europe for care emissions.
2024: EU Corporations in the World's Largest
In 2024, 90 of the top 500 largest corporations in the world measured by revenue had their headquarters in the EU.
2024: EU nominal GDP around €17.935 trillion
In 2024, EU member states generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around €17.935 trillion.
2024: Ursula von der Leyen Reelected as President of the European Commission
In 2024, Ursula von der Leyen was reelected as President of the European Commission for the 2024–2029 term, proposed by the European Council.
2024: EU Population Statistics
In 2024, the EU's population was approximately 450 million, representing 5.8% of the global population. The population density was 106 inhabitants per square kilometer, surpassing the world average. Population density was highest in central and western Europe.
July 2025: Denmark to Hold Presidency of the Council
Beginning on July 1, 2025, Denmark will hold the Presidency of the Council of the European Union.
2025: Initiation of the ReArm program
In 2025, Europe initiated the ReArm program, involving a financial investment of €800 billion to support European equipment production, enhancing the continent's overall military readiness and self-sufficiency.
2025: Estimated population of more than 450 million
In 2025, the European Union has an estimated population of more than 450 million people.
2026: Next Generation EU Operational Period
The Next Generation EU (NGEU) instrument will operate from 2021 to 2026 to help EU member states recover from the COVID-19 pandemic.
2027: Next Generation EU tied to Multiannual Financial Framework
From 2021 to 2027, the Next Generation EU (NGEU) instrument will be tied to the regular 2021–2027 budget of the EU's Multiannual Financial Framework (MFF).
2029: End of Ursula von der Leyen's Second Term
In 2029, Ursula von der Leyen's second term as the President of the European Commission ends.
2030: Target year for the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
2030 is the target year for achieving the goals set in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development (United Nations, 2015).
2030: European Union and United States pledge to cut methane emissions.
Also in 2021, the European Union and the United States pledged to cut methane emissions by 30% by 2030. The pledge is considered as a big achievement for climate change mitigation.
2030: EU Goal of 35 Member States
By 2030, one of the EU's political priorities is to prepare for a new great enlargement, with the goal of achieving 35 member states.
2030: Target Year for Ending EU Dependence on Russian Fossil Fuels
By 2030, the EU aims to end its dependence on Russian fossil fuels through the RePowerEU initiative.
2030: Target Completion Date for the TEN-T Core Network
The TEN-T Core Network is scheduled to be completed by 2030 as part of the Trans-European Transport Network project.
2050: EU Zero Carbon Economy Target
Proposals to reach a zero carbon economy in the European Union by 2050 were suggested in 2018–2019.
2050: Target Completion Date for the TEN-T Comprehensive Network
The TEN-T Comprehensive Network is scheduled to be completed by 2050 as part of the Trans-European Transport Network project.
Mentioned in this timeline
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe the second-largest on...

Ursula Gertrud von der Leyen is a prominent German politician...
The United States of America is a federal republic located...
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics USSR existed from to...
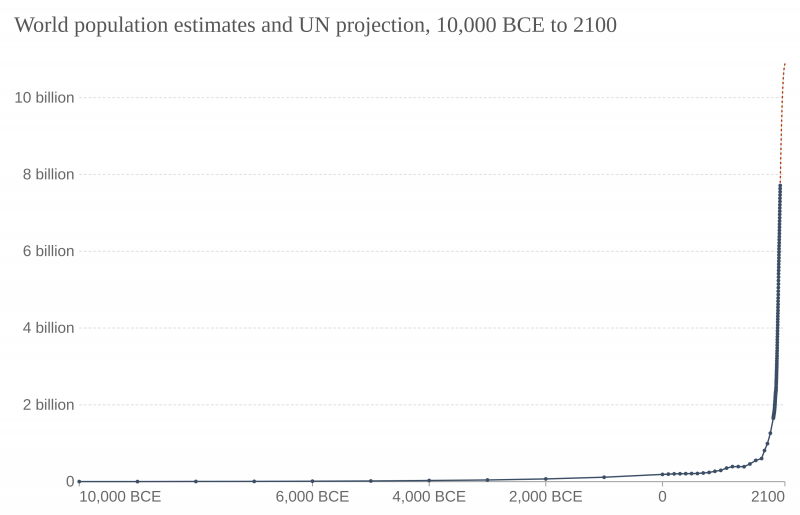
The world population the total number of living humans surpassed...
The Cold War - was a geopolitical rivalry between the...
Trending
15 minutes ago Ameren Prices $400M Senior Notes, $900M Bonds for Grid Investment, Reshaping Debt
1 hour ago Pokemon Celebrates 30 Years: A Cultural Phenomenon with Multimillion-Dollar Cards
1 hour ago Daylight Saving Time 2026: Prepare to set your clocks forward and lose sleep.

1 hour ago Indiana Investigates CenterPoint Energy Amid Bill Concerns and New Utility Law.

1 hour ago Galatasaray's Champions League opponent revealed; Liverpool legend comments on Juventus match; Real Madrid faces Man City.

3 hours ago Google Maps to fully function in South Korea after data agreement.
Popular

Jesse Jackson is an American civil rights activist politician and...

Barack Obama the th U S President - was the...

Susan Rice is an American diplomat and public official prominent...

XXXTentacion born Jahseh Dwayne Ricardo Onfroy was a controversial yet...

Michael Joseph Jackson the King of Pop was a highly...

Kashyap Pramod Patel is an American lawyer who became the...